Population
advertisement

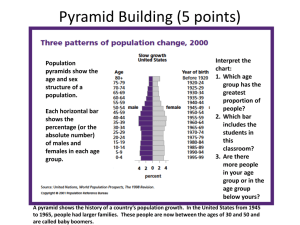
Population Chapter 2 National and World Population http://www.census.gov/main/www/popclock.html Where in the World do People Live and Why? World Population Distribution and Density East Asia - ¼ of world population here South Asia - bound by the Himalayas and a desert in Pakistan Europe - population is concentrated in cities North America - megalopolis A Population Bomb? Malthus (early 1800s) worried about population growing exponentially and resources growing linearly. (1960s) warned of a population bomb because the world’s population was outpacing food production. Alternative Views of Population Growth Julian Simon- argued that increasing wealth and technology make more resources available Ester Boserup- argued that the more people there are, the more hands there are to work. As population increases, more pressure is placed on the existing agricultural system, which stimulates invention. Ehrlich/Simon Wager 1980 they bet over price of copper in 10 years Ehrlich said it would go up, Simon said it would go down Population increased 800 million- largest increase ever at that point Simon won Ehrlich Doubling Time population 1804– reached 1 billion 1927- 2 billion 1960- 3 billion 1975- 4 billion 1983- 5 billion 1999- 6 billion 2011- 7 billion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4BbkQiQyaYc RNI Currently about .6% in USA Currently about 3% in Burkina Faso Currently about .02% in Japan The higher the RNI the faster the population is growing. A negative RNI means the population is decreasing TFR The higher the TFR the faster the RNI. 2.1 is replacement TFR TFR TFR TFR in USA is about 2 in Japan is about 1.4 in Burkina Faso is 6.4 Why do you think women in some countries have fewer children than in other countries? Population Growth in India Significant demographic variations occur within countries. In India, growth rates are higher in the east and northeast. Why do Growth Rates Vary in India? 1960s population planning program 1970s country began forced sterilization program for men with 3 or more children. 22.5 million men were sterilized. Why do Growth Rates Vary in India? 2004 state of Uttar Pradesh began guns for sterilization program. Today, most states use advertising and persuasion to lower birth rates. Birth Rate Higher birth rate means higher population growth USA Birth rate is 14 Burkina Faso’s birth rate Japan’s birth rate is 8 is 45 Death Rate USA’s death rate is 8 Japan’s death rate is 9 Burkina Faso’s death rate is 15 Why do you think these vary in the way they do? Demographic Transition Model The Demographic Transition in Great Britain Studied the change in birth rates, death rates, and natural growth rates over the course of British industrialization. Found a transition occurred when death rates decline and then birth rates decline, resulting in a low or sustained growth rate. The Demographic Transition Stage 1: Low Growth Stage 2: High Growth Stage 3: Moderate Growth Stage 4: Low Growth or Stationary Stationary population level (SPL)? Why does Population Composition Matter? Population Composition Population Composition is concerned with: Gender distribution Age distribution within a country, region, or place. Population Pyramids for Poor Countries Population Pyramids for Wealthy Countries Infant Mortality in the United States Age Structure of a Population The populations of many countries are aging. - eg. Europe - eg. Japan Aging Populations To replace the population, TFR must be 2.1. TFR in Bologna, Italy is 0.8 Why are women having fewer children? What What are the impacts of an aging population on a country? are the “solutions” to an aging population? How do Governments Affect Population Change? Government Population Policies Expansive Population Policies - Encourages population growth. Eugenic Population Policies - Favors one racial or cultural sector over others. Restrictive Population Policies - range from toleration of unapproved birth control to outright prohibition of large families. China’s One Child Policy