Chapter 6
advertisement

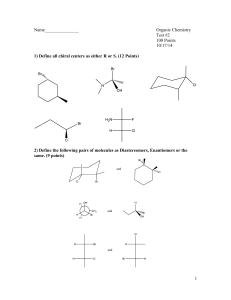
Chapter 6 – Isomers and Stereochemistry Chirality - Stereoisomers are possible for carbons with 4 different groups attached (C*). These are called chirallity center or asymmetric centers. Chiral objects have no mirror image plan of symmetry Achiral objects have a plane of symmetry CHM 201 – Dang 1 *All chiral objects have non-superimposable mirror images (every chiral molecule has an enantiomer) *All achiral objects are exactly the same as mirror images (an achiral molecule does not have an enantiomer) *E and Z allow us to draw exact substitution patterns around the double bonds. *The symbols, R and S allow us to draw exact 3D shapes of tetrahedral atoms. CHM 201 – Dang 2 R/S Nomenclature of Chiral center The stereochemistry of each chiral carbon (chirality center with four different groups) is designated as either R or S configuration 1. Assign priorities to four groups: #1 has the highest atomic number, #4 has the lowest atomic number a. I > Br > Cl > S > F > O > N > C > H > lone pair of electrons. b. If there is a tie, move away one atom at a time until you find a difference c. A double bond can be treated as two single bonds 2. With the lowest priority group ( #4) pointing away from you, go from # 1 #2 #3 a. If rotation is clocker (CW), then R is assigned (R = Latin rectus/right-handed) b. If rotation is counterclockwise (CCW), the S is assigned (S = Latin sinister/left) E.g CHM 201 – Dang 3 How to draw R and S absolute configurations from a name: 1. Write out a two dimensional structure from the name 2. Locate all chiral centers (4 different groups at sp3 atoms) and assign the priorities of the groups at each chiral atom. 3. Draw a genetic tetrahedral center and place the low priority group away 4. Fill in any convenient (obvious) group, …say 1. 5. Add in other two groups in specified order ( R would have 2 to the right and S would have 2 to the left 6. If the assignment is correct, you are finished. If it is incorrect, then interchange any two convenient groups and it will be correct. Draw (S) – 2- bromopentane Draw the enantiomer of (S) – 2- bromopentane Fisher Projections (15.0) A short –hand way to draw chiral center Basic rules 1. Place the longest chain in vertical direction 2. Put the highest priority (nomenclature priority) in the top half of your representation 3. Horizontal groups project toward the front (in front of the page/surface) 4. Vertical groups project away from the viewer (in back of the page/surface) 5. A carbon atom is indicated at each intersection of vertical and horizontal lines Convert the following bond-line drawing into Fisher projection. Determine the configuration of stereocenter and then draw the enantiomer CHM 201 – Dang 4 Molecules with 2 chiral centers (6.9, 6.10) Relationship between A & B : ………………………… C & D: ………………………… A& C: ………………………… All stereoisomers are either enantiomers (chiral and all chiral inverted) OR Diastereomers (cis/trans alkenes or some but not all chiral centers inverted Any other pairs? …………….. CHM 201 – Dang 5 Enantiomers have identical physical properties (b.p, solubility, IR, mp, etc) except they have equal and opposite optical roation [α] (“specific rotation”) Diastereomers have different in everything E.g Draw all stereoisomers of 2,3-dichlorobutane Optical activity + other physical properties (6.7, 6.8, 6.12) Chiral molecules rotate a plane of polarized light Angle of rotation (α) is measured by a polarimeter Achiral species are not optically active [α= 0o]*There is no relationship between R/S and +/-. The value of [α] must be measured, can’t be predicted. CHM 201 - Dang6 When do enantiomers behave differently? When interacting with another chiral molecule or in a chiral environment E.g R/L hand + coffee mug no difference R/L hand + R glove difference +/- molecule + chiral receptor difference a drug + an enzyme Racemic mixture (Racemate) (6.8) - 1:1 mixture of enantiomers Optically inactive [α=0o] Can be separated, but it’s difficult process Nature makes single enantiomers of chiral compounds, but lab synthesis give racemates Most chiral drugs are sold as racemates but it is likely that a single enantiomers is more effective Identify relationship between structures A) B) C) D) E) Constitutional isomers Enantiomers Diastereomers Same compound Unrelated CHM 201 - Dang7 CHM 201 - Dang8