Course Outline New version spring 2010
advertisement
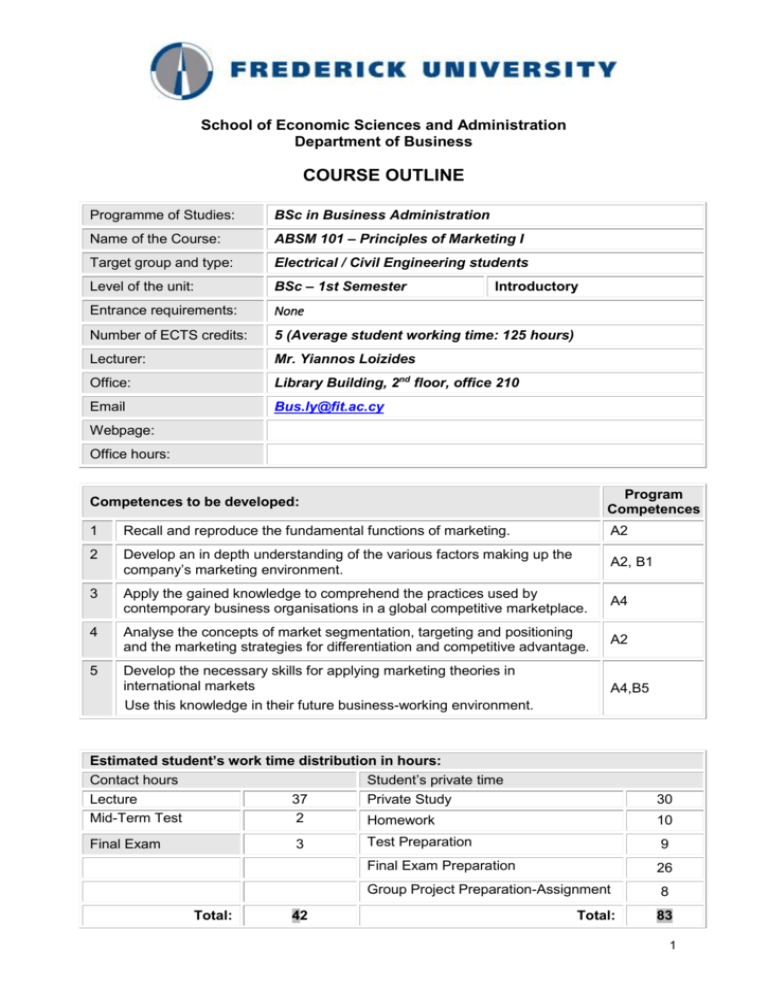
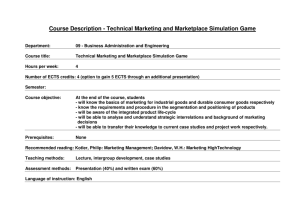
School of Economic Sciences and Administration Department of Business COURSE OUTLINE Programme of Studies: BSc in Business Administration Name of the Course: ABSM 101 – Principles of Marketing I Target group and type: Electrical / Civil Engineering students Level of the unit: BSc – 1st Semester Entrance requirements: None Number of ECTS credits: 5 (Average student working time: 125 hours) Lecturer: Mr. Yiannos Loizides Office: Library Building, 2nd floor, office 210 Email Bus.ly@fit.ac.cy Introductory Webpage: Office hours: Competences to be developed: Program Competences 1 Recall and reproduce the fundamental functions of marketing. A2 2 Develop an in depth understanding of the various factors making up the company’s marketing environment. A2, B1 3 Apply the gained knowledge to comprehend the practices used by contemporary business organisations in a global competitive marketplace. A4 4 Analyse the concepts of market segmentation, targeting and positioning and the marketing strategies for differentiation and competitive advantage. A2 5 Develop the necessary skills for applying marketing theories in international markets A4,B5 U Use this knowledge in their future business-working environment. Estimated student’s work time distribution in hours: Contact hours Student’s private time Lecture 37 Private Study Mid-Term Test 2 Homework Final Exam 3 Total: 42 30 10 Test Preparation 9 Final Exam Preparation 26 Group Project Preparation-Assignment 8 Total: 83 1 Learning outcomes Students should be able to: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships: Describe marketing and understand the marketplace and consumer needs. Discuss the twofold goal of marketing and the process by which we create value for customer and build customer relationships. Learn different definitions of important marketing terms such as what is a need, demand and want est. Learn about the five marketing concepts and the preparation of a marketing program and plan. Learning how important is to build and capture value from customers in the new marketing landscape. Elaborate on Customer relationship management and when a company can suffer from marketing myopia. Company and Marketing Strategy: Partnering to Build Customer Relationships: Define strategic planning and the steps, which need to be taken. Analyse how a mission statement is composed and their important role in the management of a company. Analyse business portfolio and explain how management can design it. Explain what a BCG growth share matrix is and how companies use it. Discuss possible advantages and disadvantages of this method and bring out alternatives. Discuss the key elements of marketing planning and analyse each one of them. The Marketing Environment: Learn what is the company’s environment and the aspects of it. Discuss what microenvironment is and the actors, which can affect a firm’s ability to serve customers. Explain to what macro environment refers to and discuss its six forces: Demographic, Economic, Natural, technological, Political, Cultural. Finally a discussion on who to respond to the marketing environment is inevitable. Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Creating Value for Target Customers: Understand the concepts of market segmentation, target marketing and positioning for competitive advantage. Differentiate between consumer markets, business markets, and international markets. Discuss about the demographic segmentation variables and how these are used to segment a market. Finally elaborate on the requirements for an effective segmentation (measurable, accessible, substantial, differentiable, actionable). Product, Services, and Branding Strategy: Discuss what is a product and the decisions which need to be taken when a company deals with products and services. How to build strong brands by an efficient branding strategy. Service: Discuss the nature of services and explain how services are marketed in comparison to products. Course Content (Syllabus): 1. Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships (Ch. 1) a. Understanding the Marketplace and Consumer Needs b. Designing a Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy c. Preparing a Marketing Plan and Program d. Building Customer Relationships 2 e. Capturing Value form Customers f. The New Marketing Landscape 2. Company and Marketing Strategy: Partnering to Build Customer Relationships (Ch. 2) a. Company wide Strategic Planning: Defining Marketing’s Role b. Planning Marketing: Partnering to Build Consumer Relationships c. Marketing Strategy and the Marketing Mix d. Managing the Marketing Effort e. Measuring and Managing Return on Marketing 3. The Marketing Environment (Ch. 3) a. The company’s Microenvironment b. The company’s Macro environment c. Responding to the Marketing Environment 4. Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Creating Value for Target Customers (Ch. 7) a. Market Segmentation b. Market Targeting c. Differentiation and Positioning 5. Product, Services, and Branding Strategy (Ch. 8) a. What is a Product? b. Product and Service Decisions c. Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands d. Services Marketing e. Additional Product Considerations Teaching Methodology: The Methodology used included lecturing based on the lecture’s power point presentations, discussions, reference to real life examples related to the main marketing issues taught, as well as to the students’ business background, analysis of case studies. Coursework Tests Assignments Homework Estimated Dates Material Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Company and Marketing Strategy: Partnering to Build Customer Relationships The Marketing Environment Week 5 What is marketing Mission Statement S.W.O.T. Analysis Week 2 Week 4 Week 5 Assessment Weights Coursework Week 5 Week 8 Total Participation in class 10 Mid term exam 15 Assignments 15 50 3 Final Exam 50 Note: The assessment weights for the final exam the coursework (and the laboratory work) are decided by the Department before the beginning of the semester. The details on the number of tests/homework assignments projects etc, as well as their assessment weights are decided by the academic staff responsible for the course. Bibliography: Textbooks: Armstrong, G. and Kotler, P. (2008) ‘Principles of Marketing’, 12th edition, Prentice Hall, USA. References: Morthy, E. And Perreault, W. (1996) ‘Basic Marketing A Global-Managerial Approach’, 12th edition, McGrawHill, UK. Etzel, M., Stanton, W. and Walker, B. (1997) ‘Marketing’, 11th ed. McGraw-Hill, UK. Jobber, B. (1998) ‘Principles and Practice of Marketing’, 2nd ed., McGraw-Hill, UK. Armstrong, G., Kotler, P., Saunders, J. and Wong V. (1999) ‘Principles of Marketing’, 2nd European edition, Prentice Hall Europe, USA. 4