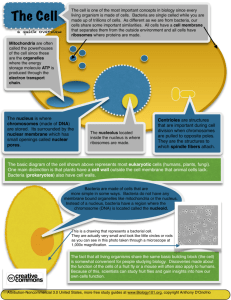
This organelle looks like a stack of
advertisement

This organelle looks like a stack of pancakes. It modifies, sorts, & packages molecules made for transport. GOLGI BODY (APPARATUS) Sac of digestive enzymes that breaks down food, unwanted cells, or cell parts. LYSOSOMES Storage space for water, food, waste, & enzymes that is larger in plant cells and smaller in animal cells. Give the function for the GOLGI APPARATUS Modifies, sorts, & packages molecules the cell makes for transport. Give the function for LYSOSOMES Sac of digestive enzymes to break down food or unwanted cells or cell parts Give the function for a VACUOLE Storage space for water, food, waste, or enzymes VACUOLE Contains the genetic material (DNA) & acts as the control center of the cell NUCLEUS Dark spot in the nucleus of a non-dividing cell where RNA for ribosomes is made Give a function for the NUCLEUS Contains the genetic material; Acts as the control center Give a function for NUCLEOLUS Makes ribosomes (RNA) NUCLEOLUS Phospholipid & protein bilayer that surrounds the cell and controls which molecules enter or leave Give a function for the CELL MEMBRANE Controls what enters and leaves cell CELL MEMBRANE Power plant of the cell with its own DNA that burns glucose for energy and stores it as ATP MITOCHONDRIA Found outside the cell membrane in plants and bacteria, this supports and protects cells. Give a function for MITOCHONDRIA Burn glucose and store energy as ATP Give a function for CELL WALL Supports and protects cell CELL WALL Plastid that has its own DNA & contains chlorophyll to carry out photosynthesis in plant cells CHLOROPLAST System of membranes which modify and transport proteins made on its attached ribosomes Give a function for a CHLOROPLAST Photosynthesis Give a function for ROUGH ER modify & transport proteins made on its ribosomes ROUGH ER Cell which has a nuclear membrane and membranes around its organelles Give an example of a eukaryote Animal or plant cell EUKARYOTE Cell which has NO nuclear membrane or membrane bound organelles PROKARYOTE Give an example of a prokaryote bacteria Folded inner membrane in mitochondria which increases surface area for chemical reactions CRISTAE Network of microtubules and microfilaments that gives the cell shape, support, and helps move structures within the cell. Inside which organelle would you find CRISTAE? MITOCHONDRIA Give a function for cytoskeleton give cell shape, support, move structures within cell CYTOSKELETON Many, short hair-like structures made of microtubules that are attached to the outside of cells which help move the cell or move things past the cell Give a function for CILIA move cell or move substances past cell CILIA Few, long hair-like structures made of microtubules that are attached to the outside of cells which help in movement Give a function for FLAGELLA Move cell FLAGELLA Small structures, free or attached to ER, which synthesize proteins RIBOSOMES Network of membranes WITHOUT RIBOSOMES which regulates calcium, makes steroids, and breaks down toxins SMOOTH ER Give a function for RIBOSOMES Make proteins Give a function for SMOOTH ER Make steroids, regulate calcium, break down toxins Integral membrane proteins with carbohydrates attached that help cells recognize “self” Give a function for glycoproteins help cells recognize “self” GLYCOPROTEINS Log-like structures in animal cells that pull the chromosomes apart during cell division CENTRIOLES Openings in the nuclear membrane that allow molecules to pass in and out of the nucleus NUCLEAR PORES Membrane sacs stacked inside chloroplasts where photosynthesis happens THYLAKOIDS Give a function for centrioles pull chromosomes apart during cell division Give a function for nuclear pores openings for substances leaving/entering nucleus Inside which organelle would you find thylakoids? CHLOROPLASTS Membrane that surrounds the genetic material in eukaryotes and controls what enters & leaves the nucleus Give the function of the NUCLEAR ENVELOPE NUCLEAR ENVELOPE / MEMBRANE Controls what enters/leaves nucleus Small internal structure in a cell which carries out a specific job Give an example of an organelle ORGANELLE Mitochondria, Golgi, ER, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, etc Molecule used by cells to store and transport energy for cell activities like active transport ATP Organelle where ATP is made mitochondria DNA and proteins that are spread out in the nucleus of non-dividing cells CHROMATIN Programmed cell death or “cell suicide” for the good of the organism APOPTOSIS Process in which cells change into different kinds of cells with different functions DIFFERENTIATION or SPECIALIZATION Describes membranes which allow certain substances to pass through but keeps other substances out SELECTIVELY (Semi)PERMEABLE Group of similar CELLS that work together to