Bacteria & Viruses

Name _______________________________________ Date ____________________ Period ________
Bacteria & Viruses –Review 2016
1. Prokaryotes are unlike all other organisms in that their cells lack a ____ nucleus ________________.
2. Which of these cells is prokaryotic?
*
3. The structure labeled E in Figure 19–1 represents __ nucleoid or DNA .
4. Which structure shown in Figure 19–1 is the pili and describe its
function? __ D –to attach to surfaces and other bacterial cells
5.
Identify the bacterial shape labeled A in Figure 19–2_ bacilli .
Figure
19–2
6.
Identify the bacterial shape labeled B Figure 19–2 _ spirillum
7.
Identify the bacterial shape labeled C in Figure 19–2 __ cocci .
8.
The illustration below is an example of what process?_
Binary fission _____
Figure
19–1
9.
10.
What are the roles of bacteria in the roots of plants? Nitrogen fixation
11.
A photo of a virus is shown. The projections on the surface of the
Virus allow it to attach to other cells ?
12.
All viruses are living or nonliving? _ nonliving __.
13.
What contains proteins, nucleic acid, and cannot be seen by any microscope? Bacteria or Virus
14.
Viruses must invade other cells in order to? _ reproduce
15.
What are the differences between the Lytic and Lysogenic cycles? Lytic cycle has a quick onset and destroys the cells.
16.
Draw the structure of a bacteriophage.
17.
When a person’s cells are infected by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus affects the body by damaging immune cells while using their machinery to _ reproduce ?
18.
Antibiotics treat infections from [bacteria or viruses].______________________.
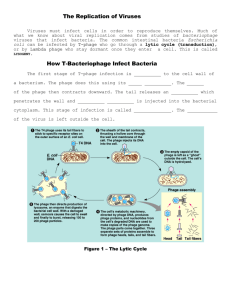
19.
Which letter in Figure 19–6 indicates the stage at which a bacteriophage injects its
DNA into a host cell? ___ G ____
20.
Look at both cycles shown in Figure
19–6. During which cycle is the host cell destroyed? ____ Lytic _ cycle.
Figure
19–6
21.
A student placed a disk of filter paper in each of the following solutions: disinfectant 1, disinfectant 2, disinfectant 3, and distilled water. While the four disks were soaking in their respective solutions, she streaked a sterile nutrient agar dish with a culture of E. coli bacteria. Then, she placed each disk carefully onto the nutrient agar dish, placed the lid on the dish, taped it shut, and incubated the dish at 37°C for several days. Figure 19–3 shows how the nutrient agar dish looked on Day 1 and Day 4.
Figure 19–3
Inferring: Look at the dishes in Figure 19–3. Which disinfectant was the least effective at controlling the growth of E. coli? a.
distilled water b.
disinfectant 1 c.
disinfectant 2 d.
disinfectant 3
21. The diagram to the right represents a virus with its surface markers. The diagrams below show various animal cells with receptor sites. Which of the following cells is most likely affected by this virus?
*
22. The graph illustrates a single species of bacteria grown at various pH
The most likely reason there are no colonies in cultures of this species at at pH 10 is that – a.
these bacteria could successfully compete with other species of bacteria at these pH values levels. pH 4 and b.
there are more predators feeding on these bacteria at pH 4 and pH 10 than at other pH levels c.
at pH 4 and pH 10 the environment is either too acidic or too basic for the bacteria to grow d.
fertilization cannot occur in these bacteria at pH4 or pH 10
23. What would a research immunologist have to study if they want to develop and antiviral drug?
Mechanism used by the virus to infect cells
24. List the similarities and differences between bacteria and viruses.
Bacteria- alive, killed by antibiotics, can reproduce, has DNA, can attach to other cells
Viruses: not alive, cannot be killed with antibiotics, cycle can be interrupted with antivirals, cannot reproduce on their own, has DNA, can attach to other cells