Chemistry Study Guide - Atomic structure and the Periodic Table 2010
advertisement

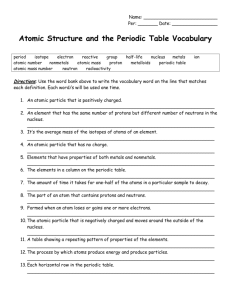
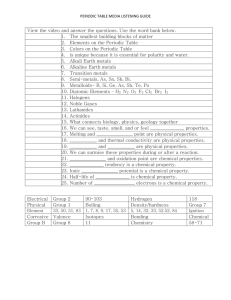
Chemistry Study Guide - Atomic structure and the Periodic Table 2010 Standards 3. Each of the more than 100 elements of matter has distinct properties and a distinct atomic structure. All forms of matter are composed of one or more of the elements. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. What is the structure of the atom and how are protons, neutrons, and electrons arranged b. How can you use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. 7. The organization of the periodic table is based on the properties of the elements and reflects the structure of atoms. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Identify regions of the periodic table that correspond to metals, nonmetals, and inert gases. b. Be able to illustrate that each element has a specific number of protons in the nucleus (the atomic number) and each isotope of the element has a different but specific number of neutrons in the nucleus. c. Give examples how elements can be classified by their properties, including their melting temperature, density, hardness, and thermal and electrical conductivity. Vocabulary Atom Electron Molecule Atomic mass Family/group Neutron Energy level Element Atomic number Proton Valence electron Compound Period Questions Part 1 1.What are protons, neutrons and electrons and where are each located in the atom. 2. Where are the valence electrons and what are their functions? 3. Explain how to calculate the atomic mass and atomic number by using the periodic table. 4. What are isotopes. Write or draw an example. 5. What is the Bohr model of the atom look like? 6. What did Mendeleev do for science? 7. Know the general characteristics of the periodic table a. how it is arranged b. what information you can read from it c. the differences in the columns and periods d. the reactivity from right to left. 8. Know general characteristics of metals, nonmetals and metalloids. metals nonmetals metalloids