Second Grade Science
advertisement

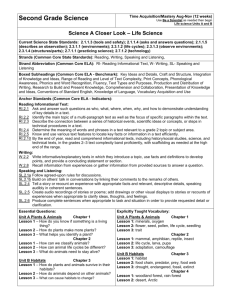
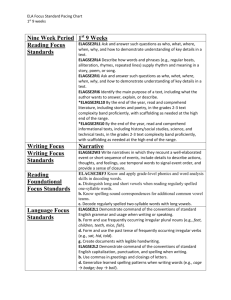
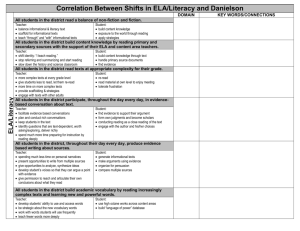
Third Grade Science Time Acquisition/Mastery Aug-Nov (12 weeks) Use Be a Scientist as needed then begin Life science Units A and B Science A Closer Look – Life Science Current Science State Standards: 3.1.1.1 (asks questions answered by investigating); 3.1.1.2 (plans investigation); 3.1.1.3 (tools and safety); 3.1.1.4 (communicates/critiques investigations); 3.2.1.2 (classifies by more than one property); 3.3.1.1 (compare/contrasts organisms); 3.3.1.2 ( compare organisms in environment); 3.3.1.3 (organisms survive); 3.3.2.1 (compare/asks questions about life cycles); 3.4.1.4 (observers fossils); 3.5.2.3 (works with others); 3.5.2.4 (people in science); 3.6.2.1 (defines pollution); 3.6.2.3 (practices recycling); 3.7.1.1 (science inquiry by asking questions); 3.7.1.2 (people making scientific contributions) Strands (Common Core State Standards): Reading, Writing, Speaking and Listening, Strand Abbreviation (Common Core ELA): RI- Reading Informational Text, W- Writing, SL- Speaking and Listening Boxed Subheadings (Common Core ELA - Benchmark): Key Ideas and Details, Craft and Structure, Integration of Knowledge and Ideas, Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity, Print Concepts, Phonological Awareness, Phonics and Word Recognition, Fluency, Text Types and Purposes, Production and Distribution of Writing, Research to Build and Present Knowledge, Comprehension and Collaboration, Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas, Conventions of Standard English, Knowledge of Language, Vocabulary Acquisition and Use Anchor Standards (Common Core ELA - Indicators): Reading Informational Text: RI.3.1 Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the basis for the answers. RI.3.2 Determine the main idea of a text; recount the key details and explain how they support the main idea. RI.3.3 Describe the connection between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text, using language that pertains to time, sequence, and cause/effect. RI.3.4 Determine the meaning of general academic and domain-specific words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 3 topic or subject area. RI.3.5 Use text features and search tools to locate information relevant to a given topic efficiently. RI.3.6 Distinguish their own point of view from that of the author of a text. RI.3.7 Use information gained from illustrations and the words in a text to demonstrate understanding of the text. RI.3.8 Describe the logical connection between particular sentences and paragraphs in a text. RI.3.9 Compare and contrast the most important points and key details presented in two texts on the same topic. RI.3.10 By the end of the year, read and comprehend informational texts, including history/social studies, science, and technical texts, at the high end of the grades 2–3 text complexity band independently and proficiently. Writing: W.3.2 Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas and information clearly. W.3.8 Recall information from experiences or gather information from print and digital sources; take brief notes on sources and sort evidence into provided categories. Speaking and Listening: SL.3.1a Come to discussions prepared having read or studied required material; explicitly draw on that preparation and other information known about the topic to explore ideas under discussion. SL.3.1b Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions SL.3.1c Ask questions to check understanding of information presented, stay on topic, and link their comments to the remarks of others. SL.3.1d Explain their own ideas and understanding in light of the discussion. SL.2.2 Determine the main ideas and supporting details of a text read aloud or information presented in diverse media and formats, including visually, quantitatively, and orally. SL.3.4 Report on a topic or text, tell a story, or recount an experience with appropriate facts and relevant, descriptive details, speaking clearly at an understandable pace. SL.3.6 Speak in complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation in order to provide requested detail or clarification. Essential Questions: Explicitly Taught Vocabulary: Unit A Living Things Chapter 1 Lesson 1 – How are all living things alike? Lesson 2 – How do plants structures compare? Lesson 3 – What helps animals survive in their environments? Lesson 4 - Which features can we use to