ELEMENTS OF FICTION
advertisement

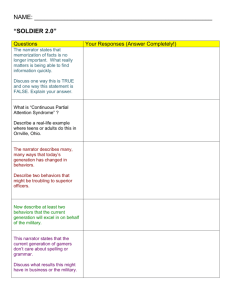
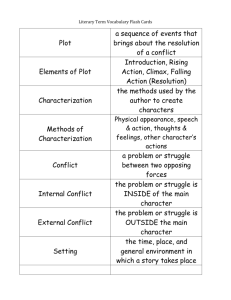
ELEMENTS OF FICTION character- a person, animal, or imaginary creature who takes part in the action of a story. A) main- a character whom the story revolves around. B) minor- a character who helps the story move along. 1) static- a character who does not change in the course of a story. 2) dynamic- a character who changes as a result of the story’s events. conflict- a struggle or clash between two or more opposing characters or forces. A) external- a struggle against any outside force. B) internal- a struggle between opposing needs, desires, or emotions within a character’s mind. 1) man vs. man 2) man vs. self 3) man vs. nature 4) man vs. society 5) man vs. technology 6) man vs. supernatural dialogue- a conversation between two or more characters. fiction- a prose account that is created or imaginary rather than true. flashback- an interruption in the action of a plot to tell what happened at an earlier time. foreshadowing- the use of clues to suggest events that will happen later in the plot. irony- a contrast between expectations and reality. A) verbal- a contrast between what is said or written and what is meant. B) situational- occurs when what happens is very different from what is expected to happen. C) dramatic- occurs when the audience or the reader knows something a character does not know. mood- the overall emotion created by a work of literature. novel- a fictional story that is usually between 100-500 book pages long. personification- a figure of speech in which a nonhuman thing or quality is given human qualities or characteristics. point of view- the vantage point from which a story is told. A) third person omniscient- “all-knowing”, the narrator knows everything about the characters and their problems. B) third person limited- the narrator focuses on the thoughts and feelings of only one character. C) second person- the main character, the narrator is “YOU”. Usually restricted to choose your own adventure stories. D) first person- the narrator, one of the characters, using the personal pronoun “I”, is telling the story. plot- the series of related events that make up a story. This is the actual events, the “what happens” in a story. storyline- the general pattern that every story takes. A) exposition- the introduction; characters are introduced, setting is established, conflicts begin. B) complications- problems that arise within the story. C) climax- the most emotional, interesting, exciting, or suspenseful point in a story. D) resolution- the conclusion; problems are solved & the story ends. setting- the time and place in which the events of a story take place. A) time- past, present, or future; day or night; any season. “when” B) place- real or imaginary. “where” short story- a fictional prose narrative that is usually 10-20 pages long. suspense- the uncertainty or anxiety the reader feels about what will happen next in a story. tone- the attitude a writer takes toward the audience, a subject, or character. theme- the idea about life revealed in a work of literature. the main message a writer wishes to share with the reader. It may be a lesson about life or a belief about people and their actions. WHAT LESSON CAN BE LEARNED???