Human Population Dynamics
advertisement

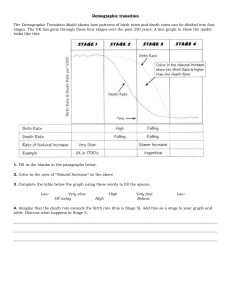
Human Population Dynamics How do populations change • Immigration – movement of people or species into a population • Emmigration – movement of people or other species out of a population ** In general these are not significant factors in population size& DO NOT affect global population *** Fertility Rates • Replacement level fertility (RLF) – Number of children a couple must have to replace themselves – 2.1 in developed countries (DCs) 2.5 in some lessdeveloped ones (LDCs) – Have to take infant mortality into account • Total Fertility Rate The number of children a woman will bear during her lifetime. • Total Fertility Rate is decreasing globally however world population is still increasing. *** TFR = most significant addition to human population****** Projected Birth Rates by Region World Population Growth Rate Goal • Total fertility rate = replacement rate • Still does not equal zero population growth because of people living longer Factors that affect the growth rate of Human Populations Anything that impacts TFR (total fertlility rate) impacts population growth. Examples> Availability of birth control Demand for children in the labor force Urbanization (rural communities have children for labor) Base level of education for women Religious beliefs, customs and traditions You do • Identify and describe two factors that affect TFR • Explain the difference between TFR and RLF Factors not related to TFR that affect population DEATH RATE ALSO AFFECTS population!!!! The reason the worlds population has grown in the past 100 yrs is due more to later death rate than higher birth rate Why are people living longer? • Industrial Revolution improved standard of living • Clean water • Better sanitation (fewer diseases) • Dependable food supply • Better health care 2 generalization about population • The more industrialized or developed the nation the longer the life span • Overall health of a population can be estimated by looking at lifespan AND mortality rate of infants. Life span: Afghanistan = 44yrs. Japan = 80yrs Infant Mortality: Afghanistan=121/1000 US= 6/1000 Age Structure pyramids Demographic Transition Model Used to predict population trends based on birth and death rates of a population. • Environmental Resistance- anything that slows a population’s growth – such as harsh living conditions, lack of clean water, lack of medical care etc. Zero population growth occurs when either: a. High birth rates and high death rates b. Low birth rates and low death rates. Demographic Transition - When a population moves from situation a- to situation b There are 4 stages that occur before a demographic transition happens!! 1. • • • • Pre Industrial StateSlow growth High birth rate High death rate Harsh living conditions 2. Transitional State• RAPID population growth • High birth rates • Lower death rates due to food, clean water, and improved health care 3. Industrial State: • SLOW population growth • Birth rate drops • Birth rate and death rate are close but not equal • *** Developing countries are in this state** 4. Post Industrial State • Population approaches or reaches zero population growth!!!! • Populations can drop below zero population growth (negative growth) (russia) Homework questions • Describe in your own words the stages of the demographic transition model • What stage has high birth and low death? WHY • Why do countries tend towards zero population growth when industrialization occurs? Identify and describe 2 reasons. Endangered/extinction • • • • • One reason so many big cats are endangered Habitat destroyed Prey dies Predator has no food Species without food go extinct