WWII VUS 11b Battles _Turing Point _Answers
advertisement
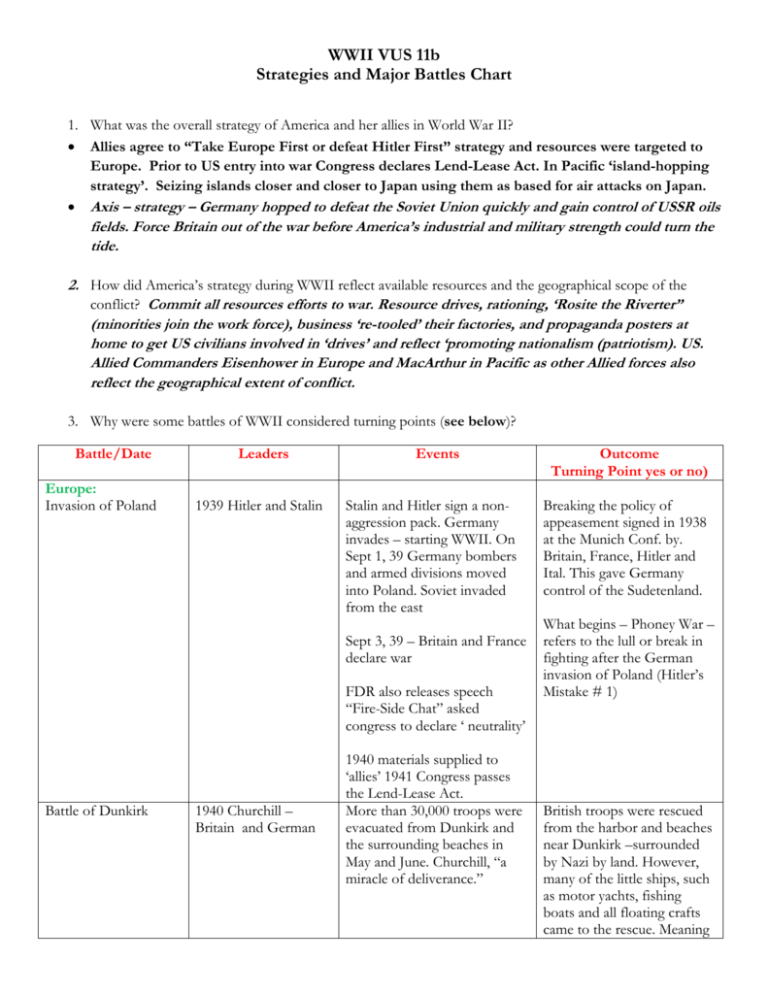
WWII VUS 11b Strategies and Major Battles Chart 1. What was the overall strategy of America and her allies in World War II? Allies agree to “Take Europe First or defeat Hitler First” strategy and resources were targeted to Europe. Prior to US entry into war Congress declares Lend-Lease Act. In Pacific ‘island-hopping strategy’. Seizing islands closer and closer to Japan using them as based for air attacks on Japan. Axis – strategy – Germany hopped to defeat the Soviet Union quickly and gain control of USSR oils fields. Force Britain out of the war before America’s industrial and military strength could turn the tide. 2. How did America’s strategy during WWII reflect available resources and the geographical scope of the conflict? Commit all resources efforts to war. Resource drives, rationing, ‘Rosite the Riverter” (minorities join the work force), business ‘re-tooled’ their factories, and propaganda posters at home to get US civilians involved in ‘drives’ and reflect ‘promoting nationalism (patriotism). US. Allied Commanders Eisenhower in Europe and MacArthur in Pacific as other Allied forces also reflect the geographical extent of conflict. 3. Why were some battles of WWII considered turning points (see below)? Battle/Date Europe: Invasion of Poland Leaders 1939 Hitler and Stalin Events Stalin and Hitler sign a nonaggression pack. Germany invades – starting WWII. On Sept 1, 39 Germany bombers and armed divisions moved into Poland. Soviet invaded from the east Sept 3, 39 – Britain and France declare war FDR also releases speech “Fire-Side Chat” asked congress to declare ‘ neutrality’ Battle of Dunkirk 1940 Churchill – Britain and German 1940 materials supplied to ‘allies’ 1941 Congress passes the Lend-Lease Act. More than 30,000 troops were evacuated from Dunkirk and the surrounding beaches in May and June. Churchill, “a miracle of deliverance.” Outcome Turning Point yes or no) Breaking the policy of appeasement signed in 1938 at the Munich Conf. by. Britain, France, Hitler and Ital. This gave Germany control of the Sudetenland. What begins – Phoney War – refers to the lull or break in fighting after the German invasion of Poland (Hitler’s Mistake # 1) British troops were rescued from the harbor and beaches near Dunkirk –surrounded by Nazi by land. However, many of the little ships, such as motor yachts, fishing boats and all floating crafts came to the rescue. Meaning Battle of Britain Dresden D-Day or Normandy Turing Point Battle Stalingrad Turning Point Battle North Africa: El Alamein Turning Point Battle Pacific: Midway (islandhopping campaign) Turning Point Battle Iwo Jima Germany’s attempt to gain superiority over the Royal Air Force (RAF). July – Oct 1940 Give take p.o.v. Churhill & German City 1945 June 6, 1944 Eisenhower commander of Operation Overlord. Hitler attempts to neutralize the RAF. Then carry out an amphibious assault on the British Isles. Thousands of bomb destroy Dresden. 