Name
advertisement
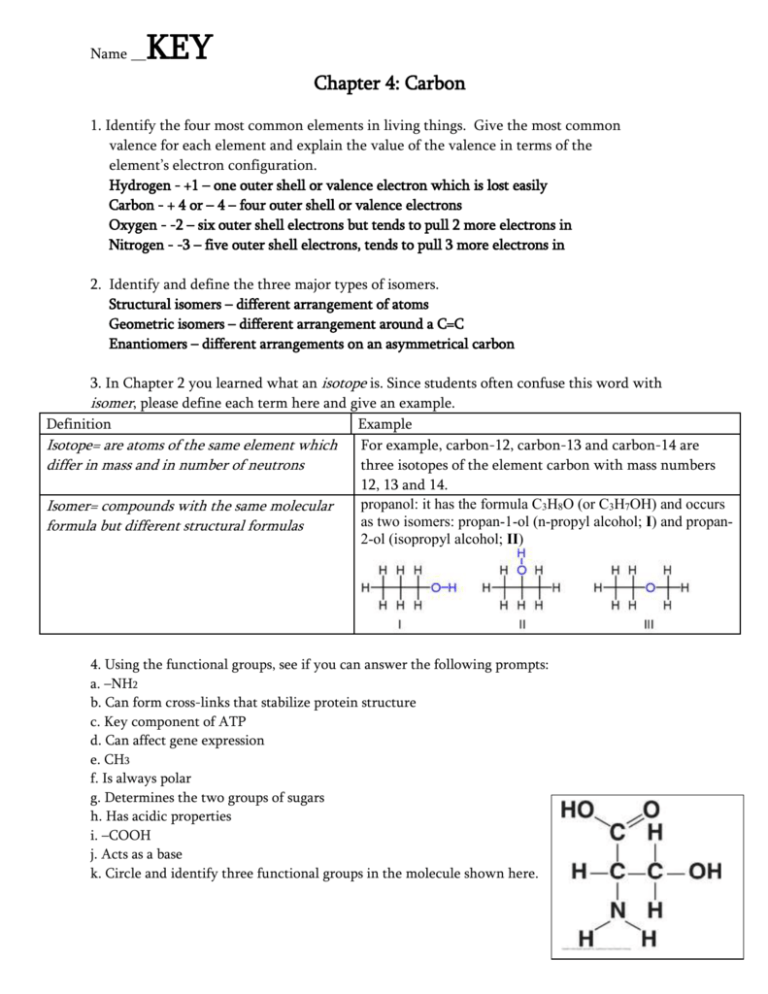
Name __ KEY Chapter 4: Carbon 1. Identify the four most common elements in living things. Give the most common valence for each element and explain the value of the valence in terms of the element’s electron configuration. Hydrogen - +1 – one outer shell or valence electron which is lost easily Carbon - + 4 or – 4 – four outer shell or valence electrons Oxygen - -2 – six outer shell electrons but tends to pull 2 more electrons in Nitrogen - -3 – five outer shell electrons, tends to pull 3 more electrons in 2. Identify and define the three major types of isomers. Structural isomers – different arrangement of atoms Geometric isomers – different arrangement around a C=C Enantiomers – different arrangements on an asymmetrical carbon 3. In Chapter 2 you learned what an isotope is. Since students often confuse this word with isomer, please define each term here and give an example. Definition Example Isotope= are atoms of the same element which For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are differ in mass and in number of neutrons three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14. propanol: it has the formula C3H8O (or C3H7OH) and occurs Isomer= compounds with the same molecular as two isomers: propan-1-ol (n-propyl alcohol; I) and propanformula but different structural formulas 2-ol (isopropyl alcohol; II) 4. Using the functional groups, see if you can answer the following prompts: a. –NH2 b. Can form cross-links that stabilize protein structure c. Key component of ATP d. Can affect gene expression e. CH3 f. Is always polar g. Determines the two groups of sugars h. Has acidic properties i. –COOH j. Acts as a base k. Circle and identify three functional groups in the molecule shown here. Word Roots hydro- = water (hydrocarbon: an organic molecule consisting only of carbon and hydrogen) iso- = equal (isomer: one of several organic compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and, therefore, different properties) enanti- = opposite (enantiomer: molecules that are mirror images of each other) carb- = coal (carboxyl group: a functional group present in organic acids, consisting of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and a hydroxyl group) sulf- = sulfur (sulfhydryl group: a functional group that consists of a sulfur atom bonded to an atom of hydrogen) Multiple Choice 5. Which is an organic molecule? a. Ne b. O2 c. CH4 d. NaCl e. H2O 6. Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of the molecules used by living organisms because _____. a. carbon is the central atom of carbon dioxide, a necessary molecule for photosynthesis b. carbon is the central atom in urea, a molecule used by many living organisms to transport wastes from the body c. each carbon atom acts as an intersection point from which a molecule can branch off in up to four directions d. carbon can combine with hydrogen to form hydrocarbons e. all of the above 7. Which of the following functional groups is present in all amino acids? a. –SH b. –COH c. –OH d. -NH2 e. -OPO3-2 8. Which one of the following molecules has a carboxyl functional group? a. R-NH2 b. R-COH c. R-COOH d. R-OPO3-2 e. R-SH 9. Which one of the following molecules is a weak base? a. R-NH2 b. R-SH c. R-OH d. R-COOH e. none of the above 10. Which of the following molecules is a weak acid? a. R-NH2 b. R-SH c. R-OH d. R-COOH e. none of the above







