Nervous System Review Sheet: Anatomy & Physiology
advertisement

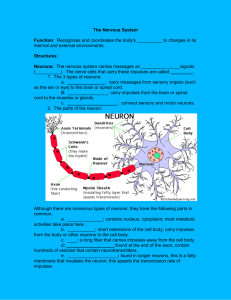
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 6 Nervous System Review Sheet Name ______KEY_______________ Date ______________ Hr _______ 1. What are the three major overlapping functions of the nervous system? a) Sensory input—information gathered from stimuli inside and outside the body b) Integration—processes and interprets sensory input and decides what should be done c) Motor output—response performed by activating muscle or glands 2. What are the two major divisions of the nervous system? What does each include? Central Nervous System (CNS)—consists of brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)—consists of nerves that extend from brain and spinal cord 3. The main portion of a nerve cell is called the __cell body_________________. 4. What other cell parts are housed in this main area? nucleus, nucleolus, all other cellular organelles 5. The nerve processes that conduct the impulse/action potential away from the cell body are called ___axons___________. 6. The part of a nerve cell that receives impulses and carries them toward the cell body is called a/an _____dendrite________. 7. ____motor/efferent____ neurons conduct impulses away from the CNS. 8. ____sensory/afferent____ neurons conduct impulses to the CNS. 9. The white fatty substance around the neurons that speeds up impulse transmission is called ____myelin sheath_________. 10. A self-propagating wave of electrical negativity that travels along the surface of the neuron membrane is called a/an ___action potential_______. 11. Indentations between the Schwann cells/myelin sheaths are called the __Nodes_ of _Ranvier__. 12. Nerve cells are also known as ______neurons_____. 13. Chemical compounds released from the synaptic knobs of axon terminals into synaptic clefts to carry impulses across the synapse are called ____neurotransmitters__________. 14. The gap or space between the dendrites of receiving neurons and the axon of sending neurons is called the ______synaptic cleft/synapse_______. 15. The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and ___spinal cord____________. 16. Stimulating a nerve cell increases the permeability of the membrane to ___sodium________ ions. 17. The movement of sodium through the membrane into the cell creates a __positive____ charge inside and a ___negative____ charge outside the membrane. 18. List the 4 types of neuroglial cells and their functions. a. Astrocytes—form a living barrier between capillaries and neurons, make exchanges between them b. Microglia—phagocytes that dispose of (eat) debris, such as dead brain cells, bacteria, etc. c. Ependymal cells—line cavities of brain & spinal cord, cilia circulate cerebrospinal fluid, cushions CNS d. Oligodendrocytes—in CNS, produce myelin sheaths (fatty insulating coverings) around neurons (Schwann cells do this in PNS) Match the following: 19. Axon __C___ 20. Dendrite __B___ 21. Depolarization _D____ 22. Repolarization __E___ 23. Myelin __A___ 24. Dura mater __A__ 25. Pia mater __C__ 26. Arachnoid __E__ 27. CSF __B__ 28. Ventricles __D__ 29. Synaptic vesicles __C___ 30. Choroid plexus __A___ 31. Corpus callosum __B__ 32. Brain stem __D___ 33. Cerebrum __B___ 34. Cerebellum __D___ 35. Medulla oblongata __C___ 36. Diencephalon __E___ 37. Spinal cord __A___ a. b. c. d. Insulates the axon. Receives the nerve impulse. Sends the nerve impulse to the next neuron or effector. The process of positive ions moving across the neuron membrane by facilitated diffusion, and generating an action potential. e. The process of ions moving across the neuron membrane by active transport and thereby restoring the electrical potential of the neuron. a. b. c. d. e. Thickest, most outer membrane layer. Cushions, provides nutrients, and removes waste. Innermost membrane layer that adheres to the brain or spinal cord. Space within the brain where cerebrospinal fluid circulates. Middle, spider web-like membrane layer. a. Produces cerebrospinal fluid. b. A deep bridge of nerve fibers that connects the cerebral hemispheres. c. Release neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine. d. Consists of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. a. Serves as the center for spinal reflexes. b. Provides higher mental functions, including memory and reasoning. c. Controls vital functions such as respiration and heart rate. d. Regulates posture, maintains balance, and coordinates complex skeletal muscle movements. e. Central relay station for incoming sensory impulses, and maintains homeostasis. 