Tea Act Preview
advertisement

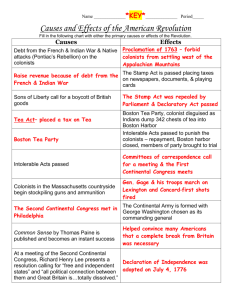
Preview – Tea Act/Boston Tea Party Tea Act The Tea Act was a 1773 Act that gave a monopoly on tea sales to the East India Company. In other words, American colonists could buy no tea unless it came from that company. Why? Well, the East India Company wasn't doing so well, and the British wanted to give it some more business. The Tea Act lowered the price on this East India tea so much that it was way below tea from other suppliers. But the American colonists saw this law as yet another means of "taxation without representation" because it meant that they couldn't buy tea from anyone else (including other colonial merchants) without spending a lot more money. Their response was to refuse to unload the tea from the ships. This was the situation in Boston that led to the Boston Tea Party. 1. What was the purpose of the Tea Act? 2. Did this increase or decrease the tension between the colonists and the British government? Explain. HBO – John Adams Lesson 1.5, Preview Episode One M. Frank - 2008 Boston Tea Party Angry and frustrated at a new tax on tea, American colonists calling themselves the Sons of Liberty and disguised as Mohawk Native Americans boarded three British ships (the Dartmouth, the Eleanor, and the Beaver) and dumped 342 whole crates of British tea into Boston harbor on December 16, 1773. Similar incidents occurred in Maryland, New York, and New Jersey in the next few months, and tea was eventually boycotted throughout the colonies. 1. What do you think the colonist hoped to accomplish with the Boston Tea Party? 2. Why were boycotts effective? Information source: www.socialstudiesforkids.com HBO – John Adams Lesson 1.5, Preview Episode One M. Frank - 2008