Second Grade Science
advertisement

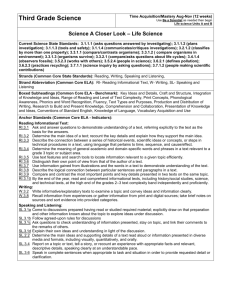
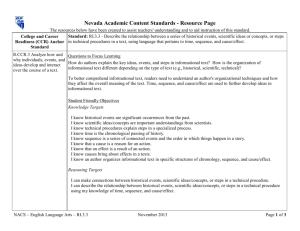
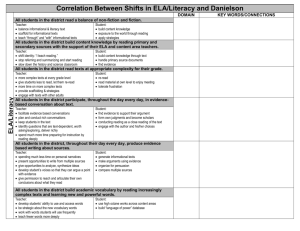
Second Grade Science Time Acquisition/Mastery Aug-Nov (12 weeks) Use Be a Scientist as needed then begin Life science Units A and B Science A Closer Look – Life Science Current Science State Standards: 2.1.1.3 (tools and safety); 2.1.1.4 (asks and answers questions); 2.1.1.5 (describes an observation); 2.3.1.1 (environments); 2.3.1.2 (life cycles); 2.3.1.3 (observe environments); 2.3.1.4 (structures/parts); 2.7.1.1 (practicing science); 2.7.1.2 (technology) Strands (Common Core State Standards): Reading, Writing, Speaking and Listening, Strand Abbreviation (Common Core ELA): RI- Reading Informational Text, W- Writing, SL- Speaking and Listening Boxed Subheadings (Common Core ELA - Benchmark): Key Ideas and Details, Craft and Structure, Integration of Knowledge and Ideas, Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity, Print Concepts, Phonological Awareness, Phonics and Word Recognition, Fluency, Text Types and Purposes, Production and Distribution of Writing, Research to Build and Present Knowledge, Comprehension and Collaboration, Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas, Conventions of Standard English, Knowledge of Language, Vocabulary Acquisition and Use Anchor Standards (Common Core ELA - Indicators): Reading Informational Text: RI.2.1 Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why, and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text. RI.2.2 Identify the main topic of a multi-paragraph text as well as the focus of specific paragraphs within the text. RI.2.3 Describe the connection between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text. RI.2.4 Determine the meaning of words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area. RI.2.5 Know and use various text features to locate key facts or information in a text efficiently. RI.2.10 By the end of year, read and comprehend informational texts, including history/social studies, science, and technical texts, in the grades 2–3 text complexity band proficiently, with scaffolding as needed at the high end of the range. Writing: W.2.2 Write informative/explanatory texts in which they introduce a topic, use facts and definitions to develop points, and provide a concluding statement or section. W.2.8 Recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question. Speaking and Listening: SL.2.1a Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions. SL.2.1b Build on others’ talk in conversations by linking their comments to the remarks of others. SL.2.4 Tell a story or recount an experience with appropriate facts and relevant, descriptive details, speaking audibly in coherent sentences. SL.2.5 Create audio recordings of stories or poems; add drawings or other visual displays to stories or recounts of experiences when appropriate to clarify ideas, thoughts, and feelings. SL.2.6 Produce complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation in order to provide requested detail or clarification. Essential Questions: Explicitly Taught Vocabulary: Unit A Plants & Animals Chapter 1 Lesson 1 – How do you know if something is a living thing? Lesson 2 – How do plants make more plants? Lesson 3 – What helps you identify a plant? Chapter 2 Lesson 1 – How can we classify animals? Lesson 2 – How can animal life cycles be different? Lesson 3 – What do animals need to stay alive? Unit A Plants & Animals Chapter 1 Lesson 1: minerals, oxygen Lesson 2: flower, seed, pollen, life cycle, seedling Lesson 3: trait Chapter 2 Lesson 1: mammal, amphibian, reptile, insect Lesson 2: life cycle, larva, pupa Lesson 3: adaptation, camouflage Unit B Habitats Chapter 3 Lesson 1 – How do plants and animals survive in their habitats? Lesson 2 – How do animals depend on other animals? Lesson 3 – What can cause habitats to change? Unit B Habitats Chapter 3 Lesson 1: habitat Lesson 2: food chain, predator, prey, food web Lesson 3: drought, endangered, fossil, extinct Chapter 4 Lesson 1: woodland forest, rain forest Lesson 2: desert, Arctic Chapter 4 Lesson 1 – How do living things survive in a forest habitat? Lesson 2 – What are desert habitats like? Lesson 3 – What are some different water habitats? Lesson 3: ocean, pond Inquiry Skills: observe, infer, compare, classify, put things in