Study Guide
advertisement

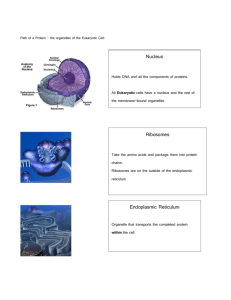
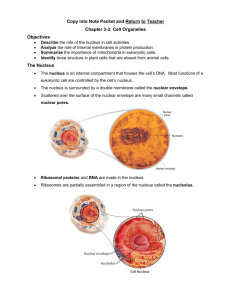
Cells Study Guide-glue in assignments and write answers on opposite page. Chapter 2 NAME:___________________________________________________ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. The first person to describe cells was: The tool you use to look at cells is: In Latin, the word cells means: What are the three parts of cell theory? Any of the smaller units that has a specific function in a cell: Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells have: Organisms whose cells lack membrane-bound organelles and nuclei are called: A molecule that carries the instructions for protein making is: Cell walls are found in: The ___________ _________________ acts as a fence, letting things in and out. Lipids are an important component of: The cytoskeleton keeps: The nucleus contains the _________________ and acts as a ____________ ____________. 14. The ____________________ makes ribosomes. 15. Proteins are made in the: 16. Proteins are made of: For the following, write a brief word or phrase to answer the question: 17. The __________________ ________________ ______________________ is covered in ribosomes. 18. The _______________ _________________ _____________________ makes lipids and breaks down toxins. 19. ATP is the energy source for cells made in the _______________________. 20. Carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight are all needed for the process of ________________________. 21. Only plants have _____________________________, which are filled with chlorophyll. 22. The _______________________ works closely with the endoplasmic reticulum, sending proteins and other items out of the cell. 23. The bubbles that transport materials within and out of the cell are called _____________________. 24. The _____________________ is the storage area of the cell. In plants, it’s very large and holds water. 25. The ____________________________ are responsible for digestion. These are mostly found in ____________________cells. For the following, give a brief explanation: 26. What is similar about mitochondria and chloroplasts? 27. What is different about mitochondria and chloroplasts? 28. Why do plants need the large central vacuole? Cells Study Guide-glue in assignments and write answers on opposite page. Chapter 2 NAME:___________________________________________________ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. The first person to describe cells was: The tool you use to look at cells is: In Latin, the word cells means: What are the three parts of cell theory? Any of the smaller units that has a specific function in a cell: Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells have: Organisms whose cells lack membrane-bound organelles and nuclei are called: A molecule that carries the instructions for protein making is: Cell walls are found in: The ___________ _________________ acts as a fence, letting things in and out. Lipids are an important component of: The cytoskeleton keeps: The nucleus contains the _________________ and acts as a ____________ ____________. 14. The ____________________ makes ribosomes. 15. Proteins are made in the: 16. Proteins are made of: For the following, write a brief word or phrase to answer the question: 17. The __________________ ________________ ______________________ is covered in ribosomes. 18. The _______________ _________________ _____________________ makes lipids and breaks down toxins. 19. ATP is the energy source for cells made in the _______________________. 20. Carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight are all needed for the process of ________________________. 21. Only plants have _____________________________, which are filled with chlorophyll. 22. The _______________________ works closely with the endoplasmic reticulum, sending proteins and other items out of the cell. 23. The bubbles that transport materials within and out of the cell are called _____________________. 24. The _____________________ is the storage area of the cell. In plants, it’s very large and holds water. 25. The ____________________________ are responsible for digestion. These are mostly found in ____________________cells. For the following, give a brief explanation: 26. What is similar about mitochondria and chloroplasts? 27. What is different about mitochondria and chloroplasts? 28. Why do plants need the large central vacuole?