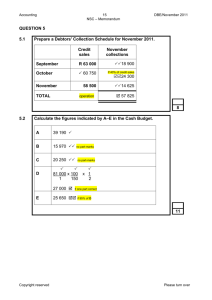
chap-1 -Final accounts with adjustment
advertisement

www.Padasalai.Net Sri Vidhya Nikethan Matric Higher Secondary Sechool, Varadhapampalayam. [chap-1 -Final accounts with adjustment][ 5 marks] q.no.38 1.Commission received given in Trial Balance Rs 1,000 as on that date 31.12.1994.Commission accrued but not received Rs 150,Show the adjusting entry and how will appear in the final accounts. 2.Give adjusting entry and transfer entry for Interest on capital Rs 6,000 3.Give adjusting entry and transfer entry for bad debts Rs 5,000 4.Rent Received is shown in the Trail balance as on 31.12.2003 Rs 10,000.Rent received in advance is Rs 1,000.You are required to show how it appears in the profit and Loss a/c and balance sheet. 5.The Trial Balance shows the following as on 31.03.2006 Bank loan @ 10% [on 01.04.2005] Rs 3,00,000 Interest paid Rs 10,000 Provide for interest on bank loan outstanding pass adjusting entry and how will appears in the final accounts. 6.Give adjusting entry and transfer entry for interest on drawings Rs 3,000 7.As per Trial Balance Capital is Rs 9,00,000 drawings Rs 80,000 Adjustment; Calculate interest on drawings @6% p.a pass adjusting entry and transfer entry 8.Trial Balance as on 31.3.2007 shows Rent received Rs 30,000.Rent received in advance Rs 6,000 Pass adjusting entry 9.Give adjusting and transfer entry for interest on capital Rs 5,000 10.Commission Received given in Trial Balance is Rs 5,000 as on 31 st December 2006 Commission accrued but not yet received is Rs 150 Show the adjusting entry. 11.As per 31.3.2005 Trial Balance bank loan @ 10% Rs 8,00,000 Interest paid Rs 50,000 Adjustment: Provide for interest on bank loan outstanding .Pass adjusting entry and show how will this item appear in the final accounts. 12.Give adjusting entry and transfer entry for interest on drawings: Rs 2,000 13.Give adjusting and transfer entry for write off bad debts Rs 3,000 14.Pass adjusting entry and transfer entry for interest on drawings Rs 10,000 15.Give adjusting entry and transfer entry for bad debts Rs 2,500 16.As per The Trial balance Capital as on 31.12.2005 is Rs 90,000.Adjustment:Provide 6% interest on capital pass adjusting entry and transfer entry. www.TrbTnpsc.com www.Padasalai.Net 17.Giving adjusting entry and transfer entry for write off bad debts Rs 10,000 18.Give adjusting entry and transfer entry for Depreciation at 10% per annum on Machinery of Rs 25,000 19.The Trial balance 31.3.2005 shows Rs 40,000 as Insurance premium paid. Unexpired insurance premium Rs 5,000.pass adjusting entry and show how this item will appear in the Profit and loss account and Balance sheet. 20.Trial balance as on 31.3.2005 show rent received Rs 30,000 Rent received in advance Rs 6,000. Pass adjusting entry and show how this item will appear in the Profit and loss account and Balance sheet. 21.As per Trial balance 31.3.2005 capital is Rs 6,00,000.provided 6% interest on capital. pass adjusting entry and show how this item will appear in the Profit and loss account and Balance sheet. 22.The Trial Balance shows the following as on 31.03.2006 Bank loan @ 10% [on 01.04.2005] Rs 10,00,000 Interest paid Rs 60,000 Provide for interest on bank loan outstanding pass adjusting entry and how will appears in the final accounts. 23.Rent received shown in the Trial balance as on 31st December 2001.Rs 10,000.Rent received in advance is Rs 1,500.You are required to show how it appears in the profit and Loss a/c and balance sheet. 24.How will the following adjustment appear in the balance sheet as on 31.12.2000 Sundry debtors Rs 21,000 bad debts to be written off Rs 1,000 Adjustment: Provide @ 5% provision for bad and Doubtful debts and 2% provision for discount on debtors. 