universidad de especialidades espíritu santo
advertisement

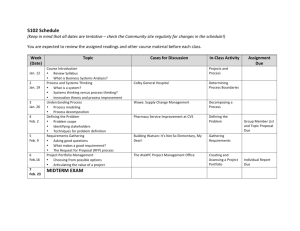
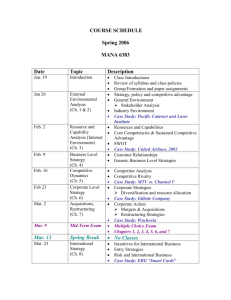
UNIVERSIDAD DE ESPECIALIDADES ESPÍRITU SANTO FACULTAD DE ESTUDIOS INTERNACIONALES SYLLABUS ENGLISH VERSION FOR DAC 11 VER 12 03 09 SUBJECT: Development & Eval of Proj 2 FACULTY: James Keeley, PhD CONTACT HOURS: 48 YEAR: 2011 DAYS: Monday – Thursday ROOM: F209 CODE: UGER 381 CREDITS: 3 NON CONTACT HOURS: 96 PERIOD: Spring I SCHEDULE: 11:10-1250 am SYLLABUS DATE: Feb 2011 1. COURSE DESCRIPTION This course teaches all the academic theory of the evaluation, development and management of projects (part ii). It covers topics such as project development, product development, life cycle, handling resources, management, risks and contingencies, earned value projects, advanced work breakdown structure, project research and development and project team skills. It uses case methodology to explain and historic examples of complex projects to analyze. Technology projects are emphasized. 2. JUSTIFICATION This course enables students to identify, analyze and understand the specific processes involved in the development and sustainment of business, social and governmental projects on both large and small scales. This allows students a better appreciation of the elements involved with project planning, delivery, sustainability and evaluation. 3. OBJECTIVES The objectives of this course are to provide a comprehensive examination of project evaluation and design. The student will be introduced to evaluation technique and schemata through summative, formative, process, and outcomes evaluation methods. Exposure to the various methods of project evaluation and design will allow the student to gain comprehensive insight into methodologies involved within the scope of program evaluation, design and assessment. a. GENERAL The student will gain insight into the value of a properly planned program design, evaluation and final assessment through the classroom activities. b. SPECIFIC During each class session, the student will identify key terminology and concepts associated with program design and evaluation. Additionally, the student will demonstrate, define and apply their understanding of program design and evaluation through the rudimentary construction of a program evaluation scheme. The student is responsible for 3.125 hours of daily reading outside of class (non-contact hours) for each class period during the term. After completion of the course, students will be able to: 1. Explain common components related to project planning; 2. Explain the salient components related to project implementation; 3. Explain various methods of evaluating projects as on-going and completed. 4. COMPETENCIES This course will allow the student to use basic problem solving techniques in order to solve project management issues as they arise; make appropriate decisions based on the requirements of the task and allow for recognition of organizational structure and policy to guide strategic thinking skills in order to complete a project within established time and fiscal parameters. 5. COURSE CONTENT OUTLINE Class Meeting # Competencies CONTENT Introduction and Overview ↑ 1 Monday Mar 14 2 Tuesday Mar 15 Newell (2002) pages 1-44 The student defines the salient characteristics of a project and explains the need for project management Formative Evaluation Technique ↓ Kerzner Chapter 2 p. 69-86 Newell (2002) pages 77-102 Kerzner Chapter 4 p. 139-146 PERFORMANCE INDICATORS Explores the various components related to all phases of project planning and implementation Identifies salient characteristics of program evaluation and individual assessment Matches the program evaluation type to the appropriate program ↑ Summative Evaluation Technique The student describes the various mechanisms for evaluation ↓ Summative Evaluation Technique, Continued Kerzner Chap 4 p. 146-163 Determines how program evaluation is used during the life of the project ↑ Developing Outcome Measures Kerzner Chap 4 p. 163-190 Illustrates the use of a logic model 4 Thursday Mar 17 6 Tuesday Mar 22 Kerzner Chapter 2 p. 52-69 Newell (2002) pages 46-75 Formative Evaluation Technique, Continued 3 Wednesday Mar 16 5 Monday Mar 21 HOMEWORK (96 HRS.) Kerzner, Chapter 2 p. 35-52 Determines how program evaluation is used in program planning 7 Wednesday Mar 23 The student develops a work breakdown structure using established tools and techniques to achieve stated project objectives, measures and indicators Developing Outcome Measures, Continued Newell (2002) pages 104-130 Kerzner Chap 5 p. 207-223 Develops project indicators measurable by a % and/or # Constructing Indicators Kerzner Chap 5 p. 223-239 Measures project indicators for project efficiency Case Study Analysis In-Class Handout ↓ ↑ 10 Tuesday Mar 29 Impact Evaluation Kerzner Chap 5 p. 239-258 Estimates project actual versus real milestone achievement MID TERM EXAM MID TERM EXAM Explores issues related to problems that were not planned for Control Variables Kerzner Chap 7 p. 299-307 Examines variables that impact the project timeline Qualitative Evaluation Methods Kerzner Chap 20 p. 831-841 Calculates and interprets data related to project research Unintended Consequences Control Variables Kerzner Chap 7 p. 258-299 Qualitative Evaluation Methods, Continued In-Class Hand out Calculates and interprets data related to project outcomes using statistical analysis Calculates and interprets data related to project attainment 12 Thursday Mar 31 ↓ 14 Tuesday Apr 5 ↑ 15 Wednesday Apr 6 16 Thursday Apr 7 Recognizes