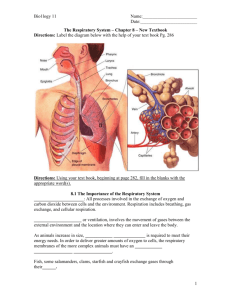
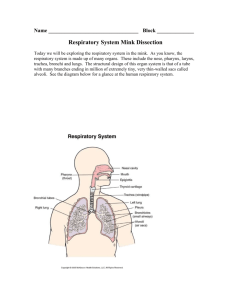
Alveolar ducts – alveolar sacs – alveoli (300,000,000)
advertisement

Respiratory System Lecture Outline Facts: Unicellular organisms – only organisms without resp. system – gasses exchange through membrane. Oxygen in atmosphere: 21% oxygen – anything below 15% humans can’t survive Diagram of Resp. Syst.: Mouth\nose – nasal cavity – pharynx – larynx – trachea – bronchi – bronchioles – alveoli (gas exchanges here) Purpose of respiratory system a. supply cells with oxygen b. remove carbon dioxide from cells Upper Resp. Stem: (Nose, Pharynx, Larnyx) Air enters external nares (nostrils) into nasal cavities. Nasal Conchae bones: increase surface area by being folded into 3 ridges Conchae and entire lining of nose covered by mucus membrane – clean dust and debris from air. Three functions of nasal cavity: a. Clean out dirt and dust (mucus and nose hairs) b. Warm the air you breathe (blood vessels in nasal cavity raise air temp.) c. Moisten incoming air. Four pairs of sinuses – drain into nose Lightens the skull and acts as a resonance chamber for sound. Nasal Cavity – Pharynx – back of mouth; food and air. Pharynx ends at the glottis (opening to the larynx) Glottis is a narrow slit: males 23 mm, females 17 mm Around the rim of the glottis are vocal chords – vibrations produce sound. Epiglottis is a cartilage flap that covers the glottis when you are swallowing. Larynx = voice box Aka adam’s apple Made of thyroid cartilage (upper part) and cricoid cartilage (lower part) Lower respiratory Tract – trachea, bronchi lungs Trachea: 11 cm long and 2 – 2.5 cm wide. Made of alternating bands of cartilage and membrane Rings of cartilage are open at the back Esophagus is just behind the trachea Trachea is lined with ciliated epithelium and mucus. Bronchi: Trachea divides into 2 primary bronchi Bronchi – Bronchioles - Alveolar ducts – alveolar sacs – alveoli (300,000,000) Surface area is the size of a tennis court Ducts, sacs, and alveoli are made of thin squamous epithelial tissue (for better gas exchange) Lungs: Left Lung – superior and inferior lobes Right lung – superior, middle and inferior lobes Visceral pleura – membrane covering lungs Parietal pleura – membrane lining thoracic cavity Pleural cavity – between the two membranes and is filled with fluid to reduce friction when breathing. Sound: Size and shape of nose, mouth, pharynx, and sinuses determine sound quality. Diaphragm: Large flat muscle that allows the lungs to inflate and deflate Inhale: diaphragm pushes down Exhale: diaphragm pushes up Lung capacity: total capacity is 6 Liters, but we only exchange .6 liters under normal breathing conditions. Vital Capacity: max amount of air that can be moved in and out of resp. system Hemglobin: red colored protein that is found in blood that has attachment site for oxygen molecules. Sensory Receptors Responsible for sending signals to the brain about oxygen and Carbon Dioxide levels Carotoid artery in neck Aorta in heart More concerned about Carbon Dioxide levels being too high. CO2 + O2 -> H2CO3 Carbonic Acid Changes blood pH which is what receptors respond to. Asphyxiation: suffocation from blockage Heimlich (abdominal thrusts) – procedure to remove blockage. Tracheotomy: puncture a hole in the trachea