25.The Trial balance as on 31.3.2003 show sundry debtors Rs 60,000.Write off bad debts Rs 4,000.pass adjusting entry and show how this item will appear in the Profit and loss account and Balance sheet. 26.The Trial balance shows the value of Furniture on 31.3.2009 as Rs 60,000.Adjustment; Furniture is to be depreciated at 10% .Give adjusting entry and Transfer entry. 27.The Trial Balance shows the following as on 31.03.2008 Bank loan @ 10% [on 01.04.2007] Rs 4,00,000 Interest paid Rs 14,000 Provide for interest on bank loan outstanding pass adjusting entry and how will appears in the final accounts. 28.Give journal entry and transfer entry for interest on drawings Rs 6500 www.TrbTnpsc.com www.Padasalai.Net 29.Give journal entry and transfer entry for interest on drawings Rs 6000 12 marks: (q.no.45 a compulsory sums) 1.The following balances have been extracted from the Trial balance of Mr. Ashok as on 31.3.2002 Trail balance as on 31.3.2002 particulars Debit Rs Credit Rs Debtors Bad debts 2,01,200 1,200 - Adjustments: 1.Write off additional bad debt of Rs 5,000 2.Create provision of 10% for bad and doubtful debts on debtors 3.Create provision of 2% for discount on debtors Give necessary adjustment entries and show how these items will appear in the Profit and Loss account and Balance sheet. 2.The Trial Balance show on 31.3.2009 as follows Sundry debtors Rs 85000 Adjustment: 1.Write off bad debt of Rs 5,000 2.Create provision of 5% for bad and doubtful debts on debtors 3.Create provision of 2% for discount on debtors Give necessary adjustment entries and show how these items will appear in the Final accounts 3.The Trial Balance show on 31.3.2007, Sundry debtors Rs 78,000 Adjustment: 1.Write off bad debt of Rs 8,000 2.Create provision of 5% for bad and doubtful debts on debtors 3.Create provision of 2% for discount on debtors Give necessary adjustment entries and show how these items will appear in the Final accounts 4.The following items are found in the Trial Balance Of Mr.Kumar as on 31.3.2004 Sundry debtors Rs 64,000 Bad debts Rs1,200 Adjustment: 2.Create provision of 5% for bad and doubtful debts on debtors Give necessary adjustment entries and show how these items will appear in the Final accounts 5.The Trial Balance show on 31.3.2007 as follows Sundry debtors Rs 52,000 Adjustment: 1.Write off bad debt of Rs 2,000 2.Create provision of 5% for bad and doubtful debts on debtors 3.Create provision of 2% for discount on debtors www.TrbTnpsc.com www.Padasalai.Net Give necessary adjustment entries and show how these items will appear in the Final accounts 6.The Trial Balance shows Sundry debtors as Rs 1,25,000 ,bad debts Rs 4,000 as on 31.3.2003 Adjustment: 1.Write off bad debt of Rs 5,000 2.Create provision of 5% for bad and doubtful debts on debtors 3.Create provision of 1 ½ % for discount on debtors Give necessary adjustment entries and show how these items will appear in the Final accounts 7.The Trial balance shows as on 1st December 2006 Sundry Debtors-Rs 10,500 Adjustment: 1.Bad debts to be written off Rs 500 2.provide 5% provision for bad and doubtful debts 3.@ 2% provisions for discount on debtors pass the journal entries and show how they appear in the final accounts. 8.The Trial balance shows on 31.3.2005 Sundry debtors -Rs 56,000 Adjustment: 1.Write off bad debt of Rs 6,000 2.Create provision of 5% for bad and doubtful debts on debtors 3.Create provision of 2% for discount on debtors Give necessary adjustment entries and show how these items will appear in the Final accounts 9.The Trial Balance shows on 31.3.2006 Sundry Debtors Rs 1,50,000.provide 5% provision for bad and doubtful debts on Sundry debtors .Pass adjusting entry and show how this item will appear in the final accounts. 