Chapter 5 Notes: Birds
advertisement
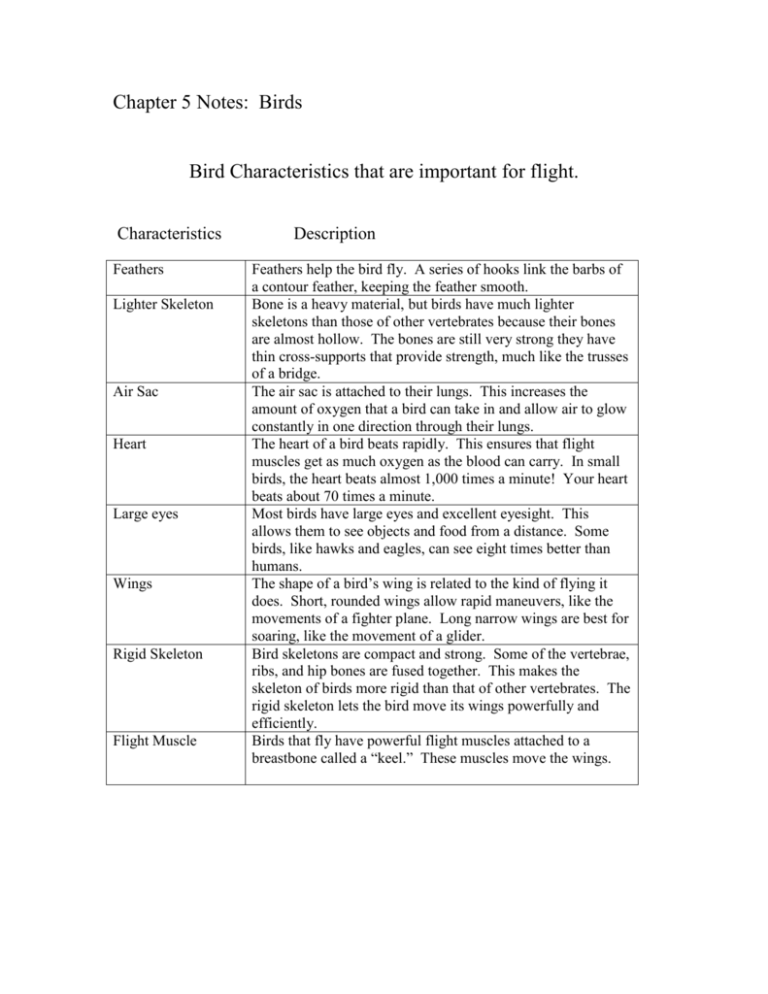
Chapter 5 Notes: Birds Bird Characteristics that are important for flight. Characteristics Feathers Lighter Skeleton Air Sac Heart Large eyes Wings Rigid Skeleton Flight Muscle Description Feathers help the bird fly. A series of hooks link the barbs of a contour feather, keeping the feather smooth. Bone is a heavy material, but birds have much lighter skeletons than those of other vertebrates because their bones are almost hollow. The bones are still very strong they have thin cross-supports that provide strength, much like the trusses of a bridge. The air sac is attached to their lungs. This increases the amount of oxygen that a bird can take in and allow air to glow constantly in one direction through their lungs. The heart of a bird beats rapidly. This ensures that flight muscles get as much oxygen as the blood can carry. In small birds, the heart beats almost 1,000 times a minute! Your heart beats about 70 times a minute. Most birds have large eyes and excellent eyesight. This allows them to see objects and food from a distance. Some birds, like hawks and eagles, can see eight times better than humans. The shape of a bird’s wing is related to the kind of flying it does. Short, rounded wings allow rapid maneuvers, like the movements of a fighter plane. Long narrow wings are best for soaring, like the movement of a glider. Bird skeletons are compact and strong. Some of the vertebrae, ribs, and hip bones are fused together. This makes the skeleton of birds more rigid than that of other vertebrates. The rigid skeleton lets the bird move its wings powerfully and efficiently. Birds that fly have powerful flight muscles attached to a breastbone called a “keel.” These muscles move the wings. 3 Types of feathers 1. Contour feathers – a large feather that gives shape to a bird’s body 2. Flight Feathers – these are the long contour feathers that extend beyond the body on the wings and tail. They help the bird to balance and steer during flight. 3. Down Feathers – short fluffy feathers that are specialized to trap heat and keep the bird warm. These feathers are found right next to the bird’s skin, at the base of the contour feathers. Birds have a two-loop circulatory system and a four-chambered heart. The advantage of a four-chambered heart is that oxygen-rich blood does not mix with oxygen-poor blood. Category Water Fowl Flightless Perching Birds of Prey Four major Classifications of birds Description Examples Usually have webbed feet for Cranes, ducks, geese, swimming, but they are also swans, pelicans, loons, strong flyers. and many others. These birds do not have a large Ostriches, kiwis, emus, keel for flight. Though they penguins (these birds cannot fly, many flightless birds have a large keel but their are fast runners wings have been modified into flippers) These birds have special Songbirds, like robins, adaptations for perching on a wrens, warblers, and branch, its feet automatically sparrows. close around the branch. Birds of prey are meat eaters. Eagles, hawks, falcons, They may eat mammals, fish, owls, ospreys and others. reptiles, birds, or other animals. The sharp claws on their feet and their sharp, curved beaks help these birds catch and eat their prey. They also have very good vision. Most hunt during the day. Precocial – These birds hatch from an egg ready to run around and eat bugs. They are covered with downy feathers and follow their parents as soon as they can stand up. Examples of these birds are chickens, ducks, shorebirds. Altricial – These chicks are born weak, naked and helpless. Their eyes are closed when they are born. These birds cannot fly or walk. Their parents must keep them warm and feed them for several weeks. The difference in pressure above and below the wings as a bird moves through the air produces an upward force that causes the bird to rise. That upward force is called lift.






