Notes: Evolution as Genetic Change
advertisement

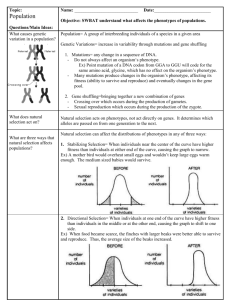
Notes: Evolution as Genetic Change Natural selection can affect phenotypes in a population in 3 ways 1. Directional Selection higher fitness at _____ _______ of the curve than at the other all phenotypes in the population shift towards __________ ___________ Example bird population where food becomes scarce Birds with ___________ beaks gather food and survive & reproduce Average beak size of the population _______________ & shifts right new graph shifts in the ___________ of higher fitness 2. Stabilizing Selection a. Higher fitness at the _____________of the curve b. Middle Stays _____________ c. Ends get ______________ d. Example- birth weight of human babies i. Smaller than average babies = _______ likely to be healthy ii. Larger than average babies = ________ likely to be healthy e. New graph shifts toward middle and is __________________ 3. Disruptive Selection a. Higher fitness at ________ends of the curve b. Middle phenotype ______________ in frequency c. Example- large seeds and small seeds become more common and there are few medium seeds i. Both birds with _________ beaks and _________ beaks are best adapted to eat those seeds ii. Can result in _______ subgroups d. New graph is ______________ in the middle. Genetic Drift o ___________ change in allele frequency Happens by ___________ ___________ and happens in _________ _______________ NOT _____________ _______________ o Bottleneck Effect A large percentage of a population is _______________ or prevented from _________________ ______________ genetic drift Event in which the population is __________________________. Example- Northern Elephant Seals o Bottleneck Event = ___________________________ o Population decreased to ____ seals & now have __________ seals with reduced ____________ o Founder Effect Example- The cocklebur main population has lots of ____________ a _____ hitch a ride and start a new ____________ they are the ____________ and their __________ gives rise to new ______________ A type of __________ ____________ After a _______________ breaks away to form a new population Example- Amish community in Pennsylvania with Ellis-von Creveld Syndrome o high numbers of _______ fingers & toes, abnormal ___________, hole in _____________ o Founders = ________________________ o Chance events = _________________________________________________________ Evolution versus Genetic Equilibrium o Genetic Equilibrium = When allele frequencies in a population __________ ____________ o Hardy-Weinberg principle = says allele frequencies in a population will remain ____________ (don’t change) if 5 things are true… 1) Random Mating = Everyone gets an ________ chance to pass on alleles. _______ mate selecting 2) Large Population = Less effect of ____________ ___________ 3) No Movement Into or Out of the Population = No ______________. Keep ___________ separate 4) No Mutation = No ________ alleles in the population 5) No Natural Selection = All genotypes have equal ___________. No ________________ for anyone