Field of subject: Textual Analysis / Genres
advertisement

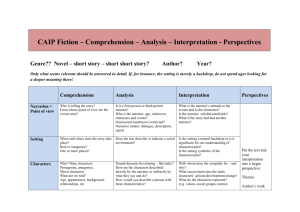
Field of subject: Textual Analysis / Genres We have read some texts about: Textual analysis o The purpose of textual analysis is to open the text, to make it say more than it does at first glance o Important norms Your observations ad conclusions must be based on what is actually said in the text Your arguments and conclusions must be logically coherent so that others can check your line arguments. You must use terms and concepts that are generally understood and accepted o Genre The genre explains the literary form; Novel o Extended fictional prose narrative o Several characters o Distinct plot Short story o Relatively short fictional narrative written in a prose form o 500 words to 20,000 word (long short story) o Deals with single events o Having a well-defined opening, a middle section and an ending o Few characters o The plot takes place within a short period of time Poem o Compact, powerful, concrete language o Usually presents Truth Emotion Beauty through rhythmic and orderly arrangement Autobiography o The story of a person’s life written by him or herself o Diaries o Journals o Letters Biography o The story of a person’s life o Written by another person Drama o A creatively constructed story o Acted out on a stage Essay o A short prose piece of writing which focuses upon a specific topic o Usually written in a opinionated manner The genre raises certain expectations with the reader. The reason why there are so many different kinds of genres is because it varies what the categories are based upon Classified by form Classified by layout + style Classified by content and theme Have to be conscious about the genre The author can trick you, you think you are reading an autobiography but actually you are not. o Composition Analysis of the composition of a complex text makes it easier for you too understand the text o Plot o The structure of the action in the text Why do things happen the way they do? Why does the text end as it does? o Rewriting Setting Time Place Environment Concrete: London General: A big city, once upon a time o Characters Main character Subordinate characters Types of characters Round: Complicated personalities (real people) o You don’t know what do expect Flat: You know them after a brief introduction o They won’t do anything surprising Types of characterisation Direct o What the narrator tells us about a character Indirect o What we don’t get told but what we can conclude from the character’s language, behaviour, thought, relations to other etc. o Point of View Through whose eyes do we see what is going on? Who is the narrator (first person/ third person)? Omniscient narrator moves freely in time and place and can comment on the persons thoughts etc. Omniscient narrator – limited, only has focus on a single person and only tells about the persons thoughts, feelings etc. External observation – we don’t hear about the characters feelings etc. (third person) First person – we see and hear the story to a first person narrative o Themes The themes of a text are the issues or problems which the text deals with Love Hate Violence etc. o The Message What is the message of the text What does it try to make you see, understand etc? o Love is good o You shouldn’t hate your family o You shouldn’t not commit violent crimes against other peoples The Lottery Flowers for Algernon