classify animals? Chapter 2 Lesson 1 – How do plants grow and reproduce? Lesson 2 – How do animals grow and reproduce? Lesson 3 – How do organisms get their features? Unit A Living Things Chapter 1 Lesson 1: organism, respond, reproduce, environment, cell Lesson 2: structure, root, nutrient, stem, leaf, photosynthesis Lesson 3: lung, gills, shelter Lesson 4: vertebrate, invertebrate, exoskeleton, bird, reptile, amphibian, fish, mammal Chapter 2 Lesson 1: seed, embryo, flower, pollination, fruit, life cycle, cone Lesson 2: metamorphosis, egg, larva, pupa Lesson 3: trait, heredity, inherited trait, learned trait Unit B Ecosystems Chapter 3 Lesson 1 – How do living things interact? Lesson 2 – How do ecosystems compare? Lesson 3 – How do organism’s traits help it survive? Chapter 4 Lesson 1 – How can people and other living things change their environments? Lesson 2 – How can changes in an environment affect living things? Lesson 3 – What can we learn about living things of the past? Inquiry Skills: observe, infer, compare, classify, put things in order, communicate, interpret data, record data, investigate, predict, make a model, draw conclusions, experiment, form a hypothesis, use numbers Teacher Resource for building teacher informational background: Teacher Manual TR40 Yellow pages Unit B Ecosystems Chapter 3 Lesson 1: ecosystem, habitat, food chain, producer, consumer, decomposer, food web Lesson 2: climate, soil, desert, forest, ocean, wetland Lesson 3: adaptation, camouflage, nocturnal, mimicry, hibernate, migrate Chapter 4 Lesson 1: resource, competition, pollution, reduce, reuse, recycle Lesson 2: flood, drought, population, community, endangered Lesson 3: fossil, extinct District Resources: Textbook – Macmillan/McGraw-Hill Science A Closer Look; Literature Big Books; Activity Flipchart; Key Concept Cards; Reading Essentials Books; Leveled Readers; Vocabulary cards; Photo sorting cards, Materials Kit, Teacher Works Plus CD-ROM, Classroom Presentation Toolkit CD-ROM, Puzzle maker CD-ROM, Science CD, Science: Teacher DVD Set, Science Activity DVD http://nsdl.org/refreshers/science/ Differentiated Instruction: Look for Differentiated Instruction boxes in each chapter. Differentiated instruction suggestions vary from drawing a picture, working with objects, to differentiated oral questions. The science leveled readers offer a great opportunity for independent reading and research. Then reporting back to the group what was read. Also note the ELL Support boxes in each chapter as they can provide support for all students struggling with a concept. Approved Supplemental Resources: Science Links for grades K-4 Games, Worksheets http://www.sciencewithme.com/ Lesson Plans, etc. http://www.apples4theteacher.com/science.html Lessons, Puzzle makers http://school.discoveryeducation.com/ Assessment: Teacher observation Technology and Supplemental Resources: Online teacher’s edition, animations, vocabulary games. http://www.macmillanmh.com EBooks: teacher and student books http://connected.mcgraw-hill.com/connected Third Grade Science Time Acquisition/Mastery Nov - Feb (12 weeks) Earth Science Units C and D Science A Closer Look - Earth Science Current Science State Standards: 3.1.1.1 (asks questions answered by investigating); 3.1.1.2 (plans investigation); 3.1.1.3 (tools and safety); 3.1.1.4 (communicates/critiques investigations); 3.2.1.1 (uses tools to measure properties); 3.2.1.2 (classifies by more than one property); 3.4.1.1 (earth materials); 3.4.1.2 (soil types); 3.1.4.3 (water cycle); 3.4.1.4 (observers fossils); 3.4.2.1(moon and stars); 3.4.2.2 (shadows); 3.4.2.3. (sun, light and heat); 3.4.3.1.(earth’s surface); 3.4.3.2 (weather changes); 3.5.2.3 (works with others); 3.5.2.4 (people in science); 3.5.2.5 (use tools to observe); 3.6.1.2 (safety); 3.6.2.1 (defines pollution); 3.6.2.3 (practices recycling); 3.7.1.1 (science inquiry by asking questions); 3.7.1.2 (people making scientific contributions) Strands (Common Core State Standards): Reading, Writing, Speaking and Listening, Strand Abbreviation (Common Core ELA): RI- Reading Informational Text, W- Writing, SL- Speaking and Listening Boxed Subheadings (Common Core ELA - Benchmark): Key Ideas and Details, Craft and Structure, Integration of Knowledge and Ideas, Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity, Print Concepts, Phonological Awareness, Phonics and Word Recognition, Fluency, Text Types and Purposes, Production and Distribution of Writing, Research to Build and Present Knowledge, Comprehension and