Electricity
advertisement

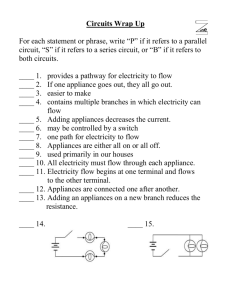
CURIT – CURRICULUM UNIT REVISION INFUSING TECHNOLOGY UNIT IMPLEMENTATION PLAN DISTRICT/STATE East Granby, CT SCHOOL/GRADE LEVEL East Granby High School SUBJECT Science UNIT TITLE Physical Science - Electricity SECTION 1: GENERAL INFORMATION SECTION 2: CURRICULUM ALIGNMENT UNIT PLAN CONTENTS SECTION 3: EVIDENCE OF STUDENT LEARNING SECTION 4: TEACHING AND LEARNING STRATEGIES SECTION 5: WORK EXAMPLES SECTION 6: UNIT TASKS/MANAGEMENT STATE CONNECTICUT – CURRICULAR CONTENT AREAS CONNECTICUT – K-12 INFORMATION AND TECHNOLOGY FRAMEWORK CONNECTICUT – PK-12 COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY COMPETENCY STANDARDS FOR STUDENTS CONNECTICUT – TEACHER TECHNOLOGY COMPETENCIES STANDARDS/FRAMEWORKS INTERNET LINKS CONNECTICUT – ADMINISTRATOR TECHNOLOGY STANDARDS NATIONAL TECHNOLOGY STANDARDS/RESOURCES NETS – STUDENTS NETS – TEACHERS NETS – ADMINISTRATORS NETS – ALIGNED RESOURCES I NSTRUCTIONS INSTRUCTIONS/RESOURCES TEACHER(S) INFORMATION R ESOURCES Object Embedding Hyperlinking Project Management Tools FIRST AND LAST NAME(S) Barbara Samuelsen EMAIL ADDRESS(ES) East Granby High School SCHOOL PHONE bsamuelsen@eastgranby.k12.ct.us Project Calendar F OR MORE DETAILS ABOUT THE CURIT PROCESS , PLEASE VISIT – CURIT . WIKISPACES . COM OR CONTACT : CURIT CONTACT INFORMATION RATOSHA TERRY EDUCATION TECHNOLOGY SPECIALIST CAPITOL REGION EDUCATION COUNCIL - CREC 111 CHARTER OAK AVENUE HARTFORD, CT 06106 RTERRY@CREC.ORG / 860-524-4007 REV. 6/30/2010 CREC Educational Technology Services 111 Charter Oak Avenue – Hartford, CT 06106 www.crec.org / 860-524-4053 Page 1 of 8 CURIT – CURRICULUM UNIT REVISION INFUSING TECHNOLOGY UNIT IMPLEMENTATION PLAN SECTION 1: GENERAL INFORMATION UNIT TITLE UNIT SUMMARY Electricity This unit is designed to extend and expand the student’s understanding of electricity. Students will become aware of the role of energy in our world and the role electricity and energy plays within that. The students will identify characteristics of how we get electricity to our school and home. They will understand static electricity through shocks in the wintertime and that it will not transfer if there are no materials to transfer through. Electricity is transmitted differently depending on the medium; some materials are conductors others are insulators. Students will recognize that electricity is conducted and absorbed depending on the properties of materials. Students will perceive that factors affect the resistance of materials. To effectively engage students and enhance their knowledge, this unit encompasses a variety of learning opportunities, some of which include, but are not limited to: internet resources, Smart Board activities, literature, worksheets, etc. PERQUISITE SKILLS UNIT DURATION (EX. 2 WKS.) Two weeks SECTION 2: CURRICULUM ALIGNMENT ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS CURRICULUM STANDARDS TECHNOLOGY STANDARDS/ 21ST CENTURY SKILLS CONNECTIONS How is electrical energy produced? What is the difference between static and current electricity? What is the difference between direct and alternating current? What are some important electrical safety issues? Gr. 9 Electricity Standards.doc NETS for Students NETS for Teachers Students are expected to know: CONTENT CONNECTIONS How electrical energy is produced How electric charges are transferred and explain why electrical discharges occur That negative charges are more mobile than positive charges How to describe conduction and classify materials as good electrical insulators or conductors How voltage produces and electric current How to compare direct and alternating currents How to analyze circuit diagrams for series and parallel circuits How to solve equations that relate electric power to current, voltage and electrical energy; relate ways to avoid electrical mishaps Students will be able to: SKILLS ATTAINED Electricity Unit Skills Attained.doc CREC Educational Technology Services 111 Charter Oak Avenue – Hartford, CT 06106 www.crec.org / 860-524-4053 Page 2 of 8 CURIT – CURRICULUM UNIT REVISION INFUSING TECHNOLOGY UNIT