Cell Biology Study Guide: Vocabulary & Cell Structures
advertisement

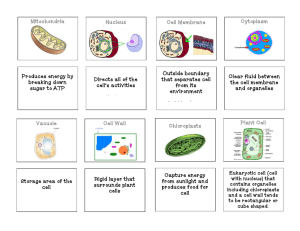
Name: ________________________________ Date: ______________Period: ____________ Unit 3: Cell Biology Study Guide Vocabulary In your own words, write a definition for each of the following terms in the space provided. 1. cell: membrane-covered structure containing all life materials and performing all life processes; the basic unit of living things 2. unicellular: an organism made of a single cell 3. multicellular: an organism made of many cells 4. cellulose: the indigestible carbohydrate that makes up the plant cell wall 5. cell membrane: a structure that keeps the cytoplasm inside, allows nutrients in and keeps waste products out 6. organelle: a structure within a cell sometimes surrounded by a membrane 7. cytoplasm: cellular fluid surrounding a cell's organelles 8. prokaryote(prokaryotic cell): a cell that does not have a nucleus or other membrane-covered organelles (bacterium) 9. eukaryote (eukaryotic cell): a cell that contains a central nucleus and a complicated internal structure 10. nucleus: the membrane-covered organelle found in eukaryotic cells that contains DNA and serves as the control center of the cell 11. cell wall: a structure that surrounds the cell membrane of plant cells that provides strength and support to the cell 12. mitochondria(mitochondrion): cell organelles surrounded by two membranes that break down food molecules 13. chloroplast: an organelle found in plants and algae where photosynthesis occurs 14. hereditary: having to do with the passing of traits from parents to offspring 15. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid, the hereditary material that controls all the activities of the cell; it contains all the information needed to make new cells and proteins 16. photosynthesis: the process by which plants capture light energy from the sun and covert it into sugar; the process also produces oxygen from water 17. microscopic: very small, needing a microscope to view 18. chlorophyll: a green pigment in chloroplasts that absorbs light energy for photosynthesis Cell Biology Unit GJUHSD – MLK v.1 1 Study Guide 2006-2007 19. cellular respiration: the process of producing ATP in the cell from oxygen and sugar which releases carbon dioxide and water Fill in the blank 20. Plants and animals are eukaryotic cells because they have membrane-bound organelles. 21. Two organelles found in plant cells, but not animal cells, are chloroplasts and cell wall. 22. In plant and animal cells the DNA, the cell's hereditary material, is stored in the nucleus. 23. Nearly all the energy that fuels life comes from the sun. 24. The cell membrane holds the cell together, and allows materials to be exchanged in and out of the cell. 25. The cell wall provides support and protection for plant cells like roses, Christmas trees, and carrots. 26. The cell wall is made of cellulose. 27. Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplast organelle. 28. The pigment involved in photosynthesis is chlorophyll. 29. The hereditary material of a cell is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). 30. The largest and most visible organelle in animal cells is the nucleus. 31. Cells are the basic units of living things that perform all life processes. 32. Cells are microscopic which means that they are too small to see with the naked eye. 33. A person is made of about 200 different kinds of cells that are each specialized to do a particular job. This means that a person is multicellular. 34. Cells in bone are different from skin cells, or lung cells, or nerve cells because both cells have different functions. 35. You are made of about 100 trillion cells; however, you began as a single cell. 36. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells because they do not have membrane-bound organelles. 37. There are four basic life processes that all cells need to perform: all cells reproduce, use energy, remove wastes, and transport nutrients. Cell Biology Unit GJUHSD – MLK v.1 KEY 2 Study Guide 2006-2007 38. The two energy-converting organelles are chloroplasts and mitochondria. 39. The chloroplast is the organelle that uses sunlight to produce sugar. 40. Sugars are broken down to release energy by mitochondria. 41. The instructions needed by the cell to live, grow, and reproduce come from DNA Short Answer – Answer using compete sentences 42. Draw a plant cell and label the following parts: cell wall, cell membrane, chloroplast, nucleus, DNA, mitochondria. 43. Draw an animal cell and label the following parts: cell membrane, chloroplast, nucleus, DNA, mitochondria. 44. Fill out the following chart: Organelle Plant cell only Nucleus DNA Cell wall Cell membrane Mitochondria Chloroplast Animal cell only Both plant and animal cell X X X X X X 45. Why don’t animal cells have chloroplasts? Animal cells do not have chloroplasts because animals eat food which is converted to energy. Cell Biology Unit GJUHSD – MLK v.1 KEY 3 Study Guide 2006-2007 46. Describe the function of mitochondria. Explain why it is necessary for plants to have mitochondria as animals do. Both animals and plants need to convert sugar into usable energy. 47. Predict what would happen if the mitochondria in a cell didn’t work properly. You can consider that the mitochondria functions like a power plant, so if the cell's power plant stops working, the level of energy would decrease and the level of sugar would increase. 48. Describe the function of chloroplasts. Give examples of organisms that have chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are energy converting organelles in plant cells. Chloroplasts are the organelles where photosynthesis occurs. Chloroplasts have a function similar to a solar panel which converts solar energy into electricity that can be used in our homes. Chloroplasts contain the pigment, chlorophyll that makes plant cells and algae green. Plants and Algae have chloroplasts. 49. Why are plants green? Most plants are green because they contain chlorophyll--one of the main pigments that absorb sunlight. The chloroplasts in most plant cells have green chlorophyll. 50. Explain why photosynthesis is important for almost all organisms on Earth. The products of photosynthesis are sugar and oxygen which animals and plants use. Photosynthesis is the process that converts sunlight into sugar and oxygen. Nearly all the energy that fuels life comes from the sun, using the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis means "made by light." 51. Why do plant cells need chloroplasts? Plants do not eat and need to convert light energy (sunlight) into sugar 52. Give an example of cells that are not able to survive on their own. Any specialized body cell of an organism, such as a nerve cell, a blood cell, or a muscle cell. All cells are NOT able to survive on their own. Cell Biology Unit GJUHSD – MLK v.1 KEY 4 Study Guide 2006-2007