issues related to project success Newell (2002) pages 211-216 The student 11 utilizes earnedWednesday value concepts Mar 30 for project milestone control 13 Monday Apr 4 Discriminates between service “needs” and service “wants” through effective evaluation and assessment Identifying Indicators 8 Thursday Mar 24 9 Monday Mar 28 Kerzner Chap 5 p. 191-207 Quantitative Evaluation Methods 17 Monday Apr 11 18 Tuesday Apr 12 The student analyzes optimal labor utilization for cost effectiveness and labor utilization through statistical analysis Quantitative Evaluation Methods, Continued Revenue Streams and the Cost of Capital Project Business Analysis Control Issues 19 Wednesday Apr 13 Control Issues, Continued 20 Thursday Apr 14 21 Monday Apr 18 22 Tuesday Apr 19 23 Wednesday Apr 20 24 Thursday Apr 21 ↓ The student defines the elements of project quality management and applies them to the final project reporting feature Demonstrates knowledge related to milestone achievement and planning for contingencies Kerzner Chap 20 p. 841-851 Kerzner Chap 20 p. 851-862 Newell (2002) pages 132-161 In-Class Handout Empirical Data and Testing Methods Kerzner Chap 20 p. 870-883 Empirical Data and Testing Methods, Continued In-Class Handout Reporting the Results Discounting the Cost of Capital . Quantitative Evaluation of Projects – IRR FINAL EXAM Newell (2002) pages 165-179 In-Class Handout Calculates and interprets data related to project outcomes using statistical analysis Calculates and interprets data related to project outcomes using statistical analysis Defines salient control issues and discusses how they impact the project Defines salient control issues and discusses how they impact the project Determines the best method of project evaluation Determines the best method of project evaluation using a real project Communicates the results in a formal report format Newell (2002) pages 181-193 Financial Evaluation of Projects Pgs. 111 Project Calculates the Business Internal Rate of Analysis Pages Return on a project 8 - 39 6. METHODOLOGY This is a lecture-based course that will require continuous student attendance. Student knowledge and competencies will be evaluated through daily class participation, question-and-answer sessions and examination through authentic assessment i.e., demonstrating what has been learned. Note that students may complete make-up work by reading original research through the UEES ProQuest subscription. Students are highly encouraged to maintain a consistent presence during all scheduled class times. 7. EVALUATION The student will be assessed through daily participation and evaluation by written work and testing. By the conclusion of this class the student will be able to recognize and identify key objectives and will be able to fundamentally apply what was learned based upon the information given in this bimester of instruction. 7.1 Assessment Criteria Completion and knowledge of the assigned course readings, Consistent use of electronic media, Completion of assigned homework Classroom participation is subjectively considered in the final score 7.2 Performance Markers Identifies the difference between program evaluation and research, Explains the salient characteristics of program evaluation and individual assessment, Determines how program evaluation is used in program planning, Discriminates between service “needs” and service “wants” through effective evaluation and assessment, Identifies and determine the informational needs of program managers through evaluation and assessment methodology, Manipulates target data and collection technique to answer evaluation questions, Matches the type of data collected to the needs of the program, Designs and perform appropriate evaluations, Communicates quantitative and qualitative information to evaluation consumers. 7.3 Weighting Unit Exams Homework 50% 50% 8. BIBLIOGRAPHY 8.1 REQUIRED MAIN TEXTBOOK(s): Newell, M. (2002). Preparing for the project management professional certification exam, 2nd Edition. This textbook is in pdf format and will be sent to the student to print. A Guide to the Business Analysis Body of Knowledge. International Institute of Business Analysis (ND). This textbook is in pdf format and will be sent to the student to print. Kerzner, H. (ND) Project management – A systems approach to planning, scheduling and controlling. Newport Press, CA. Chapter 2 p. 35 – 86 Chapter 4 p. 139 – 190 Chapter 5 p. 191 – 258 Chapter 7 p. 289 – 307 Chapter 20 p. 831 – 883 8.2 COMPLEMENTARY TBA 8.3 HANDOUTS: Financial Evaluation of Projects What are project outcomes? 8.4 WEBLIOGRAPHY: This website is comprehensive in nature that includes many links to other relevant evaluation and assessment sites: ProQuest Database: Access portal through the UEES homepage at: www.uees.edu.ec Evaluation Resources, US Govt: http://www.cdc.gov/eval/resources.htm The Project Management Center: http://www.infogoal.com/pmc/pmchome.htm The International Research Network on Organizaing by Projects: http://www.irnop.org/ E-Project Central: http://www.eprojectcentral.com/ The Three Little Pigs Project: http://www.eng.uwo.ca/research/ttlpp/overview.htm The Woody 2000 Project: http://www.maxwideman.com/papers/woody2000/intro.htm 9. FACULTY INFORMATION NAME: James W. Keeley, PhD drjwkeeley@yahoo.com jkeeley@uees.edu.ec ACADEMIC CREDENTIALS: B.A.A.S Bachelors of Arts and Sciences GRADUATE: M.Ed. Master of Education M.B.A. Master of Business Administration Ph.D. Doctor of Philosophy Prepared by: James W. Keeley, PhD Date: February 18, 2011 Reviewed by: Dean Monica Reynoso Date: February, 2011