IMPLEMENTATION PLAN SECTION 3: EVIDENCE OF STUDENT LEARNING Students will: PERFORMANCE TASKS Electricity Unit Performance Tasks.doc CULMINATING PROJECT OTHER EVIDENCE Students will: Test conductors and insulators Snap circuits kits to make electrical connections Design a series circuit and a parallel circuit Power rating for various electrical appliances Fuses and circuit boards Current Event on electricity, computers, digital cameras Water flow attracted to a charged comb demonstration ELL/IEP Students - Battery and wire to light a light bulb Highly-Capable Students - Snap kit to make various electrical appliances TEACHER REFLECTION (POST IMPLEMENTATION) http://www.emints.org/ethemes/index.shtml ADDITIONAL UNIT RESOURCES See accompanying SMART Notebook Lesson – Attached separately CREC Educational Technology Services 111 Charter Oak Avenue – Hartford, CT 06106 www.crec.org / 860-524-4053 Page 3 of 8 CURIT – CURRICULUM UNIT REVISION INFUSING TECHNOLOGY IMPLEMENTATION PLAN SECTION 4: TEACHING AND LEARNING STRATEGIES OBJECTIVE/FOCUS QUESTION How is electrical energy produced? INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES LESSON/CHAPTER: 1-20.1 APPROX. TIME 45 MIN. Show video of history of electricity. Worksheet that they fill out while watching the video. HOMEWORK: READ CH.20.1 PG. 600-603, QUESTIONS PG. 603:1-10 Factors that affect the strength and direction of electric forces and fields LESSON/CHAPTER: Describe how electric charges are transferred and explain why electric discharges occur. LESSON/CHAPTER: APPROX. TIME 45 3-20.1 APPROX. TIME 45 DIFFERENTIATION MATERIALS AND RESOURCES Students fill in the blanks in the video guide. We can review the answers in the blanks at the end of the video Power Plant Video from Modern Marvels Students have bar magnets—write journal entries of observations The Case of the Missing iPod Webquest Circuits and Conductors Activity All That Static Smart board Static Electricity Smartboard Lesson Students have one battery, one flashlight bulb, and one wire to create a complete circuit How Electricity Works Short Video Electric Current Simulator Power Plants Video Guide.doc MIN. Review the questions on pg. 603:1-10. Have bar magnets so students can see attraction and repulsion. Have metal fillings on overhead with bar magnets to see the strength and direction of the electric forces and field. HOMEWORK: 20.1 REVIEW SHEET Students draw a picture of the bar magnet and the metal fillings for exit pass. MIN. Charge a balloon by friction and hang it on the wall. Video on lighting to show static discharge. Changes can be transferred by friction, contact, and induction. HOMEWORK: Describe the two different types of current and factors that affect resistance 2-10.1 ASSESSMENT Electricity - Fill in the Blank Worksheet HW - 20.1 - Electric Charge LESSON/CHAPTER: 4-20.2 APPROX. TIME 45 MIN. Compare direct current (dc), like batteries, and alternating current (ac), which is electricity at school and home. Test conductors and insulators to see how they work. A wire’s thickness, length, and temperature can affect its resistance. HOMEWORK: READ 20.2 PG. 604-607, QUESTIONS PG.607:1-8 CREC Educational Technology Services 111 Charter Oak Avenue – Hartford, CT 06106 www.crec.org / 860-524-4053 Page 4 of 8 CURIT – CURRICULUM UNIT REVISION INFUSING TECHNOLOGY IMPLEMENTATION PLAN SECTION 4: TEACHING AND LEARNING STRATEGIES OBJECTIVE/FOCUS QUESTION Explain how voltage produces electric current. Calculate voltage, current, and resistance using Ohm’s law INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES LESSON/CHAPTER: APPROX. TIME 45 MIN. Explain potential difference so that charges flow from a higher to a lower potential energy, which is measured in volts. Class work is electric current 20.2 questions. Do problems using Ohm’s law. HOMEWORK: Analyze circuit diagrams for series circuits and parallel circuits. 