Literary Terms Power Point
advertisement

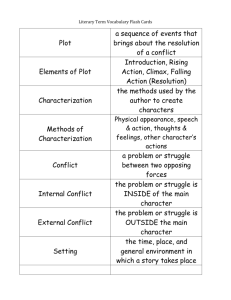
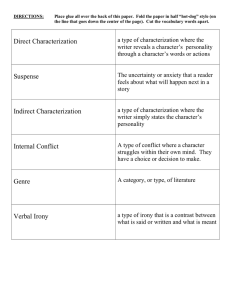
Language that communicates ideas beyond the ordinary, literal meaning of words. ◦ **things do not mean what the words actually say ◦ Examples: metaphor, simile, idiom, personification, etc. A comparison between two objects; often says that one thing is another. ◦ Ex: He is a bear on the football field! A comparison between two objects using "like", "as", or "than". ◦ Ex: She is as quick as a cat! The repetition of the initial consonant sound. ◦ Ex: Sally sells sea shells by the sea shore A reference to someone or something in history or literature. ◦ Ex: But I'll be hood forever I'm the new Sinatra And since I made it here Giving human qualities or characteristics to animals or objects. ◦ Ex: The pen danced across the paper Extreme exaggeration for effect. ◦ Ex: It took me “FOREVER” to finish the project! An expression common to a certain group of people. ◦ Ex: Don’t bite off more than you can chew. The character who opposes the hero; provides the story’s conflict ◦ Ex: the wolf in “The Three Little Pigs” the main character in a story, novel, drama, or other literary work; the character that the reader or audience empathizes with ◦ Jack in “Jack and the Beanstalk” 1st person-story is being told by a character within the story (I, we, us) 2nd person-speaking to “you”; often as in a letter or directions 3rd person limited-outside narrator; reader is informed of all ACTIONS of characters and thoughts of 1character 3rd person omniscient – narrator is allknowing; reader is informed of all thoughts and actions of characters Hints or clues as to what is going to happen later in a story ◦ Example: In “The Legend of Sleepy Hollow” - the description of Brom’s horse Daredevil that mentions he is full of mischief and mettle just like his owner ◦ (hints that the horse and rider are/will be up to something) the use of words and phrases to create a mental picture ◦ Example: There was a tree at that corner, a straight but little tree with slim branches and shiny dark leaves. – from “The Osage Orange Tree” Characterization is the process by which the writer reveals the personality of a character. ◦ Stated Characterization tells the audience what the personality of the character is. Example: “The patient boy and quiet girl were both well mannered and did not disobey their mother.” ◦ Implied Characterization shows things that reveal the personality of a character. ◦ There are five different methods of implied characterization: Speech: What does the character say? How does the character speak? Thoughts: What is revealed through the character’s private thoughts and feelings? Effect on others toward the character: What is revealed through the character’s effect on other people? How do other characters feel or behave in reaction to the character? Actions: What does the character do? How does the character behave? Looks: What does the character look like? How does the character dress? Are uncomplicated and do not change throughout the course of a work ◦ Example: Injun Joe are complex and undergo development/ change ◦ sometimes extreme changes to surprise the reader ◦ Example: Tom Sawyer, Huck Finn something which represents something else besides itself ◦ Example: The dove, with olive branch in beak, Glides over all the land Searching for a place to light. Storms of war linger on every hand, Everywhere the hawk does fight. ◦ The dove is a symbol of peace, and the hawk is a symbol of war. Using them in poetry gives an image without having to explain in detail. Verbal irony: saying something, but meaning the opposite (sarcasm) ◦ Example- I LOVE it when people talk as I try to teach!! Situational irony: the opposite of what was expected happens ◦ Example- the fire house catches on fire Dramatic irony: where the audience is aware of a situation and the characters are not ◦ Example- you see the murderer in the closet, the young babysitter does not, she goes into the room and …