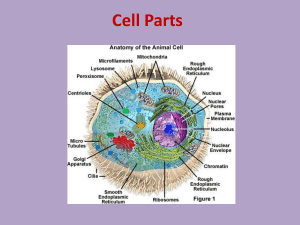
Path of a Protein – the organelles of the Eukaryotic Cell:
advertisement

Path of a Protein – the organelles of the Eukaryotic Cell: Nucleus Holds DNA and all the components of proteins. All Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and the rest of the membrane-bound organelles Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus Ribosomes Take the amino acids and package them into protein chains. Ribosomes are on the outside of the endoplasmic reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum Organelle that transports the completed protein within the cell Golgi Apparatus Transports the completed protein from the ER to the outside of the cell. Vesicles carrying the proteins break off the Golgi apparatus moving the proteins outside of the cell Plasma Membrane Selectively permeable membrane that allows passage of many materials into and out of the cell. Transport proteins on the surface help send out messenger proteins to other cells. Once proteins leave the cell they will be received by another cell. In this way, cells are able to communicate with each other. All cells have protein receptors on them which recognize specific proteins. Diffusion refers to movement from high concentration to low - hypertonic solutions are higher in solute concentration than their surroundings. Hypotonic solutions are lower in concentration. Isotonic solutions are equal. Passive transport refers to this movement across a membrane – which because it is selectively permeable allows for diffusion of small and non-polar (charged) molecules Osmosis refers to the movement of water from areas of high water concentration to where water is less concentrated. Osmosis, like diffusion is passive transport and requires no energy. Plant Cells have cell walls for structural support. In animals, the skeleton provides this function Plant cells have chloroplasts –the site of photosynthesis which converts energy from the sun and carbon dioxide to sugars. These sugars are used to produce energy in the mitochondria. ALL CELLS have mitochondria Energy In Cells Mitochondria Site of energy production in all cells. ATP is the high energy molecule produced in the mitochondria during the process of cellular respiration. Sugar is converted to this high energy molecule in the membrane of this organelle. Increased surface area, provided by folds in the walls allows for greater amounts of ATP to be produced Chloroplasts Present only in plant cells, chloroplasts convert CO2 and the sun’s energy into sugars during the process of photosynthesis. The sugars are then transported into the mitochondria where cellular respiration occurs. The chloroplasts can often be seen as small circular blobs around the outer wall of plant cells