650,000 incendiaries and 8,000lb of high explosives and hundreds of 4000lb bomb in two waves of attack destroyed the ciry. Normandy France, U.S. invades Omaha Beach 156,000 allied troops successfully stormed the beaches. 2000 American causalities civilian helped rescued the British troops. Had Nazi been successful could have changed the outcome of Battle of Britain. Hitler’s goal to destroy aircraft production and ground infrastructure. (Hitler’s mistake # 2 failed. Third Reich’s first major defeat! 12 hours in total Death toll from firestorm, suffocation is estimated between, 25,000 to 100,000 mostly civilian. Consider Churchill’s’ mistake. Considered Turing point of War. Allies fought their way across the French countryside By the end of 1944 Paris was liberated and German’s had been removed. V-E Day May 8, 1945 Soviet victory humiliation for Hitler (Mistake # 3 for Hitler) 1942-1943 Stalin and Germany Hitler orders Germany to hold all grounds at all costs. Wanted USSR oil fields. Winter sets in and were under siege. German surrender 1942 Rommel (Dessert Fox) British army and the German-Italian forces British General Montgomery – showed allied superiority. Rommel lost North African campaign Between El Alamein and Stalingrad (turning points of the war) proved to the watershed of the war against Germany (defeats). 1942 Japan and U.S. Pacific Fleet Commander Admiral Chester W. Nimitz. Six months after Pear Harbor Dec 7, 1941. U.S. defeated Japan in naval battle in part to code breaking able to ambush using aircraft carriers. Start of ‘island-hopping campaign.’ Strategy to take the island of Japan several islands at a time (refueling and pushing back). Ended Japan’s threat to Hawaii. 1945 US – Japan. Pacific Island Need for a base near the Japanese coast. U.S. marine divisions landed on island. Iwo Jima was defended by about 23,000 Japanese army and navy Difficult conditions due to elaborate network of caves, dugouts and tunnels. U.S. marines win. Planting flag – famous photo and statue. troops. American losses 5900 and 17400 wounded. Cited for one reason Truman drop Atomic bomb Japan looses 77,000 and allies 65,000 with 14,000 dead. Cited for one of the reasons for Truman to drop the Atomic bomb. Both Iwo Jima and Okinawa - civilians committed suicide rather than surrender. Emperor Hirohito announced his country’s surrender on a radio address ‘new and most cruel bomb.’ August 15, 1945. Need for U.S. forces to invaded Japan avoided. V-J Day 9/2/45 Japan surrenders in the USS Missouri. Okinawa 1945 Japan and US Involved 287,000 US troops and 130,000 Japanese soldiers. 82 day campaign. Hiroshima & Nagasaki Harry Truman orders the use of bombs on Japan August 6 1945 B-29 bomber (Enola Gay.) And then again on Aug 9th Wanted to force the Japanese to surrender. Tens of thousands died as a result of the bomb. Little Boy and Fat Man (name of bombs)