Literary Devices

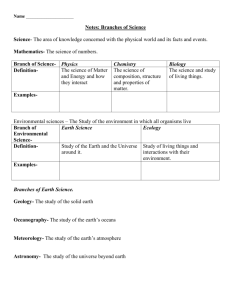
American Studies
Literary Devices
Simile: a direct comparison, using like or as, between two basically unlike things. (The comparison helps to better express something.)
Example- He is as hungry as a bear.
Metaphor: a comparison, without like or as, between two basically unlike things
Example- Summertime is a rollercoaster.
Extended Metaphor: two unlike things are compared at some length in several ways
(throughout a paragraph, stanza or an entire selection)
Example-
Personification: the representation of ideas, animals, or inanimate objects as human beings by giving them human qualities
Example- The spicy food tickled my throat.
Hyperbole: an exaggeration used for emphasis or humorous effect
Example- It took a million years to get from Acton to downtown Boston.
Alliteration: the repetition of a consonant sound
Example- The wind whistled wildly in the night.
Assonance: the repetition of a vowel sound
Example- “And so, all the night-tide, I lie down by the side.”
Allusion: a reference to a well-known work of literature, a famous person, or a historical event with which the reader is assumed to be familiar
Example- allusions in The Simpsons, “The Raven” Halloween episode
Imagery: the use of specific language to communicate a sense impression, stir emotions, or express an idea
Example- The last tomato plants of the summer were blooming, and their smell drifted across the field through every room in the house.
Symbol: something relatively concrete, such as an object, action, character, or scene, that signifies something relatively abstract, such as a concept or idea
Example- fire = death, hell the ring = evil
Foreshadowing: a hint given to the reader of what is to come
Example- Juliet to Romeo: “Methinks I see thee, thou art so low,/As one dead in the bottom of a tomb”
(3.5.55-56)
Soliloquy: a speech that a character delivers while on stage alone
Aside: words spoken on stage by one character to be heard by the audience and/or another character only
Paradox: a seeming contradiction
Example- cheerful rainstorm, “O brawling love/ O loving hate”
Pun: a play on multiple meanings of words
Example- The baker makes a lot of dough.
Mood: the feeling, or atmosphere, that a writer creates for the reader (how a reader respond to a work of literature)
Example-
Tone: the attitude a writer takes toward a subject (all of the elements in a work of literature create this)
Example-
Irony: the term used to describe the contrast between the actual meaning and the suggestion of another meaning
(1) verbal irony: when one says something and means the opposite
Example: A man who weighs 500 lbs is nicknamed Slim.
(2) situational irony: when an occurrence is contrary to what is expected or intended
Example: A fire at the fire station.
(3) dramatic irony: situation in which events or facts not known to a character are known to another character and the audience
Example: Romeo and Juliet, The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn
Characterization : techniques used by a writer to develop a character
(1) the character’s speech and behavior
(2) the character’s physical traits and personality
(3) the character’s thoughts and feelings
(4) the reactions of other characters to an individual
Conflict: the struggle between opposing forces that is the basis of plot in dramatic and narrative literature
Diction: a writer’s choice of words
Rhythm: pattern of stressed or unstressed sounds in spoken or written language
Onomatopoeia: the use of a word whose sound suggests it meaning
Apostrophe: an address to a person or personified object not present
Theme: the author's major idea, meaning, or message—this is not one word!!