order, communicate, record data, investigate, predict, make a model, draw conclusions District Resources: Teacher Resource for building teacher informational background: Teacher Manual TR56 Yellow pages http://nsdl.org/refreshers/science/ Textbook – Macmillan/McGraw-Hill Science A Closer Look; Literature Big Books; Activity Flipchart; Key Concept Cards; Reading Essentials Books; Leveled Readers; Vocabulary cards; Photo sorting cards, Materials Kit, Teacher Works Plus CD-ROM, Classroom Presentation Toolkit CD-ROM, Puzzle maker CD-ROM, Science CD, Science: Teacher DVD Set, Science Activity DVD Differentiated Instruction: Look for Differentiated Instruction boxes in each chapter. Differentiated instruction suggestions vary from drawing a picture, working with objects, to differentiated oral questions. The science leveled readers offer a great opportunity for independent reading and research. Then reporting back to the group what was read. Also note the ELL Support boxes in each chapter as they can provide support for all students struggling with a concept. Approved Supplemental Resources: Science Links for grades K-4 Games, Worksheets http://www.sciencewithme.com/ Lesson Plans, etc. http://www.apples4theteacher.com/science.html Lessons, Puzzle makers http://school.discoveryeducation.com/ Assessment: Teacher observation Technology and Supplemental Resources: Online teacher’s edition, animations, vocabulary games. http://www.macmillanmh.com EBooks: teacher and student books http://connected.mcgraw-hill.com/connected Second Grade Science Time Acquisition/Mastery Nov - Feb (12 weeks) Earth Science Units C and D Science A Closer Look - Earth Science Current Science State Standards: 2.1.1.1 (properties); 2.1.1.2 (classifies); 2.1.1.3 (tools and safety); 2.1.1.4 (asks and answers questions); 2.1.1.5 (observation); 2.2.1.1 (properties of objects); 2.4.1.1 (observes and compares); 2.4.2.1 (recognizes objects in the sky); 2.4.2.2 (sun); 2.4.3.1 (observes weather); 2.4.3.3 (weather safety); 2.5.1.2 (science through technology); 2.7.1.1 (practicing science); 2.7.1.2 (technology) Strands (Common Core State Standards): Reading, Writing, Speaking and Listening, Strand Abbreviation (Common Core ELA): RI- Reading Informational Text, W- Writing, SL- Speaking and Listening Boxed Subheadings (Common Core ELA - Benchmark): Key Ideas and Details, Craft and Structure, Integration of Knowledge and Ideas, Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity, Print Concepts, Phonological Awareness, Phonics and Word Recognition, Fluency, Text Types and Purposes, Production and Distribution of Writing, Research to Build and Present Knowledge, Comprehension and Collaboration, Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas, Conventions of Standard English, Knowledge of Language, Vocabulary Acquisition and Use Anchor Standards (Common Core ELA - Indicators): Reading Informational Text: RI.2.1 Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why, and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text. RI.2.2 Identify the main topic of a multi-paragraph text as well as the focus of specific paragraphs within the text. RI.2.3 Describe the connection between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text. RI.2.4 Determine the meaning of words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area. RI.2.5 Know and use various text features to locate key facts or information in a text efficiently. RI.2.10 By the end of year, read and comprehend informational texts, including history/social studies, science, and technical texts, in the grades 2–3 text complexity band proficiently, with scaffolding as needed at the high end of the range. Writing: W.2.2 Write informative/explanatory texts in which they introduce a topic, use facts and definitions to develop points, and provide a concluding statement or section. W.2.8 Recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question. Speaking and Listening: SL.2.1a Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions. SL.2.1b Build on others’ talk in conversations by linking their comments to the remarks of others. SL.2.4 Tell a story or recount an experience with appropriate facts and relevant, descriptive details, speaking audibly in coherent sentences. SL.2.5 Create audio recordings of stories or poems; add drawings or other visual displays to stories or recounts of experiences when appropriate