Protists Lab
advertisement

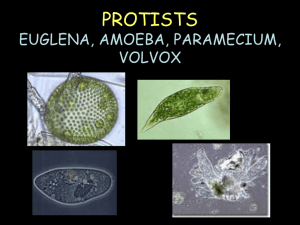
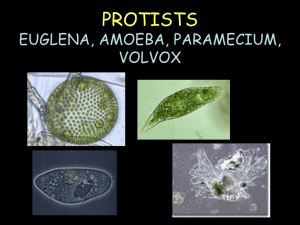
Comparing Protists Lab Name: __________________________ Hour: ______ The kingdom Protista (Protists) includes algae, protozoans, and slime molds. Protists live in aquatic environments, including fresh water, salt water and damp soil. Some live independently, while others live in colonies. Some protists are parasites and must live off of another living organism to survive. Protists can be autotrophic or heterotrophic. In this investigation, you will observe and compare common protozoans, draw and label their structures, and make notes and answer questions regarding their general behavior. PROCEDURE: Make wet mounts slides of the following cultures, observe the organisms under the microscope, draw and label their structures, and answer questions. 1. AMOEBA Observe the amoeba and draw what you see. Identify in the microscope and on your drawing the cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, food vacuole, and pseudopods. A. What is the general shape of the amoeba? B. What structures does the amoeba use to move? C. Can you find the food vacuoles circulating through the cell? How did food get into the cell? D. When the food is digested, from where will the remaining waste be discharges? 1 2. PARAMECIUM- Add a few strands of cotton or some detain to slow the organisms. Observe the paramecium and draw what you see. Identify in the microscope and on your drawing the cell membrane, nuclei, cytoplasm, cilia, contractile vacuole, food vacuole, and oral groove. A. The outer edge of the paramecium cell is a pellicle. Does the pellicle give the organism a definite shape? If so, what is the shape of the paramecium? B. What structures does the paramecium use to move? C. Find the contractile vacuole. What is its purpose? If you can see the contractile vacuole, observe a paramecium for 1 minute and count the number of times the contractile vacuole contracts. 3. EUGLENA Observe the euglena and draw what you see. Identify in the microscope and on your drawing the cell membrane, cytoplasm, eyespot, and flagellum. 2 A. What is the color of the euglena cell? Why does it appear this color? B. What structure does the euglena use to move? C. Find the red eyespot. What is its purpose? D. The euglena has a gullet and reservoir in the rounded end; however, in most euglena neither structure is used to take in food all of the time. Explain why. 4. VOLVOX Observe the volvox and draw what you see. Identify in the microscope and on your drawing the cell membrane and flagella. A. Are volvox algae or protozoans? B. Are volvox unicellular and colonial or multicellular? C. How does the volvox obtain its energy? 3 5. MIXED PROTISTS Make a wet mount slide from the culture labeled “mixed protists”. Draw and identify three different protists that we have not looked at earlier in the lab. CONCLUSION QUESTIONS: 1. Name three structures that all protists have in common. 2. Which of the protists observed have both autotrophic and heterotrophic structures? 3. What organelle or structure present in most protozoans is used to pump excess water out of the cell and stop the organism from swelling? 4. Name the four types of protozoans and give a specific example of each. 4