5-20.2 ASSESSMENT DIFFERENTIATION Ohms’s law activity on the computer Post students’ “big ideas” in the room about how charges flow Draw a sample of a circuit diagram for a series circuit and also for a parallel circuit using the electrical symbols Check with another student who has achieved a circuit and the bulb is lit MATERIALS AND RESOURCES HW - 20.2 Electric Current LESSON/CHAPTER: 6-20.3 APPROX. TIME 45 MIN. Learn the symbols for drawing a series and a parallel circuit. See if they have a circuit diagram for their home. Design a series circuit and compare it to a parallel circuit. Use the kit. Solve equations that relate electric power to current, voltage, and electrical energy. Class work is Electric Circuits Worksheet. HOMEWORK: READ 20.3 PG. 609-613, QUESTIONS PG.609:1-8 FOR H, 1-6 FOR CP Describe devices and procedures for maintaining electrical safety and at home LESSON/CHAPTER: Home safety devices LESSON/CHAPTER: 7-20.3 APPROX. TIME 45 MIN. Show a video on lightning and discuss safety procedures during a storm. HOMEWORK: 20.3 REVIEW SHEET 8-20.3 APPROX. TIME MIN. Discuss safety features like fuses, circuit breakers, GFCI, and grounding. HW - 20.3 Circuits HOMEWORK: CREC Educational Technology Services 111 Charter Oak Avenue – Hartford, CT 06106 www.crec.org / 860-524-4053 Page 5 of 8 Peer to peer collaboration Students can report on their experiences in lightning storms Check your own home for safety features and list them. Circuits SmartBoard Lesson Circuits SmartBoard Review Series and Parallel Circuits Smartboard CURIT – CURRICULUM UNIT REVISION INFUSING TECHNOLOGY IMPLEMENTATION PLAN SECTION 4: TEACHING AND LEARNING STRATEGIES OBJECTIVE/FOCUS QUESTION INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES Explain how electronic signals convey information LESSON/CHAPTER: Illustrate how semiconductors are used to make three kinds of solid-state components LESSON/CHAPTER: Review electricity concepts to study for the test LESSON/CHAPTER: APPROX. TIME 9-20.4 45 MIN. Describe electronic devices used to control electron flow. Compare analog and digital signals and the big difference in these signals. HOMEWORK: READ 20.4 PG. 614-622, QUESTIONS PG.622-1-8 APPROX. TIME 10-20.4 45 DIFFERENTIATION Students explain the comparison and contrast of analog and digital signals Conductors and Insulators SmartBoard Lesson MIN. APPROX. TIME 11-20 45 MIN. 45 MIN. REVIEW THE WHOLE CHAPTER TO GET READY FOR THE TEST LESSON/CHAPTER: Electricity Review Questions.doc 12-20 APPROX. TIME Jeopardy whole-class review for test. Jeopardy.doc HOMEWORK: STUDY FOR THE TEST Static Electricity MATERIALS AND RESOURCES How diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits have changed electronics. HOMEWORK: 20.4 REVIEW SHEET HOMEWORK: STUDY FOR THE TEST Review of the chapter 20 ASSESSMENT LESSON/CHAPTER: 13-20 APPROX. TIME 45 MIN. Review Static Electricity CREC Educational Technology Services 111 Charter Oak Avenue – Hartford, CT 06106 www.crec.org / 860-524-4053 Page 6 of 8 Use Van de Graaff generator and have students light up a fluorescent light bulb CURIT – CURRICULUM UNIT REVISION INFUSING TECHNOLOGY IMPLEMENTATION PLAN SECTION 4: TEACHING AND LEARNING STRATEGIES OBJECTIVE/FOCUS QUESTION INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES Ch. 20 Test LESSON/CHAPTER: Ch. 20 Electricity Test ( H).doc 14-20 ASSESSMENT APPROX. TIME 45 MIN. Ch. 20 Electricity Test CP.doc CREC Educational Technology Services 111 Charter Oak Avenue – Hartford, CT 06106 www.crec.org / 860-524-4053 Page 7 of 8 DIFFERENTIATION MATERIALS AND RESOURCES CURIT – CURRICULUM UNIT REVISION INFUSING TECHNOLOGY IMPLEMENTATION PLAN SECTION 5: WORK EXAMPLES TEACHER STUDENT SECTION 6: UNIT TASKS/MANAGEMENT NOTES/TO DO’S SUPPLIES TECHNOLOGY – HARDWARE (CLICK BOXES OF ALL EQUIPMENT NEEDED) COMPUTER(S) VCR PROJECTION SYSTEM PRINTER DIGITAL VIDEO CAMERA SMARTBOARD™ DIGITAL STILL CAMERA SCANNER VIDEO CONFERENCING OTHER TECHNOLOGY – SOFTWARE (CLICK BOXES OF ALL SOFTWARE NEEDED) MICROSOFT WORD MICROSOFT FRONT PAGE KIDPIX MICROSOFT EXCEL MICROSOFT INTERNET EXPLORER INSPIRATION/KIDSPIRATION/WEBSPIRATION MICROSOFT POWERPOINT SMART™ NOTEBOOK CLASSROOM RESPONDER SYSTEM (CRS) PUBLISHER ENCARTA REFERENCE MATERIALS IMAGE BLENDER/PHOTO EDITOR OTHER CREC Educational Technology Services 111 Charter Oak Avenue – Hartford, CT 06106 www.crec.org / 860-524-4053 Page 8 of 8