Collaboration, Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas, Conventions of Standard English, Knowledge of Language, Vocabulary Acquisition and Use Anchor Standards (Common Core ELA - Indicators): Reading Informational Text: RI.3.1 Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the basis for the answers. RI.3.2 Determine the main idea of a text; recount the key details and explain how they support the main idea. RI.3.3 Describe the connection between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text, using language that pertains to time, sequence, and cause/effect. RI.3.4 Determine the meaning of general academic and domain-specific words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 3 topic or subject area. RI.3.5 Use text features and search tools to locate information relevant to a given topic efficiently. RI.3.6 Distinguish their own point of view from that of the author of a text. RI.3.7 Use information gained from illustrations and the words in a text to demonstrate understanding of the text. RI.3.8 Describe the logical connection between particular sentences and paragraphs in a text. RI.3.9 Compare and contrast the most important points and key details presented in two texts on the same topic. RI.3.10 By the end of the year, read and comprehend informational texts, including history/social studies, science, and technical texts, at the high end of the grades 2–3 text complexity band independently and proficiently. Writing: W.3.2 Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas and information clearly. W.3.8 Recall information from experiences or gather information from print and digital sources; take brief notes on sources and sort evidence into provided categories. Speaking and Listening: SL.3.1a Come to discussions prepared having read or studied required material; explicitly draw on that preparation and other information known about the topic to explore ideas under discussion. SL.3.1b Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions SL.3.1c Ask questions to check understanding of information presented, stay on topic, and link their comments to the remarks of others. SL.3.1d Explain their own ideas and understanding in light of the discussion. SL.2.2 Determine the main ideas and supporting details of a text read aloud or information presented in diverse media and formats, including visually, quantitatively, and orally. SL.3.4 Report on a topic or text, tell a story, or recount an experience with appropriate facts and relevant, descriptive details, speaking clearly at an understandable pace. SL.3.6 Speak in complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation in order to provide requested detail or clarification. Essential Questions: Explicitly Taught Vocabulary: Unit C Earth & Its Resources Chapter 5 Lesson 1 – What shapes can the land take? Lesson 2 – How can Earth’s surface change quickly? Lesson 3 – How can Earth’s surface change slowly? Chapter 6 Lesson 1 – What makes rocks different from one another? Lesson 2 – How does soil affect living things? Lesson 3 – How are fossils and energy related? Lesson 4 – How do we use air and water? Unit C Earth & Its Resources Chapter 5 Lesson 1: ocean, continent, landform, crust, mantle, core Lesson 2: earthquake, volcano, lava, landslide, flood Lesson 3: weathering, erosion, glacier, deposition Chapter 6 Lesson 1: rock, minerals, igneous rock, sediment, sedimentary rock, metamorphic rock Lesson 2: soil, humus, natural resource Lesson 3: fossil, fuel, renewable resource, nonrenewable resource, solar energy, Lesson 4: groundwater, pollution, conserve Unit D Weather & Space Chapter 7 Lesson 1 – What information is used to predict the weather? Lesson 2 – Where does water go? Lesson 3 – How do weather patterns change? Chapter 8 Lesson 1 – How do the Sun and Earth interact? Lesson 2 – What can we learn about the Moon? Lesson 3 – How can Earth compared to the other object in the solar system? Lesson 4 – What can we see in the night sky? Inquiry Skills: Observe, infer, compare, classify, put things in order, communicate, interpret data, record data, investigate, predict, make a model, draw conclusions, experiment, form a hypothesis, use numbers, use variables, measure Teacher Resource for building teacher informational background: Teacher Manual TR56 Yellow pages Unit D Weather & Space Chapter 7 Lesson 1: atmosphere, weather, temperature, precipitation, wind, air pressure Lesson 2: cloud, evaporation, water vapor, condensation, water cycle, condensation, water cycle, tornado, hurricane, blizzard