38. What is the difference between an afferent/sensory system and the efferent/motor system? Afferent/sensory—nerve fibers that convey impulses to the CNS Efferent/motor—nerve fibers that carry impulses from the CNS to effector organs, muscles, & glands 39. The _Parasympathetic____ division dominates control of many visceral organ effectors under normal, everyday conditions. 40. The _Sympathetic__ division serves as the emergency or stress system (fight or flight) in the body. 41. What is the difference between multipolar, bipolar, and unipolar neurons? Multipolar—contains several processes extending from the cell body, most common type Bipolar—contains two processes, an axon and a dendrite Unipolar—contains a single process extending from the cell body that then branches in two directions 42. List the 4 major portions of the brain: a. Cerebrum (cerebral hemispheres) b. Diencephalon c. Brain stem d. Cerebellum 43. What is the major difference between gray matter and white matter in the CNS? Gray matter—contains mostly unmyelinated fibers and cell bodies White matter—consists of dense collections of myelinated fibers (tracts) 44. The __corpus callosum_____ connects the two hemispheres of the brain. 45. The cerebrum is divided into lobes and the two halves are called _______hemispheres___________. 46. The largest part of human brain is the _______cerebrum (cerebral hemispheres)_____________ . 47. The inferior portion of the brain stem that joins the spinal cord to the brain and contains the reflex centers for heartbeat, respiration, and blood pressure is called the ______ medulla oblongata______. 48. The ridges or convolutions of the cerebrum are called _________gyri____________. 49. The second largest part of brain, which controls coordination, is called the ________cerebellum__________. 50. The three major structures that make up the diencephalon are: epithalamus, thalamus, hyopothalamus 51. What are the functions of the hypothalamus? Important autonomic nervous system center, plays role in regulation of body temperature, water balance, and metabolism 52. Why is cerebrospinal fluid important to the brain and the spinal cord? Watery fluid that circulates through the brain and spinal cord, formed from blood, functions as a watery cushion to protect the nervous tissue from blows and other trauma 53. What is the importance of the blood-brain barrier? Maintains the internal environment of the brain by not letting wastes, toxins, proteins, and drugs enter the brain. Only water, glucose, fats, gases, and essential amino acids can pass through the capillaries that form this barrier Diseases/Developmental Aspects of the Nervous System 54. What is Alzheimer’s and what causes it? Alzheimer’s is a progressive degenerative disease of the brain usually seen in elderly people that results in dementia (mental deterioration), memory loss, mood swings, confusion, violence, and hallucinations. It is caused by abnormal protein deposits and twisted fibers within neurons and localized brain atrophy (shrinkage). 55. What is a cerebrovascular accident? What is it also called? What causes it? A cerebrovascular accident (CVA), also called a stroke, is a form of brain damage caused when blood circulation to the brain is blocked due to a blood clot or ruptured blood vessel and part of the brain tissue dies. Label the following diagrams: Label the Diagram with the areas of the brain and Match the following functions: 1. __E___ Regulates balance, movement & coordination. 2. __D___ It controls vital functions such as heartbeat, breathing, etc. 3. __A___ Center of vision and reading ability; conscious seeing. 4. __C___ Center of intellectual processes; reasoning, emotions; translation of thought patterns into speech. 5. __B___ This region is involved in the interpretation of auditory sensations. Involved with olfaction, language, and emotional behavior. Match the structure/description with the correct letter from the diagram below: 1. __A___ Neuron cell bodies/unmyelinated fibers 2. __C___ Gyri 3. __B___ Myelinated axons 4. __D___ Sulcus