CONT313-Syllabus
advertisement

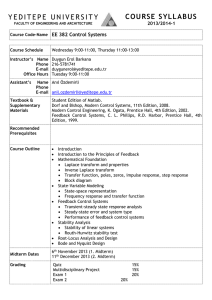
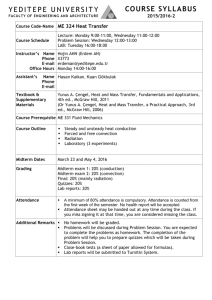
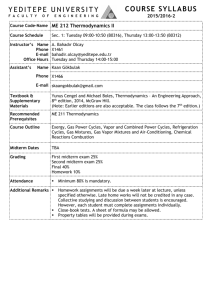
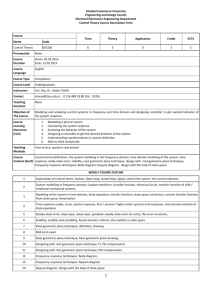
DOGUS UNIVERSITY CONT 313 Feedback Control Systems - Course Instruction Manual Faculty Department Credits / Hours Course Type Prerequisites Lecturer Engineering Faculty Control Engineering 4 (3+0+2) Compulsory Assist. Prof. Dr. Mustafa DOGAN (Room: G 502 C, Tel: (Ext) 1696) E-mail: mdogan@dogus.edu.tr The text book Recommended Texts - Modern control engineering 5th ed., Katsuhiko Ogata, Prentice Hall, 2010 Course Description Purpose Learning Outcomes Content of the Course General Skills Learning Methods Assessment 1- Modern Control Systems, 12th Edition, Richard C. Dorf, Robert H. Bishop, Prentice Hall, 2008 2- Feedback Control of Dynamic Systems, 6/E, Gene Franklin, J.D. Powell, Abbas Emami-Naeini, Prentice Hall 2010 This course gives an introduction to control systems theory for analysis and design of feedback systems to improve performance, regulation and stabilization of them. The purpose of this course is to supplement engineering students with the knowledge and capability to perform control systems analysis especially for regulation and stabilization. Control design aspects provides the means to control these processes to obtain certain desirable goals such as energy efficiency, better product quality and accurate control of the processes will be discussed. Designed laboratory experiments will be used for demonstration. By the end of the course, the students will be able to associate many problem settings with various types of system analysis methods and will be able to investigate these problems, to formulate the problems using state-space or frequency-domain models. The course also introduces students to computer modeling of control systems using modern simulation platforms like Matlab and Simulink. The students passing the course will be able to (The letters in parentheses addresses the relevant program outcomes) 1. To learn fundamentals of feedback systems, analysis methods. [1a, 1b] 2. To acquire basic understanding of various stability criteria used to build closed loop system. [1b, 2] 3. To acquire the ability to select and design suitable time and frequency domain specifications in order to meet requirements of desired closed loop system or state-space system. [2,3,4] 4. To acquire the ability to analyze and draw suitable root locus, Nyquist and Bode diagrams in order to understand the system stability and margins. [2,3,4] 5. To gain hands-on experience in designing, testing, and debugging controllers. [1b, 2,3,4,5] Modeling and simulation of dynamical systems, Transfer functions and state-space approaches in mathematical modeling, Modeling of mechanical, electrical, fluid, thermal and mixed systems, analytical and numerical solution of system responses. Introduction to feedback control systems, Criteria for transient response analysis and steady state errors, Stability analysis, Root-Locus plots, Frequency domain criteria, Bode diagrams; Nyquist diagram and Nyquist stability criterion, Closed-loop frequency response, State-space representations, solutions of statespace equations, State-space analysis, Controllability, observability and canonical forms. Acquire analytical skills A variety of teaching and learning methods are used including formal lectures, homework, laboratory experiments. The instructor will lecture in class by writing on the board and some lectures will be given as a power point presentation. Students can constitute groups for laboratory experiments. 4 HOMEWORKS ……(4%) 6 QUIZES…………….(9%) LAB…………………..(9%) 2 MIDTERMS ……….(38%) (1st midterm: 6th week / 2nd midterm: 11th week ) FINAL EXAM ……. .