Name
advertisement

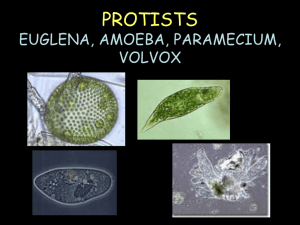
Name________________________ 4/11 Class__________ COMPARING PROTIST LAB Problem Protists are organisms that have nuclei and live in wet environments, such as ponds, oceans, and the bodies of larger organisms. Other than that, protists don’t have much in common. For example, some live independently as separate cells; others form colonies of many unattached cells. Plant-like protists are autotrophs (organisms that can make their own food). Animal-like protists and fungus-like protists are heterotrophs (organisms that cannot make their own food). In this investigation, you will observe and compare five common protists: amoebas, euglenas, paramecia, volvox, and stentor. Materials Microscope Amoeba culture tube Paramecium culture tube Volvox culture tube Euglena culture tube Stentor culture tube Procedures Observing Amoeba: 1. Use the low, medium, then high objective lens to look at the details of the amoeba. 2. Observe the amoeba and draw a sketch OR take a picture of what you see (to be placed in “Plate 1: Amoeba” ). Name your picture and save it on your flashdrive. Label: cytoplasm, pseudopods, and cell membrane 3. Record the TOTAL MAGNIFICATION. Observing Euglena: 1. Use the low, medium, then high objective lens to look at the details of the euglena. 2. Observe the euglena and draw a sketch OR take a picture of what you see (to be placed in “Plate 2: Euglena” ). Name your picture and save it on your flashdrive. Label: flagellum, cytoplasm, chloroplast (eyespot…if you see it). 3. Record the TOTAL MAGNIFICATION. Observing Paramecium: 1. Use the low, medium, then high objective lens to look at the details of the paramecium. 2. Observe the paramecium and draw a sketch OR take a picture of what you see (to be placed in “Plate 3: Paramecium” ). Name your picture and save it on your flashdrive. Label: cell membrane, oral groove, cytoplasm (cilia…if you see it). 3. Record the TOTAL MAGNIFICATION. Observing Volvox: 1. Use the low, medium, then high objective lens to look at the details of the volvox. 2. Observe the volvox and draw a sketch OR take a picture of what you see (to be placed in “Plate 1: Amoeba” ). Name your picture and save it on your flashdrive. Label: vegetative cell, daughter colony, flagella (if you see it) 3. Record the TOTAL MAGNIFICATION. Observations: Remember to label and color your drawings and write the total magnification. PLATE 1: Amoeba Magnification_________ Label: cytoplasm, pseudopods, and cell membrane Describe how it moves (avoid it looks like) __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ Length:_____________ µm* PLATE 3: Paramecium PLATE 2: Euglena Magnification ___________ Label: flagellum, cytoplasm, chloroplast (eyespot…if you see it). Describe how it moves (avoid it looks like) __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ Length:_____________ µm* PLATE 4: Volvox Magnification_________ Label: cell membrane, oral groove, cytoplasm (cilia…if Magnification ___________ Label: algal cell (daughter colony…if you see it) you see it). Describe how it moves (avoid it looks like) Describe how it moves (avoid it looks like) __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ Length:_____________ µm* __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ Length:_____________ µm* *PROTISTS measured in micrometers (µm) PLATE 5: Stentor Directions: Observe stentor for about 1 minute. Label the nuclei, buccal cavity and any algae (if seen) Magnification_________ Describe how it moves (avoid it looks like) and any other things you see it do. __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ Length:_____________ µm* DATA ANALYSIS: (use complete sentences) 1. Of the five protists, which was the largest? Smallest? (use data/observations to support your answer) ______________________________________ ________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ 2. Of the five protists, which was the fastest moving protist? Decribe its method of movement (use observations and names of parts to support your answer). __________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ 3. Which protist was the most difficult to find? ____________________________ b. Why was this protist the most difficult to find? __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ 4. What organelles do all protists have in common? (name at least TWO) __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ 5. Which protists were heterotrophs? ___________________________________ Were you able to see one or more of them eat? _______ If so, describe the method you observed. If not, use your text or notes to describe how one of these protists obtains its food. ___________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ CONCLUSION and Critical Thinking: 6. Why is the eyespot an important structure in the euglena? Be specific. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 25