Lesson 3: climate, sphere, axis, seasons Chapter 8 Lesson 1: rotate, axis, revolve, orbit, star Lesson 2: phase, crater, Lesson 3: solar system, planet, telescope, space probe Lesson 4: constellation District Resources: Textbook – Macmillan/McGraw-Hill Science A Closer Look; Literature Big Books; Activity Flipchart; Key Concept Cards; Reading Essentials Books; Leveled Readers; Vocabulary cards; Photo sorting cards, Materials Kit, Teacher Works Plus CD-ROM, Classroom Presentation Toolkit CD-ROM, Puzzle maker CD-ROM, Science CD, Science: Teacher DVD Set, Science Activity DVD http://nsdl.org/refreshers/science/ Differentiated Instruction: Look for Differentiated Instruction boxes in each chapter. Differentiated instruction suggestions vary from drawing a picture, working with objects, to differentiated oral questions. The science leveled readers offer a great opportunity for independent reading and research. Then reporting back to the group what was read. Also note the ELL Support boxes in each chapter as they can provide support for all students struggling with a concept. Approved Supplemental Resources: Science Links for grades K-4 Games, Worksheets http://www.sciencewithme.com/ Lesson Plans, etc. http://www.apples4theteacher.com/science.html Lessons, Puzzle makers http://school.discoveryeducation.com/ Assessment: Teacher observation Technology and Supplemental Resources: Online teacher’s edition, animations, vocabulary games. http://www.macmillanmh.com EBooks: teacher and student books http://connected.mcgraw-hill.com/connected Third Grade Science Time Acquisition/Mastery Feb – May (12 weeks) Physical Science Units E and F Science A Closer Look – Physical Science Current Science State Standards: 3.1.1.1 (asks questions answered by investigating); 3.1.1.2 (plans investigation); 3.1.1.3 (tools and safety); 3.1.1.4 (communicates/critiques investigations); 3.2.1.1 (uses tools to measure properties); 3.2.1.3 (objects interact); 3.2.1.4 (solids, liquids, gases); 3.2.2.1 (moves objects); 3.2.2.2 (change of position); 3.2.3.1 (sound); 3.2.3.2 (sounds of different objects); 3.2.3.3 (pitches of sound); 3.2.4.1 (magnets); 3.2.4.2 (designs a magnet experiment); 3.2.4.3.(simple circuit); 3.4.1.3 (properties of water); 3.5.2.3 (works with others); 3.5.2.4 (people in science); 3.5.2.5 (use tools to observe); 3.6.1.2 (safety); 3.7.1.1 (science inquiry by asking questions); 3.7.1.2 (people making scientific contributions) Strands (Common Core State Standards): Reading, Writing, Speaking and Listening, Strand Abbreviation (Common Core ELA): RI- Reading Informational Text, W- Writing, SL- Speaking and Listening Boxed Subheadings (Common Core ELA - Benchmark): Key Ideas and Details, Craft and Structure, Integration of Knowledge and Ideas, Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity, Print Concepts, Phonological Awareness, Phonics and Word Recognition, Fluency, Text Types and Purposes, Production and Distribution of Writing, Research to Build and Present Knowledge, Comprehension and Collaboration, Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas, Conventions of Standard English, Knowledge of Language, Vocabulary Acquisition and Use Anchor Standards (Common Core ELA - Indicators): Reading Informational Text: RI.3.1 Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the basis for the answers. RI.3.2 Determine the main idea of a text; recount the key details and explain how they support the main idea. RI.3.3 Describe the connection between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text, using language that pertains to time, sequence, and cause/effect. RI.3.4 Determine the meaning of general academic and domain-specific words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 3 topic or subject area. RI.3.5 Use text features and search tools to locate information relevant to a given topic efficiently. RI.3.6 Distinguish their own point of view from that of the author of a text. RI.3.7 Use information gained from illustrations and the words in a text to demonstrate understanding of the text. RI.3.8 Describe the logical connection between particular sentences and paragraphs in a text. RI.3.9 Compare and contrast the most important points and key details presented in two texts on the same topic. RI.3.10 By the end of the year, read and comprehend informational texts, including history/social studies, science, and technical texts, at the high end of the grades 2–3 text complexity band independently and proficiently. Writing: W.3.2 Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas and information clearly. W.3.8 Recall information from experiences or gather information from print and digital sources; take brief notes on sources and sort evidence into provided categories. Speaking and Listening: SL.3.1a Come to discussions prepared having read or studied required material; explicitly draw on that preparation and other information known about the topic to explore ideas under discussion. SL.3.1b Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions SL.3.1c Ask questions to check understanding of information presented, stay on topic, and link their comments to the remarks of others. SL.3.1d Explain their own ideas and understanding in light of the discussion. SL.2.2 Determine the main ideas and supporting details of a text read aloud or information presented in diverse media and formats, including visually, quantitatively, and orally. SL.3.4 Report on a topic or text, tell a story, or recount an experience with appropriate facts and relevant, descriptive details, speaking clearly at an understandable pace. SL.3.6 Speak in complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation in order to provide requested detail or clarification. Essential Questions: Explicitly Taught Vocabulary: Unit E Matter Chapter 9 Lesson 1 – What are all objects made of? Lesson 2 – How can you compare different kinds of matter? Lesson 3 – What are the states of matter? Chapter 10 Lesson 1 – How can matter change states? Lesson 2 – What happens when matter goes through a physical change? Lesson 3 – What happens when matter goes through a chemical change? Unit E Matter Chapter 9 Lesson 1: matter, volume, mass, property, element Lesson 2: metric system, pan balance, gravity, weight Lesson 3: states of matter, solid, liquid, gas Chapter 10 Lesson 1: melt, boil, evaporate, condense, freeze Lesson 2: physical change, mixture, solution Lesson 3: chemical change Unit F Forces & Energy Chapter 11 Lesson 1 – How can you tell something is moving? Lesson 2 – How do forces change motion? Lesson 3 – How do we work? Lesson 4 – How can a simple machine reduce force? Chapter 12 Lesson 1 – How can you describe heat? Lesson 2 – What is sound? Lesson 3 – How does light allow you to see objects? Lesson 4 – How do you use electricity? Inquiry Skills: observe, infer, compare, classify, put things in order, communicate, interpret data, record data, investigate, predict, make a model, draw conclusions, experiment, form a hypothesis, use numbers, use variables, measure Teacher Resource for building teacher informational background: Unit F Forces & Energy Chapter 11 Lesson 1: position, distance, motion, speed Lesson 2: force, magnet, gravity, weight, friction Lesson 3: work, energy, kinetic energy, potential energy Lesson 4: simple machine, lever, pulley, wheel and axel, inclined plane, screw, wedge, compound machine Chapter 12 Lesson 1: heat, thermal energy, temperature, thermometer, conductor, insulator Lesson 2: sound, vibrate, pitch, volume Lesson 3: light, reflect, absorb, opaque, shadow, transparent, translucent, refract Lesson 4: electrical charge, static electricity, electric current, circuit, switch District Resources: Textbook – Macmillan/McGraw-Hill Science A Closer Look; Literature Big Books; Activity Flipchart; Key Concept Cards; Reading Essentials Books; Leveled Readers; Vocabulary cards; Photo sorting cards, Materials Kit, Teacher Works Plus CD-ROM, Classroom Presentation Toolkit CD-ROM, Puzzle maker CD-ROM, Science CD, Science: Teacher DVD Set, Science Activity DVD Teacher Manual TR56 Yellow pages http://nsdl.org/refreshers/science/ Differentiated Instruction: Look for Differentiated Instruction boxes in each chapter. Differentiated instruction suggestions vary from drawing a picture, working with objects, to differentiated oral questions. The science leveled readers offer a great opportunity for independent reading and research. Then reporting back to the group what was read. Also note the ELL Support boxes in each chapter as they can provide support for all students struggling with a concept. Approved Supplemental Resources: Science Links for grades K-4 Games, Worksheets http://www.sciencewithme.com/ Lesson Plans, etc. http://www.apples4theteacher.com/science.html Lessons, Puzzle makers http://school.discoveryeducation.com/ Assessment: Teacher observation Technology and Supplemental Resources: Online teacher’s edition, animations, vocabulary games. http://www.macmillanmh.com EBooks: teacher and student books http://connected.mcgraw-hill.com/connected