Global I Content Review Sheet Part I
advertisement

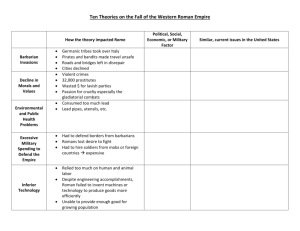
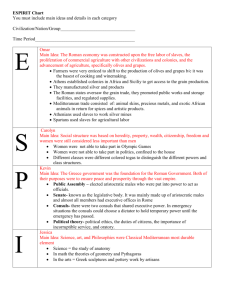
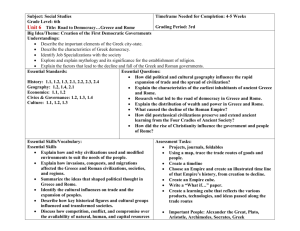
Global History and Geography Review Sheet #1 Spiconardi Early Peoples Hunters and Gatherers Nomadic people who move place to place hunting and gathering for good Neolithic Revolution Learning to farm and domestication of animals allows for Permanent settlements/villages/governments Rise of Civilizations Subsistence Farmers – ability to grow enough food to feed your immediate family Population increases The Characteristics of a Civilization Advanced Cities Specialized workers Complex institutions Record keeping Advanced technology Egypt Nile River Nile River provided drinking water and irrigation for crops Yearly floods left land rich with deposits of silt that made the land fertile Nile later serves for transportation and trade purposes Government and Religion Egypt is a theocracy Pharaoh is both a god and a king Polytheistic Dynastic Rule Social Structure and Achievements Women had a higher status in Egypt than any other ancient civilization. Women could own property and obtain a divorce Hieroglyphics Mummification Pyramids Advanced calendar Complex understanding of human body surgeries, diagnosis of diseases Mesopotamia Tigris and Euphrates rivers provide fertile land (Fertile Crescent) Lack of natural barriers leads to constant invasion and a diverse population Diverse population makes the “land between rivers” a crossroads of the world; Times Square of its day Sumerian Civilization Ziggurat temples City-state form of government Sumer grew rich from trade. Traded with people as far away as Egypt and India Contributions Cuneiform wedged shaped writing Developed early algebra and geometry Assyria Known for military tactics. Conquered entire Fertile Crescent by 612 BC 1 Global History and Geography Review Sheet #1 Spiconardi Babylon Hammurabi’s Code First major set of laws recorded Harsh punishments (eye for an eye) Upper class favored in laws NO EQUALITY UNDER THE LAW Different laws for different people Classical Civilizations China (1027 BC to 220 AD) Civilization forms near Yellow River Zhou Dynasty (1027 BC – 221 BC) Mandate of Heaven – a divine right to rule Dynastic cycle – A dynasty could lose mandate of heaven Feudal form of government Made the first books Discovered how to make silk Qin Dynasty (221 BC – 206 BC) Shi Huangdi Legalism strong laws needed to maintain order Centralizes power Abolishes feudalism Creates national coins Promotes uniform Chinese writing Repairs infrastructure Starts to build Great Wall First Nazi? Burns books Kills Confucian Scholars burns and buries alive Terra Cotta Army/Tomb Han Dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD) Emperor Wudi Establishes civil service system Bureaucracy highly organized government compromised of many departments Establishes Silk Road REGENTS like to compare Han to Roman Empire & Inca = ROADS UNITE EMPIRE India (1500 BC – 420 AD) Mauryan (321 BC – 185 BC) Well-organized government Chandragupta has secret police report on crime Asoka Brings Buddhism to India Encourages Religious Tolerance Plants trees on roads to provide shade for travelers Edicts Moral guidelines on how people in his empire should act Gupta (320 AD – 420 AD) 500 years of turmoil after Asoka. Gupta restore stability and prosperity to India 2 Global History and Geography Review Sheet #1 Spiconardi Greece (1750 BC – 133 BC) Geographical Influence Hard to unite all of Greece Dependent on seas for food and travel Little fertile land low population Mountainous = Terrace farming just like Japan and Incan Empire Polis – city states Sparta – Military was center of life. All boys and GIRLS trained to fight at age 6. Governed by an oligarchy. Athens – Cultural and intellectual center of Greece. Direct democracy for male citizens Philosophers Socrates – Socratic method: learn by questioning Plato – Government should control people’s lives; brightest should rule Aristotle – developed the “-ology” Alexander the