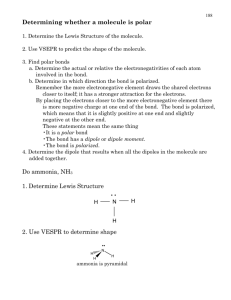
Molecular Geometry Review Packet Answer Key: Title of Worksheet
advertisement

Molecular Geometry Review Packet Answer Key: Title of Worksheet is Molecular Geometry Test Review Packet: Multiple Choice 1) A 2) B 3) A 4) D 5) B 6) C 7) C 8) A 9) A 10) A 11) A 12) A Title of Worksheet is Molecular Geometry Review Packet: 1) Any geometry where the elements attached to the central atom are all the same. Such as CF4 or PF5 2) Valance bond theory is a way of describing the electron pair bonds that form in covalent compounds. It is also known as the mixing of atomic orbitals to accommodate the spatial requirements in a molecule known as hybridization (hybridization occurs to minimize electron pair repulsions when atoms are combined to form molecules). 3) The greater the overlap between two orbitals, the stronger the bond that is form 4) H-H Bond is a s-s overlap and Cl-Cl p-p overlap 5) Hybrid orbitals are then the atomic orbitals on an atom mix to form new orbitals. They form to show the shape of the newly formed hybrid orbital 6) SP forms by mixing one s orbital with one p orbital. The geometry is linear 7) One s and two p orbitals hybridize to form sp2 (trigonal planar). One s and three p orbitals hybridize to form sp3(tetrahedral). One s mixed with three p and one d leads to sp3d (trigonal bipyramidal) 8) a) Draw Lewis Structure b) Determine electron domain geometry using VSEPR c) Specify hybrid orbitals needed to accommodate the electron pairs based on their geometric arrangements 9) Sigma bond is line joining the two nuclei passes through the middle of the overlap region Pi bond is the sideways overlap of p orbitals 10. Sigma bonds are stronger because they contain hybridized orbitals and pi bonds do not 11. 1 and 0 12. 1 and 1 13. 1 and 2 14. SKIP 15. Localized is for structures without resonance and Delocalized is for structures containing resonance 16. SKIP 17. A polar bond is the unequal sharing of electrons in a bond 18. The electron density shifts towards the more polar end of the bond 19. Arrow 20. Dipole moment is the measured polarity of a polar covalent bond 21. Equal sharing of electrons between a bond 22. Intermolecular forces are the forces between stable molecules 23. Ion-Ion is an ionic compound where electrons are donated and received (NaCl) Dipole-Dipole is forces that occur between two molecules with permanent dipoles (any polar molecule is dipole-dipole) LDF is temporarily induced dipoles but disappear quickly (any nonpolar molecule is LDF) Hydrogen bonding is intermolecular attraction with a hydrogen atom present in the bond (hydrogen needs to be directly bonded to an Nitrogen, Oxygen or Fluorine atom). 24. a. Polar and Dipole/Dipole b. Polar and Hydrogen Bonding c. Non-polar and LDF d. Polar and Dipole/Dipole e. Non-polar and LDF f. Polar and Dipole/Dipole g. Non-polar and LDF h. Non-polar and LDF i. Polar and Dipole/Dipole j. Polar and Ion/Ion k. Non-polar and LDF l. Polar and Hydrogen Bonding m. Polar and Ion/Ion n. Polar and Dipole/Dipole o. Polar and Hydrogen Bonding 25. Highest RbCl, CH3OH, CH3Cl, CH4 (weakest)