(40%) Course Plan Week Topics 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Learning Outcomes components, 1a Introduction, electrical system mechanical system components Fluid and thermal systems, servomotors Block diagrams, signal flow graphs State space description, state equations, state transition matrix, stability Transfer function decomposition, stability, controllability and observability 1st Midterm Exam Time response analysis, transient response Steady-state error analysis Root locus plotting Root locus plotting 2nd Midterm Exam Frequency response analysis, Bode plots, polar plots, gain-phase plots Nyquist stability analysis, Relative stability, gain / phase margins 1a,1b 2,4 2,3,4 2,3,4 2,3,4 2,3 2,3,4 2,3,4 2,3,4,5 2,3 2,3,4,5 Relationship Between the Course and Control Engineering Program Outcomes Contribution Level Program Outcomes 1a. Matematik, fen ve ilgili mühendislik konularında yeterli bilgi An ability to have the fundamental knowledge of mathematics, science, and relevant engineering subjects 1b. Bu bilgileri mühendislik problemlerini modelleme ve çözme için uygulayabilme becerisi An ability to apply these techniques and formations, to model and to solve engineering problems 2. Karmaşık mühendislik problemlerini saptama, tanımlama, formüle etme,çözme ve uygulama becerisi, An ability to identify, formulate, resolve and apply for complex engineering problems 3. Karmaşık bir sistemi, süreci, cihazı veya ürünü tasarlama, modern teknikleri uygulama becerisi An ability to apply modern techniques to design a complex system, process or product to meet desired requirements 4. Modern teknik ve araçları geliştirme, seçme ve kullanma becerisi; bilişim teknolojilerini etkin bir şekilde kullanma becerisi An ability to develop modern techniques and tools, also ability to select and use them; ability to use information technology effectively 5. Deney tasarlama, deney yapma, veri toplama, sonuçları analiz etme ve yorumlama becerisi. An ability to design and conduct experiments, to collect outcomes, as well as to analyze and interpret experimental data/outcomes. 6. Disiplin içi takımlarda, çok disiplinli takımlarda ve bireysel çalışabilme becerisi An ability to work individually and on multi-disciplinary teams/uniform teams. 7. Sözlü ve yazılı etkin iletişim kurma becerisi; en az bir yabancı dil bilgisi. An ability to communicate effectively verbally and in writing, at least one foreign language skills 8. Yaşam boyu öğrenmenin gerekliliği bilinci, bilgiye erişebilme, bilim ve teknolojideki gelişmeleri izleme ve kendini sürekli yenileme becerisi Awareness of the need for lifelong learning, able to access to information, to follow developments in science and technology and continuous self-renewal ability 9. Mesleki ve etik sorumluluk bilinci. An understanding of professional and ethical responsibility 10a. Proje yönetimi ile risk yönetimi ve değişiklik yönetimi gibi iş hayatı uygulamaları hakkında bilgi Information/knowledge on the applications of business life ,e.g. project management, risk management and change management 10b. Girişimcilik, yenilikçilik ve sürdürebilir kalkınma hakkında farkındalık Awareness of Entrepreneurship, innovation and sustainable development 11a. Mühendislik uygulamalarının evrensel ve toplumsal boyutlarda sağlık, çevre ve güvenlik üzerindeki etkileri hakkında bilgi A knowledge of the impact of engineering solutions in a global and societal context on health, environment and safety. 11b. Çağın sorunları hakkında bilgi A knowledge of contemporary issues 11c. Mühendislik çözümlerinin hukuksal sonuçları konusunda farkındalık Awareness of the legal consequences of engineering solutions Yukarıdaki tabloda Tam (3), Kısmi (2), Az (1) olarak gösterilmiştir.