Neurons (aka Nerve Cells)
advertisement

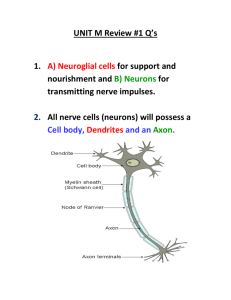
Biology 12 The Nervous System Neurons (aka Nerve Cells) A neuron is made up of three main parts: dentrites, axon and cell body o Dentrite: conducts impulse toward a cell body o Axon: conducts impulse away from a cell body o Cell body: contains the nucleus, which __________________ the cell. There are 3 kinds of neurons Type Diagram 1. Sensory Neuron (aka afferent neuron) 2. Interneuron (aka association neurons) 3. Motor Neuron (aka efferent neuron) Sensory neurons o transmits information about changes in the internal and external environment to the CNS. o have long ______________________ that extend from receptors to the CNS. o cell body is located outside of the CNS Interneuron o confined to the grey matter of the CNS o provide a link between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron o relatively short Motor neuron o transmits nerve impulases from the CNS to an effector organ (e.g. muscle or gland) thereby initiating a physiological response (e.g. muscle contraction or hormone sectretion) o have long ____________________ that extends from the cell body of the motor neuron (located within the CNS to an effector 7 Biology 12 The Nervous System Nerves comprised of many nerve fibres (axon plus supporting tissues) enclosed in a connective-tissue sheath connect CNS with organs and tissues of body three types i. motor nerve: carries only ____________ nerve fibres ii. sensory nerve: carries only ______________ nerve fibres iii. mixed nerve: carries __________________ nerve fibres o dendrites of sensory neurons and axons of motor neurons can be found in the same mixed nerve as each other o there can be hundreds of long fibres in the mixed fibres o these fibres are covered with a fatty tissue called myelin sheath. myelin sheath composed of Schwann cells that wrap around each fibre insulates long fibres of neruons from each other within the nerve and surrounding allows for faster travel of impulses points between the Schwann cells is called the nodes of Ranier o note: invertebrates generally lack myelin sheath and therefore are not capable of fast nerve responses spinal nerves are connected to the CNS either on the dorsal or ventral side of the spinal cord o sensory nerves are connected through the dorsal (towards back) root cell bodies of sensory nerves are found in the dorsal root ganglia o motor nerves are connected through the ventral (towards front) root cell bodies of motor nerves are located in the spinal cord cell bodies of motor neurons coupled with those of interneurons, gives the inner regions of the spinal cord a darker colour, called grey matter in contrast the outer regions are white because of the ___________________ of the axons Comparison of Types of Neurons Bases of Sensory Neuron Interneuron Motor Neuron Comparison Structure Function Location 8 Biology 12 The Nervous System Reflex Arch: an automatic and innate response to a particular stimulus basic functional unit of the nervous system generally involves all three types of neurons: _____________________, ____________________ and _______________________ extremely rapid response does not involve the brain to carry out o instead, sensory input is passed through the spinal cord and back out to the motor output to an effector organ o effector organ could be a muscle (causing movement) or a gland (resulting in secretion) where neurons connect with other neurons or effector organs is called a synapse e.g. the stretch reflex (one being the knee-jerk reflex) o sensor senses a stretch in the muscle of the leg o impulse is sent by sensory neurons to the spinal cord in the ____________ root o sensory neuron synapse with motor neurons and interneurons o motor neurons leave the spinal cord through the ______________ root o initiate contraction of quadriceps and relaxation of the hamstrings 9