HW4_answers
advertisement
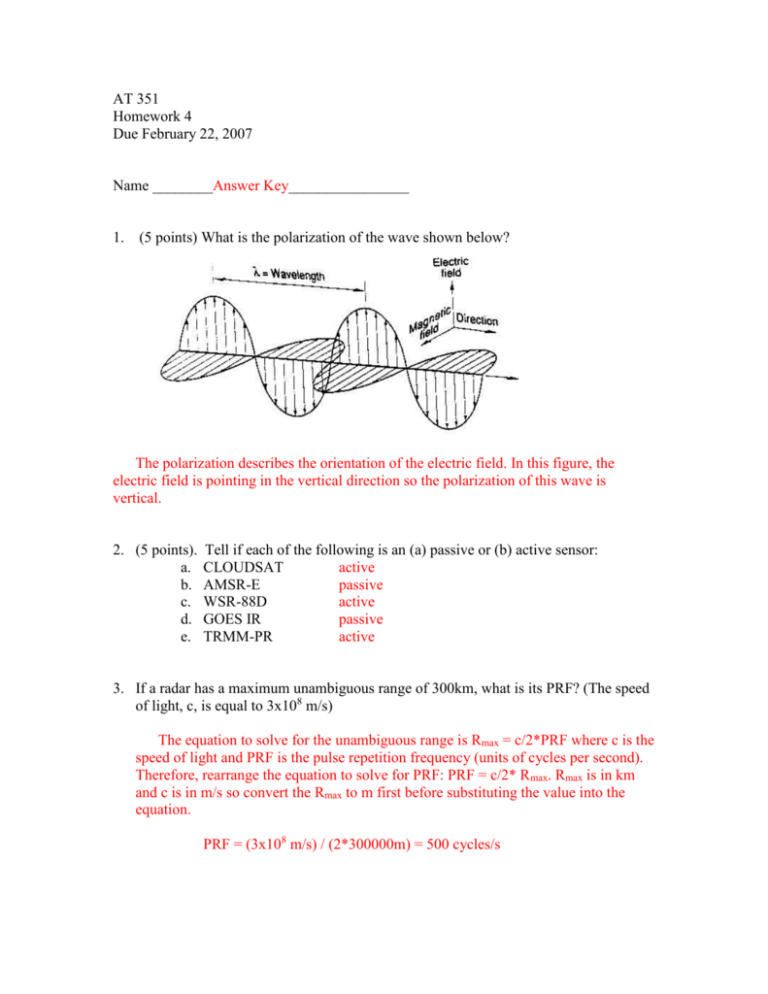
AT 351 Homework 4 Due February 22, 2007 Name ________Answer Key________________ 1. (5 points) What is the polarization of the wave shown below? The polarization describes the orientation of the electric field. In this figure, the electric field is pointing in the vertical direction so the polarization of this wave is vertical. 2. (5 points). a. b. c. d. e. Tell if each of the following is an (a) passive or (b) active sensor: CLOUDSAT active AMSR-E passive WSR-88D active GOES IR passive TRMM-PR active 3. If a radar has a maximum unambiguous range of 300km, what is its PRF? (The speed of light, c, is equal to 3x108 m/s) The equation to solve for the unambiguous range is Rmax = c/2*PRF where c is the speed of light and PRF is the pulse repetition frequency (units of cycles per second). Therefore, rearrange the equation to solve for PRF: PRF = c/2* Rmax. Rmax is in km and c is in m/s so convert the Rmax to m first before substituting the value into the equation. PRF = (3x108 m/s) / (2*300000m) = 500 cycles/s 4. Explain the presence of a bright band. The bright band is a band of high reflectivity observed within the cloud, surrounded above and below by lower reflectivities. It represents the region in the cloud where snow is melting. As snow from the upper levels of the cloud falls through the melting layer (the layer in the cloud with 0C), the snow acquires a coat of water, giving it the appearance as a large raindrop. Because reflectivity is related to the diameter of the hydrometeor to the sixth power, the water-coated snowflakes have high reflectivity values and produce the bright band on radar. 5. Using the PPI radar reflectivity image below, answer the following questions: a. Which letter indicates the location of the radar? D b. Which letter indicates the region of ground clutter? C c. Which letter indicates the region of highest reflectivity values? A d. Which letter (A or B) indicates a region of lower rainfall rates? B e. What type of precipitation system is this (supercell, snow, bow echo)? Bow echo B A C D 6. On the reflectivity and velocity images below, indicate (on both) the most probable location of the tornado? 7. What are the differences between the Clear Air Mode and the Precipitation Mode (including which features can be identified easier depending on the mode)? The Precipitation Mode is a faster scan, used when precipitation is present or expected to be present and is useful for detecting smaller particles (such as hydrometeors). The Clear Air Mode is a much slower scan used when precipitation is not present. Reflectivities that appear on this mode are due to scattering by differences in refractivity and scattering from insects and birds. The reflectivity scale used for the Clear Air Mode is much lower than the Precipitation Mode with typical maximum reflectivities usually less then 30dBZ as opposed to reflectivities exceeding 70dBZ for the precipitation mode. 8. (10 points) Explain how emissivity () affects the brightness temperature measured by a satellite. What are some factors that affect the emissivity of a surface? Brightness temperature is the temperature of an equivalent blackbody emitting radiation. A blackbody emits all the radiation it absorbs, but an equivalent blackbody only emits a certain fraction of the absorbed radiation. The amount of absorbed radiation that is emitted by the body is referred to as emissivity. The greater the emissivity, the higher the fraction of absorbed radiation being emitted, and the higher the brightness temperature will be. The emissivity over land is affected by the amount of moisture in the soil, the conductivity of the soil, the amount of vegetation cover, and other surface characteristics. Over the ocean, the emissivity is most dependent on the sea surface temperatures, as well as the wind speed over the ocean. 9. (10 points) Why is emissivity over land difficult to determine? The emissivity over land is so difficult to determine because of the influence of surface and soil characteristics, such as moisture, conductivity, vegetation, etc. These surface characteristics are difficult to determine and frequently change so determining emissivity over land is a challenge. 10. (10 points) On the Infrared image below, indicate the location of the highest clouds, lowest clouds, and clear sky. At which point is it most likely precipitating?: A B C Infrared imagery displays the brightness temperature that is computed from the amount of sensed infrared radiation. For high clouds, cloud top temperatures are colder than lower cloud tops so the high clouds appear whitest on satellite imagery. Land surfaces are warmer than clouds and therefore appear much darker on imagery. Therefore, the highest clouds are located at C, lowest clouds at A, and clear sky at B. 11. (10 points) Keeping in mind that the ITCZ is a region of rising air, indicate on the GOES visible image below the where this feature would likely be found. Extra credit: (10 points) Using the websites provided in class (or by your own searching), find a radar or satellite image of something you think is interesting, and describe what is occurring in the image. Be sure to either print out the image, or provide a web address as to where it can be found.