carry out a specific function TISSUE DNA and proteins that are scrunched up into rod shaped bodies in dividing cells CHROMOSOMES Molecules with polar heads and and hydrophobic tails used to make cell membranes PHOSPHOLIPIDS Gel-like material with organelles found between the nucleus cell membrane CYTOPLASM Group of different TISSUES that work together to perform a specific function ORGAN Group of organs that work together to carry out a specific function ORGAN SYSTEM Name the Dutch microscope maker who first saw living cells Anton van Leeuwenhoek Name the English scientist who first saw ”little boxes” in cork and coined the name “cells” ROBERT HOOKE Name the German botanist who concluded that all plants are made of cells Name the American biologist who provided evidence for the Endosymbiotic theory Lynn Margulis Name the theory that suggests that certain organelles within cells were once free-living cells themselves. ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY Name an organelle besides the nucleus that has a double membrane Matthias Schleiden mitochondria or chloroplasts Name the German zoologist who concluded that all animals are made of cells Theodor Schwann Name the German physician who saw dividing cells and concluded that cells are produced from existing cells Rudolf Virchow Name two of the parts of the cell theory All living things are made of cells; Cells are the basic unit of structure & function in living things; All cells are produced from existing cells Name a cell part made out of microtubules cilia, flagella, cytoskeleton, centrioles Cells that need a lot of energy like muscle cells have a lot of which organelle? mitochondria Cells that export molecules like pancreas cells that make insulin have a lot of which organelle? Golgi bodies Tell a way bacteria and plants are alike. Both: have a cell wall; contain DNA; ribosomes; cytoskeleton Name the molecule in plant cell walls that make them sturdy Name an organelle besides the nucleus that has its own DNA mitochondria or chloroplasts Name the molecule found in bacterial cell walls instead of cellulose CELLULOSE PEPTIDOGLYCAN According to the Endosymbiotic theory which two cell parts evolved from ancient prokaryotic ancestors mitochondria & chloroplasts Name a cell part made of microtubules in a 9+2 arrangement Name an organelle besides the nucleus with its own DNA mitochondria & chloroplasts Another name for a living thing CILIA or FLAGELLA Which is the largest kind of cell? Animal Plant Bacteria Which cell is bigger? Animal Plant ORGANISM Which is the smallest kind of cell? Animal Plant Bacteria Which cell is bigger? Eukaryote Prokaryote Tell a way plant & animal cells are different Plant –has chloroplast; cell wall; really big vacuole Animal- has centrioles; no cell wall or chloroplasts small vacuoles Tell a way Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes are different Bacteria- no nucleus; no membrane bound organelles; DNA in one circular chromosome; smaller ribosomes Eukaryotes; nucleus; membrane bound organelles; DNA in multiple rodshaped chromosomes; bigger ribosomes Tell a way bacteria & animal cells are different Bacteria –prokaryote; cell walls; no nucleus; no membrane bound organelles Animal- has centrioles; no cell wall; nucleus membrane bound organelles; eukaryote Tell a way bacteria and plants are different. Bacteria –cell walls have peptidoglycan; no nucleus; no membrane bound organelles ;prokaryote Plant- cell wall has cellulose; nucleus membrane bound organelles; eukaryote Tell a way bacteria & plant cells are ALIKE Both have DNA; cell membranes; cell walls cytoskeleton; ribosomes Tell a way bacteria & animal cells are ALIKE Both have: DNA; cell membranes; cytoskeleton; ribosomes Tell a way plants & animal cells are ALIKE Both: eukaryotes; have DNA; cell membranes; organelles with membranes; cytoskeleton; ribosomes; Tell a way Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes are different Bacteria- no nucleus; no membrane bound organelles; DNA in one circular chromosome; smaller ribosomes Eukaryotes; nucleus; membrane bound organelles; DNA in multiple rod shaped chromosomes; bigger ribosomes Tell a way bacteria & animal cells are different Bacteria –prokaryote; cell walls; no nucleus; no membrane bound organelles Animal- has centrioles; no cell wall; nucleus membrane bound organelles; eukaryote Tell a way bacteria and plants are different. Bacteria –cell walls have peptidoglycan; no nucleus; no membrane bound organelles ;prokaryote Plant- cell wall has cellulose; nucleus membrane bound organelles; eukaryote Give 2 kinds of evidence for the Endosymbiotic Theory Mitochondria/chloroplasts have: own circular DNA; DNA divides like bacteria; smaller ribosomes; inner membrane proteins/lipids similar to bacteria; Name a cell part found in plants, animals, and bacteria Cell membrane, ribosomes, DNA, cytoskeleton