Great Hellenistic Culture – Blend of Greek, Persian, Egyptian, and Indian culture Spent entire reign conquering. Only spend 3 months in Greece Focused on gaining territory, but not governing people Achievements Column style of building (government buildings in USA and Western Europe) Life-like artwork (sculpture) Pythagorean Theorem Epics (Odyssey, Illiad, Oedipus Rex) Herodotus – “Father of History” Rome (750 BC – 476 AD) Rome begins as a monarchy Becomes a republic with Brutus the Liberator Republic – when government officials are chosen by the people Senate – governing body of Rome, but DID NOT MAKE THE LAWS Patricians – Landowning upper class Plebeians – farmers, merchants, artisans; had little power until Julius Caesar’s reforms Social War – Marks beginning of the end of the republic Roman Empire After Caesar’s assassination, his grandnephew/adopted son Octavian/Augustus is crowned emperor Pax Romana – 200 year period of peace; Rome’s Golden Age Augustus Caesar reforms and rebuilds Rome; conservative in politics Achievements Law ROME HAS GIVEN THE WORLD A MODEL FOR AN EFFECTIVE LEGAL SYSTEM Twelve Tables – laws written on 12 tablets; basis of Western law Innocent until proven guilty Equality under the law Dome roofs Aqueducts & Roadways Public Plazas Stadiums/arenas Colosseum Art mosaics Trajan’s Forum prototype mall 3 Global History and Geography Review Sheet #1 Spiconardi Why did Rome Fall? Invasions from north Heavy taxation taxes went to fight wars and pay for mercenaries; not reinvested into infrastructure of the empire Too dependent on slave labor Trade deficit Romans imported more than they exported Citizens no longer worked for the good of Rome/lack of patriotism Empire divided into West (Rome) and East (Constantinople) Byzantine Empire Considered the new Rome Flourished due to trade in city of Constantinople/Byzantium/Istanbul Justinian’s Code – almost a carbon copy of Rome’s Twelve Tables Regents likes to ask how Hammurabi’s Code, Twelve Tables, and Justinian’s Code are similar: All are examples of written law or codified law or legal systems or codes of behavior Preserves Greco-Roman Culture Iconoclast Movement Schism of 1054 Separates from Roman Church over issues of papal authority language of the mass priests and marriage Filioque First Crusade Attacked by Seljuk Turks Asks Pope Urban II for help Council of Clermont Pope asks Christendom to unite and fight the Muslims Influences development of Russia Orthodox Christian Church Onion Dome Cyrillic alphabet Autocratic Government/Czar Mongols Chinggis Khan (Genghis) Created largest land empire ever by conquering other civilizations and cultures Tributary system Kublai Khan Embraces Chinese culture Spreads Chinese culture to rest of Asia Allows conquered people to serve in government Reopens Silk Road and makes travel on the trade route safe Leads to cultural diffusion between East and West Marco, Nicola, and Maffeo Polo Russia is isolated by Mongols and does not share in this cultural exchange Russia falls behind rest of Europe until Stalin catches them up in 1940s Japan Feudal society Emperor – no political power Shogun – real ruler and military leaders Daimyo – large landowners and nobles Samurai Bushido warrior code of behavior that stressed loyalty and respect Peasants, artisans, merchants Borrowed culture from Chinese by way of Koreans 4 Global History and Geography Review Sheet #1 Spiconardi Geography Limited natural resources Leads to imperialism in the late 19th/early 20th century Lack of farmland Mountainous; only 15% of land is farmable Terrace Farming Island and typhoons prevent invasion of Japan by Mongols Earthquakes reinforced steel buildings in 20 th century REGENTS: Likes to point out the similarity between the geographies of Japan and Greece (islands, little farmable land, mountains) Golden Age of Islam Preserved Greco-Roman Culture Spread through trade and conquest Split between Shiite and Sunni House of Wisdom Learning center in Baghdad; scholars came to learn Achievements Architecture Medicine Algebra Calligraphy Astronomy 5