Human Population chapter 13
advertisement

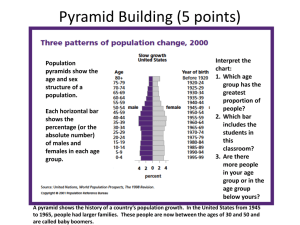
“People are everywhere. Some people say there are too may of us; but no one wants to leave” What is the Earth’s carrying capacity? Present population is 7 billion Many believe the Earth can support 4-16 billion, others up to 50 billion Changes in technology, improvements in food production and medicine plus the fact that humans can determine the number of children they have, make measuring the planet’s carrying capacity difficult For most of our history, humans were hunter- gatherers, and these populations remained small. About 10,000 years ago, people began to raise animals and grow crops. (Agricultural Revolution) Agriculture allowed people to produce more food than they could gather, and to be able to store the excess. Farming increased the earth’s carrying capacity! The human population then began to grow as more was available and people had more children to help with the farming. The human population reached 1 billion around 1800. Number of years to add 1 billion people First billion Second Third Fourth Fifth Sixth Seventh Eitgth year 1800 1930 1960 1975 1987 1999 2012 2026 years to add all of human history 130 30 15 12 12 13 14 Demography The study of human population patterns There are 3 stages of demographic transition Stage 1 reflects preindustrial societies in which the population grows slowly. Both birth and death rates are high Stage 2 reflects an increasing population due to improved health care. Death rates fall and birth rates remain high. This is seen in developing countries such as Mexico, Bangladesh, and Ethiopia. Stage 3 shows a slowing of population growth as birth rates fall. This is typical of a more developed country. Population Pyramids (histograms) are one way to illustrate population growth. Age structure categories Pre-reproductive ages (0-14) Reproductive ages (15-44) Post-reproductive ages (45-over) Males vs. females We Can Use Age-Structure Information to Make Population and Economic Projections Baby boomers Job market when they retire-job shortage The Fastest Growing Age Group Is… SENIORS! The global populations of seniors is projected to triple by 2050 in which 1 of every 6 people will be 65 or older. This graying of the population is due to declining birth rates and longer life expectancies due to medical advancements. The world’s population is increasing at a growth rate of 1.09% So, what does a 1.09% growth rate mean? There were about 83 million people added to the earth in 2010 Which is about 227,000 people every day Which is 2 more people every time your heart beats Women Having Fewer Babies but Not Few Enough to Stabilize the World’s Population Total fertility rate (TFR)- avg. # of kids TFR in 2010: 1.7 per woman in developed countries 2.7 per woman in developing countries born to a woman during reproductive years. Where are populations growing? in developing countries their population is increasing 15 times faster than developed countries By 2050, 97% of growth will be in developing countries Growth Rates and TFR US= 0.96% China= 0.49% Japan= -0.278% Mexico= 1.1% Ethiopia= 3.2% Zimbabwe = 4.31% Niger= 3.6% 2.0 1.5 1.2 2.3 6.0 3.6 7.6 From 1972- 2010, TFR in developing countries dropped from 6.2 to 2.7 and in developed countries, from 2.8 to 1.7 In China, the TFR dropped from 5.7 to 1.5 (from 19722010) Life Expectancy Increased globally from 47 to 69 years from 1955- 2010. by 2050…74 years Japan has longest life expectancy of 83 and US is 78 (50th of all nations) Angola has shortest life expectancy of 39 years. Why are people living longer? Increased food supply and distribution Better nutrition Medical advances Improved sanitation Why do growth rates increase? Immigration, decline in death rate, high TFR Most poor couples believe they need several children to work and care for them in old age Cultural preference for male children Only 48% use some form of birth control Why Do Growth Rates Decrease? Emigration- religious and political freedom, economic improvement, wars Death and Disease- HIV/AIDS Higher education levels, medical care, sanitation Problems Related To Population Growth 1. Shortage of resources Water- diseases such as cholera, typhoid and dysentery and death related to dirty water Fuelwood- many foods need to be cooked and water is sterilized by boiling 2. Urban Crisis People move to cities for work and education Not enough infrastructure- schools, medicine, fire stations, roads… • 3. Social unrest Civil wars and disputes between nations • 4. Environmental refugees Environmental changes can cause people to leave their homes Drought, floods, earthquakes Should population problems be solved? Countries with stable populations can better provide services such as education and health care. Environmental damage is decreased Families are healthier when a mother bears children after age 20, has no more than 3 children and they are spaced apart Bangladesh- TFR dropped from 6.0 in 1960 to 2.7 in 2010. Family planning and economic development are responsible for the drop. Thailand’s TFR dropped from 6.4 to 1.8 The best way to slow and stabilize population growth are through 1. promoting economic development 2. elevating the social and economic status of women 3. Encouraging family planning Empowering Women Can Slow Population Education Paying jobs Women account for 2/3 of all hours worked, but only get 10% of world's income Human rights without suppression “For poor women, the only holiday is when you are asleep” Women Make up 70% of the world’s poor 64% are illiterate (and 5-7 children) 60-80% of work associated with growing food, gathering wood and hauling wood and water In most societies, they have fewer rights and educational and economic opportunities (Sharbat Gula 1985 and 2002) (Afghanistan refugee who crossed over into Pakistan What is really the problem? Overpopulation? This is degrading our planet. (82% of population is in less developed nations) Overconsumption? Americans ecological footprints are 4.5X larger than the average Chinese and 9.5 times larger than the average Indian If the world had 100 people… http://www.100people.org/statistics_detailed_statistic s.php?section=statistics