to clarify ideas, thoughts, and feelings. SL.2.6 Produce complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation in order to provide requested detail or clarification. Essential Questions: Unit C Our Earth Chapter 5 Lesson 1 – What are parts of the Earth? Lesson 2 – How do living things use Earth’s water? Lesson 3 – How does earth Change? Chapter 6 Lesson 1 – How do we use rocks and minerals? Lesson 2 – Where does all the soil come from? Lesson 3 – How can we take care of Earth’s resources? Unit D Weather & Sky Chapter 7 Lesson 1 – How can you measure weather? Lesson 2 – How does water change? Lesson 3 – How can weather change? Explicitly Taught Vocabulary: Unit C Our Earth Chapter 5 Lesson 1: landforms, crust, mantle, core Lesson 2: fresh water, ocean Lesson 3: earthquake, volcano, flood, landslide Chapter 6 Lesson 1: natural resource, rock, minerals Lesson 2: soil, decompose Lesson 3: pollution, reuse, reduce, recycle Unit D Weather & Sky Chapter 7 Lesson 1: temperature, precipitation, anemometer Lesson 2: evaporate, condense Lesson 3: cumulus, cirrus, stratus Chapter 8 Lesson 1 – How does the sky seem to change? Lesson 2 – What happens when the Earth moves? Lesson 3 – What can you see in the sky at night? Lesson 4 – How are planets like and different? Chapter 8 Lesson 1: rotation, axis Lesson 2: orbit Lesson 3: phase, star, Lesson 4: planet, solar system Inquiry Skills: observe, infer, compare, classify, communicate, record data, investigate, predict, make a model, draw conclusions, measure District Resources: Teacher Resource for building teacher informational background: Teacher Manual TR56 Yellow pages Textbook – Macmillan/McGraw-Hill Science A Closer Look; Literature Big Books; Activity Flipchart; Key Concept Cards; Reading Essentials Books; Leveled Readers; Vocabulary cards; Photo sorting cards, Materials Kit, Teacher Works Plus CD-ROM, Classroom Presentation Toolkit CD-ROM, Puzzle maker CD-ROM, Science CD, Science: Teacher DVD Set, Science Activity DVD http://nsdl.org/refreshers/science/ Differentiated Instruction: Look for Differentiated Instruction boxes in each chapter. Differentiated instruction suggestions vary from drawing a picture, working with objects, to differentiated oral questions. The science leveled readers offer a great opportunity for independent reading and research. Then reporting back to the group what was read. Also note the ELL Support boxes in each chapter as they can provide support for all students struggling with a concept. Approved Supplemental Resources: Science Links for grades K-4 Games, Worksheets http://www.sciencewithme.com/ Lesson Plans, etc. http://www.apples4theteacher.com/science.html Lessons, Puzzle makers http://school.discoveryeducation.com/ Assessment: Teacher observation Technology and Supplemental Resources: Online teacher’s edition, animations, vocabulary games. http://www.macmillanmh.com EBooks: teacher and student books http://connected.mcgraw-hill.com/connected Second Grade Science Time Acquisition/Mastery Feb – May (12 weeks) Physical Science Units E and F Science A Closer Look – Physical Science Current Science State Standards: 2.1.1.1 (properties); 2.1.1.2 (classifies); 2.1.1.3 (tools and safety); 2.1.1.4 ( asks and answers questions); 2.1.1.5 (observation); 2.2.1.2 (sorts by properties); 2.2.1.3 (solids and liquids); 2.2.1.4 (position of objects); 2.5.1.1 (explores the way things work); 2.5.1.2 (science through technology); 2.5.1.2 (science through technology); 2.7.1.1 (practicing science); 2.7.1.2 (technology) Strands (Common Core State Standards): Reading, Writing, Speaking and Listening, Strand Abbreviation (Common Core ELA): RI- Reading Informational Text, W- Writing, SL- Speaking and Listening Boxed Subheadings (Common Core ELA - Benchmark): Key Ideas and Details, Craft and Structure, Integration of Knowledge and Ideas, Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity, Print Concepts, Phonological Awareness, Phonics and Word Recognition, Fluency, Text Types and Purposes, Production and Distribution of Writing, Research to Build and Present Knowledge, Comprehension and Collaboration, Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas, Conventions of Standard English, Knowledge of Language, Vocabulary Acquisition and Use Anchor Standards (Common Core ELA - Indicators): Reading Informational Text: RI.2.1 Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why, and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text. RI.2.2 Identify the main topic of a multi-paragraph text as well as the focus of specific paragraphs within the text. RI.2.3 Describe the connection between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text. RI.2.4 Determine the meaning of words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area. RI.2.5 Know and use various text features to locate key facts or information in a text efficiently. RI.2.10 By the end of year, read and comprehend informational texts, including history/social studies, science, and technical texts, in the grades 2–3 text complexity band proficiently, with scaffolding as needed at the high end of the range. Writing: W.2.2 Write informative/explanatory texts in which they introduce a topic, use facts and definitions to develop points, and provide a concluding statement or section. W.2.8 Recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question. Speaking and Listening: SL.2.1a Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions. SL.2.1b Build on others’ talk in conversations by linking their comments to the remarks of others. SL.2.4 Tell a story or recount an experience with appropriate facts and relevant, descriptive details, speaking audibly in coherent sentences. SL.2.5 Create audio recordings of stories or poems; add drawings or other visual displays to stories or recounts of experiences when appropriate to clarify ideas, thoughts, and feelings. SL.2.6 Produce complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation in order to provide requested detail or clarification. Essential Questions: Unit E Matter Chapter 9 Lesson 1 – How can you describe matter? Lesson 2 – What are the properties of a solid? Lesson 3 – What are the properties of liquids and gases Chapter 10 Lesson 1 – What changes matter? Lesson 2 – How does temperature affect matter? Lesson 3 – How can you make mixtures? Explicitly Taught Vocabulary: Unit E Matter Chapter 9 Lesson 1: property, matter, mass Lesson 2: solid Lesson 3: liquid, gas, volume Chapter 10 Lesson 1: physical change, chemical change Lesson 2: evaporate, condense Lesson 3: mixture, solution, dissolve Unit F Motion & Energy Chapter 11 Lesson 1 – How can you tell something has moved? Lesson 2 – What do forces do? Lesson 3 – What are magnets? Unit F Motion & Energy Chapter 11 Lesson 1: position, motion, speed Lesson 2: force, gravity, friction Lesson 3: simple machine, lever, ramp, fulcrum Lesson 4: attract, poles, repel Chapter 12 Lesson 1 – What can heat do to matter? Lesson 2 – How do we hear sounds? Lesson 3 – How does light help us to see? Lesson 4 – How do we get electricity? Chapter 12 Lesson 1: heat, fuel Lesson 2: sound, vibrate, pitch Lesson 3: light, reflect Lesson 4: current electricity, circuit, static electricity Inquiry Skills: observe, infer, compare, classify, communicate, record data, investigate, predict, make a model, measure District Resources: Teacher Resource for building teacher informational background: Teacher Manual TR56 Yellow pages http://nsdl.org/refreshers/science/ Textbook – Macmillan/McGraw-Hill Science A Closer Look; Literature Big Books; Activity Flipchart; Key Concept Cards; Reading Essentials Books; Leveled Readers; Vocabulary cards; Photo sorting cards, Materials Kit, Teacher Works Plus CD-ROM, Classroom Presentation Toolkit CD-ROM, Puzzle maker CD-ROM, Science CD, Science: Teacher DVD Set, Science Activity DVD Differentiated Instruction: Look for Differentiated Instruction boxes in each chapter. Differentiated instruction suggestions vary from drawing a picture, working with objects, to differentiated oral questions. The science leveled readers offer a great opportunity for independent reading and research. Then reporting back to the group what was read. Also note the ELL Support boxes in each chapter as they can provide support for all students struggling with a concept. Approved Supplemental Resources: Science Links for grades K-4 Games, Worksheets http://www.sciencewithme.com/ Lesson Plans, etc. http://www.apples4theteacher.com/science.html Lessons, Puzzle makers http://school.discoveryeducation.com/ Assessment: Teacher observation Technology and Supplemental Resources: Online teacher’s edition, animations, vocabulary games. http://www.macmillanmh.com EBooks: teacher and student books http://connected.mcgraw-hill.com/connected