AP ATOMS TO CELLS TEST REVIEW
advertisement

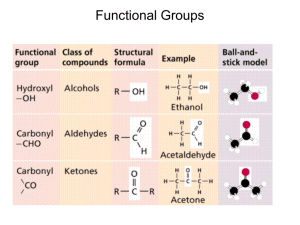
AP ATOMS TO CELLS TEST REVIEW Chapter Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chemical Foundations for Cells Carbon Compounds in Cells Cell Structure and Function A Closer Look at Cell Membranes Ground Rules for Metabolism Objectives 1. You should elementary understanding the standard theory of the fundamental particles that make up the universe. 2. You should understand the basic format of the periodic table, as well as be able to use it to determine characteristics of atoms. 3. You should understand the reasons that atoms form chemical bonds and familiar with the various types of bonding between atoms. 4. You should be familiar with the many important characteristics of water in living systems and understand how most of its characteristics are derived from its polar nature. 5. You should be familiar with various other chemical topics including isotopes, acids, bases, and salts, and how each is important in living systems. 6. You should be familiar with the structure of a carbon atom and how it structure is associated with the diverse classes of organic molecules. 7. You should be familiar the four classes of organic molecules, including the constituent molecule from with larger polymers are composed, and the structure and function of specific molecules in each class that are important to the cell. 8. You should be familiar with the function of cells, and be able to relate the supportive role that the various organelles play in cell function. 9. You should be familiar with the structure and function of a specific cell in the human body and be able to relate details regarding it shape and constituent organelles. 10. You should be knowledgeable of the various manners by which substances travel through the cell membrane, including the specific substances that are transported and specific situation in which such transport mechanism are important in living organisms. 11. You should be familiar with the characteristics and function of enzymes and how there function relates to their three dimensional quaternary structure. Vocabulary Chapter 2 elements neutrons subatomic mass ions compounds atoms atomic mass isotopes shell model mixture protons atomic number radioactive isotopes chemical bond ionic bonding electrons subatomic charge tracer molecule covalent bonding hydrogen bonding temperature cohesion hydroxide ions buffer system water polar solvent pH scale salts hydrophilic electronegative solute acids hydrophobic electropositive hydrogen ions bases Chapter 3 organic compounds hydroxyl group amino group hydrolysis polysaccharides fats sterols amino group primary structure sheets nucleotides inorganic comp. aldehyde group phosphate group carbohydrates cellulose fatty acid waxes carboxyl group secondary structure denature DNA carbon bonds ketone group dehydration syn. monosaccharides chitin triglycerides proteins R-group tertiary structure enzymes RNA functional groups carboxyl group condensation disaccharides lipids phospholipids amino acids polypeptide chain helix nucleic acids Chapter 4 cell theory Brown plasma membrane prokaryotic surface area nucleus mitochondria cytoskeleton intermediate filamts. centriole Galileo Schwann cytoplasm lipid bilayer volume endoplasmic retic. chloroplast cytomembrane sys. pseudopods 9+2 array Hooke Schleiden ribosomes fluid mosaic model microscopes golgi body vacuole microtubules flagellum Leeuwenhoek Virchow eukaryotic cell size organelle vesicles cell wall microfilaments cilium Chapter 5 phagocytosis active transport hypotonic endocytosis concentration grad. osmosis isotonic diffusion tonicity fluid pressure passive transport hypertonic exocytosis Chapter 6 enzymes induced-fit model activation energy active sites substrate quarks bottom baryons graviton strong force big bang Lewis dot diagram up charm hadrons gravity weak force accelerators structural stability down strange electrons photon boson telescopes electrical stability Other fundamental top leptons force carrier part. electromagnetic f. z-particle Bohr diagram