Solution Key - Chemistry With BT
advertisement

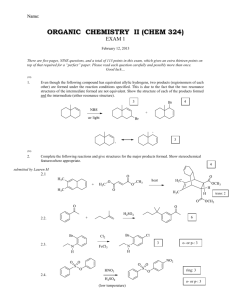
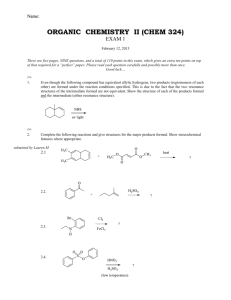
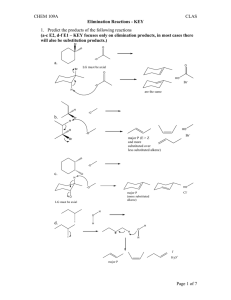
Name: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (CHEM 323) EXAM 3 November 26, 2013 There are five pages, NINE questions, and a total of 115 points in this exam, which gives an extra 15 points on top of that required for a “perfect” paper. Please read each question carefully and possibly more than once. Good luck… (15) 1. Give the major products for the reactions below. If the major product is a mixture of stereoisomers, show all the stereoisomers (in a way they can be distinguished from one another). 1.1. 1.2. 1.3. (12) 2. The following reactions are regioselective and/or stereoselective. Provide structures for the missing final major products. Show stereochemical features in a distinguishable manner (where appropriate). 2.1. 2.2. Chem 323 Exam 3 B. Terem (8) 3. Show how the following synthesis can be carried out stereoselectively. More than one step may be required. Show all reagents and intermediate products. (12) 4. Hydrogen cyanide, HCN, is not acidic enough to react with an alkene; therefore, the synthesis below requires more than one step. Show all the steps of the synthesis in the right sequence. Give the reagents used and the reaction conditions utilized (including acid base catalysis). Show the structures of all intermediate products. (12) 5. For each pair of missing precursors below, one is an alkyl bromide and the other is an organic molecule in its ionic form. Provide structures for the missing precursors from which the products shown are obtained in high yields. 5.1. 5.2. Page 2 Chem 323 Exam 3 B. Terem (21) 6. Circle the best correct answer (only ONE) for the multiple-choice questions below. 6.1. Which one of the following statements suggests that the catalytic hydrogenation of an alkene is an exothermic reaction? (1) (2) (3) (4) 6.2. Hydrogen gas is flammable A catalyst speeds up the reaction Alkenes are more stable than alkanes Alkanes are more stable than alkenes In the following reaction the transition state of the rate determining step resembles (1) The more reactive carbocation (2) The epoxide starting material (3) The more stable carbocation (4) The epoxide in its chair form (5) The transition state of an SN2 reaction 6.3. What is the product of the reaction in question 6.2? 6.4. Which of the organic products shown below is generated when 1-butanol is treated with sodium hydride in a suitable solvent? 6.5. The two reactions shown below are both carried out using bromine in an organic solvent. The starting material for one is cis-3-hexene, and the other, trans-3-hexene. What is the relationship between the two products A and B? (1) identical compounds (4) constitutional isomers (2) enantiomers (3) diastereomers (5) no isomeric relationship Page 3 Chem 323 Exam 3 B. Terem 6.6. What is the leaving group in the reaction below? 6.7. What is the molecular formula of a nine-carbon hydrocarbon with one ring and two double bonds in its structure? (1) C9H20 (2) C9H18 (3) C9H16 (4) C9H14 (5) C9H13 (17) 7. Outline a step-wise mechanism for the following reaction. Show the structures of all the intermediates formed and of the final product. Use curly arrows to illustrate bond cleavages and/or formations. 7.1. The alkene below undergoes a very similar skeletal rearrangement. Give the structure of the final product (no need for details of mechanism). (12) 8. Outline a retrosynthetic analysis for the target ketone below starting from the alkyl halide shown. You do not need to give any reagents or reaction conditions, only the intermediate products in a sequential way. Make sure that your transformations are selective and do not yield unwanted side products. Page 4 Chem 323 Exam 3 B. Terem (6) 9. The reaction shown below can be carried out only in the presence of the macrocyclic molecule (given under the chemical equation). O O O O O O 9.1. 9.2. a crown ether The macrocyclic molecule is referred to as (fill in the blank) _________________________ The macrocyclic molecule forms a host-guest complex with one of the species above. Write the species which functions as the “guest”. K+ Page 5