bus301 organisational behaviour
advertisement

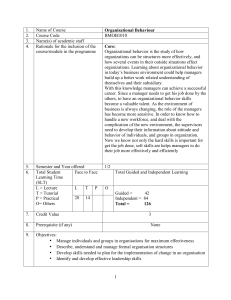
BUS301 ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOUR COURSE OUTLINE SEMESTER: SPRING 2013 Faculty Member’s Details: Name: Email: Web Site: Dr. Achilleas Karayiannis achilleaskarayiannis@hotmail.com http://www.cdacollege.ac.cy/site/business-studies/index.htm Course Description The aim of this course is to emphasize the great importance of human behaviour at work towards success and profitability. Learn what factors emerge the organizational productivity in the dynamic organizational environment. To familiarize students with the complexity of the issues surrounding today’s organizations in their internal environment and examines the contribution of behavioural science to the management process from a theoretical and functional perspective. Learning Outcomes By the end of the course, students are expected to: To familiarize students with the complexity of the issues surrounding today’s organizations in their internal environment. To examine the contribution of behavioural science to the management process from a theoretical and functional perspective. Be able to understand the role business and the market challenges within the organizational functions towards competitive advantage, Be able to understand how to deal with people in business enterprises and organizational relations. Prerequisites: Introduction to Business (BUS101) or Consent of Instructor Type of Course: Compulsory for Bachelor in Business Administration Teaching Methods and Educational Activities Lectures, presentations, problem and case studies discussion, articles discussion, independent and private study, preparation of projects, fieldwork and group work. Course Teaching Hours 39 hours a semester. The course is delivered during a 13-week semester. Assessment method and weight 50% coursework and 50% final examination. Coursework can be one or more of the following: mid-term examination, tests, assignments and projects. Passing mark 50%. 1 Business Administration Grading System % Grade 90-100 80-89 75-79 65-74 60-64 55-59 50-54 Below 50 Grade A B+ B C+ C D+ D F Grade Excellent Meaning Very Good Good Above Average Below Poor Average Failure Grade Points per 4.00 Credit 3.50 3.00 2.50 2.00 1.50 1.00 0.00 MAIN BOOK Title: Author: Publisher: Edition: Year: ISBN: Organizational Behaviour F. Luthans McGraw-Hill / Irwin 11th 2006 0071106782 Textbooks, References, Other Bibliography Title: Author: Publisher: Edition: Year: Human behaviour at work: organizational behaviour K. Davis & J. Newstrom McGraw-Hill / Irwin 11th 2002 Title: Author: Publisher: Year: Managing by communication: an organizational approach M. Myers & G. Myers McGraw-Hill 1982 LEARNING OUTCOMES TABLE WEEK Learning Outcomes and Content of the Course 1 Organizational Behaviour: A Modern Perspective and Organizational Behavior Approach; the Human Relations Movement; the Hawthorn Studies; Understanding Human Behavior; a Specific Model for Organizational Behavior. Case Study 2 A Behavioral Science and Research Perspective; Background of the Behavioral Sciences; Anthropology; Sociology; Psychology; Social Psychology; Research Methodology; Designs Used to Answer Questions and Test theories; Reliability and Validity of Measures; A Managerial Perspective: the Early Practice of Management; Classical Management Principles, the Quantitative Approach; the Systems Approach; the Contingency Approach. Case Study 2 Activities Guidelines for Assignment the 3 Personality: Development and Characteristics: The Meaning of Personality; the Development of Personality; Major Determinants of Personality; theories of personality. Case Study 4 Stress: Causes and Coping Strategies: the Meaning of Stress; the Background on Stress; the causes of Stress; the Effects of Job Stress; Coping Strategies for Stress. Case Study 5 Perception; Processes and Principles: the Nature and Importance of Perception; Sensation Versus Perception; Perceptual Selectivity; Perceptual Organization; Social Perception. Case Study 6 Motivation: Needs and Processes: the Meaning of Motivation; Primary Motives; General Motives; Secondary Motives; Work-Motivation Approaches; the Content Theories of Work Motivation; the Process Theories of Work Motivation. Case Study 7 Motivation Applied: Job Design, Appraisal, and Goal Setting: Job Design; Performance Appraisal; Goal Setting. Case Study 8 Learning Concepts and Principles: Types and Theories of Learning; Reinforcement; The Key to Learning; Techniques of Administering Reinforcement; The Effects of Punishment. Case Study 9 Organizational Behavior Modification: the Steps of Organizational Behavior; Experience with the Application of Modification; Behavioral Self-management; O.B. mod. in Perspective. Case Study 10 Interpersonal and Group Behavior, Dynamics and Influence: Groups: Formal and Informal: the Nature of Groups; Committee Organization; the Dynamics of Informal Groups; Interactive Behavior and Conflict: Intro individual Conflict; Interpersonal Conflict. Case Study 11 Communication; an Interpersonal Process; Historical Background of the Role of Communication; the Definition of Communication; Organizational and Interpersonal Communication; Superior-Subordinate Communication; Subordinate-Initiated Communication; Interactive Communication in Organizations. Case Study 3 12 Power and Politics: the Meaning and Relationship of Power and Politics; Sources and Types of Power; Political Implication of Power; Specific Political Strategies for Power Acquisition. 13 Leadership processes and Styles: The background of, and Classic Studies on, Leadership; Theories of Leadership; New Theoretical Frameworks for Leadership; Leadership Styles. Assignment due NOTES Class attendance and participation in class discussion is expected and absences will affect your final grade. The due dates for assignments are non-negotiable and late work will be penalized. All assignments are to be professional in appearance and type. OTHER INFORMATION Class attendance: Students are expected to attend the classes regularly and be punctual. Office hours: Students are encouraged and advised to visit regularly their instructor during the office hours and discuss promptly any issue that seems to be important for the student and his/her success. Humane matters: Inform your faculty member for any un-expectancies that may occur, thus not allowing you to carry out your responsibilities. Library: You are advised to visit regularly the library of our College and read articles published in academic journals. I recommend you studying regularly among others, articles of your interest, published in international journals. 4