10.Following are the balances extracted from the Trial balance of Mr. Raveendran as on 31.3.2005 Rs Sundry debtors 65,000 Bad debts 2,500 Provision for bad and doubtful debts 1,500 Adjustment: 1.Write off bad debt of Rs 1,500 2.Create provision of 3% for bad and doubtful debts on debtors Give necessary adjustment entries and show how these items will appear in the Final accounts 11.The Trial balance shows on 31.3.2006 as follows; Sundry debtors Rs 1,00,000 Adjustments: 1.Bad debts to be written off Rs 10,000 2.Provision for bad and doubtful debts be created at 5% 3.Provide discount on debtors at 2% www.TrbTnpsc.com www.Padasalai.Net Pass adjustment entries and show how these items will appear in the Final accounts 12.The following are the balances extracted from the Trial balances of Kumar as on 31.3.2002 Trial balance as on 31.3.2002 particulars Sundry debtors bad debts Provisions for bad and doubtful debts Debit Rs 1,20,000 10,000 - Credit Rs 20,000 Adjustment: Create Provision for bad & Doubtful debts @ 5% on Sundry Debtors 13.The Trial Balances shows on 31.3.2004 Sundry debtors Rs 41,500 Bad debts Rs 1,000 Adjustments: 1.Write off bad debts Rs 1,500 2.Provide 5% for bad and doubtful debts 3.Provide 2% for discount on debtors pass adjustment entries and also how this item will appear in the final accounts. 14.The Trial Balance shows on 31.3.2003 Sundry debtors1,25,000 Adjustments; 1.Bad debts to be written off Rs 5,000 2.provision for bad and doubtful debts be created at 5% 3.Provide discount on debtors at 2% pass adjusting entries also show how these items will appear in the final accounts 15.The Trial Balance shows on 31.3.2005 Sundry debtors 65,000 Adjustments; 1.Bad debts to be written off Rs 5,000 2.provision for bad and doubtful debts be created at 5% 3.Provide discount on debtors at 2% pass adjusting entries also show how these items will appear in the final accounts 16.The Trial Balance shows on 31st March 2004 Sundry debtors Rs 2,20,000 Adjustments; 1.Bad debts to be written off Rs 20,000 2. provision for bad and doubtful debts be created at 5% pass adjusting entries also show how these items will appear in the final accounts 17.The Trial Balance shows on 31.3.2003 Sundry debtors Rs 2,00,000 and Bad debts Rs 10,000 Adjustments; 1.Bad debts to be written off Rs 5,000 2.provision for bad and doubtful debts be created at 5% 3.Provide discount on debtors at 2% pass adjusting entries also show how these items will appear in the final accounts www.TrbTnpsc.com www.Padasalai.Net 18.The Trial balance shows on 31.3.2008 as follows; Sundry debtors Rs 1,25,000 Adjustments: 1.Bad debts to be written off Rs 5,000 2. Provision for bad and doubtful debts be created at 5% 3. Provide discount on debtors at 2% Pass adjustment entries and show how these items will appear in the Final accounts 19. The Trial balance shows on 31.3.2005 as follows; Sundry debtors Rs 65,000 Adjustments: 1. Bad debts to be written off Rs 5,000 2. Provision for bad and doubtful debts be created at 5% 3. Provide discount on debtors at 2% Pass adjustment entries and show how these items will appear in the Final accounts 20. How will the following adjustment appear in the profit and Loss account and balance sheet as on 31.12.2006? Adjustment: Sundry debtors Rs 21,000 Bad debts to be written off Rs 1,000 Provide @ 5% provision for bad and Doubtful Debts and 2% provision for discount on debtors Give adjusting entries. 21. The Trial balance shows on 31.3.2008 as follows; Sundry debtors Rs 1, 25,000 Adjustments: 1. Bad debts to be written off Rs 5,000 2. Provision for bad and doubtful debts be created at 5% 3. Provide discount on debtors at 2% Pass adjustment entries and show how these items will appear in the Final accounts 22. The following balances have been extracted from the Trial balance of Mr.Ashok as on 31.3.2002 Trail balance as on 31.3.2002 particulars Debit Rs Credit Rs Debtors Bad debts 2,01,500 1,500 - Adjustments: 1. Write off additional bad debt of Rs 5,000 2. Create provision of 10% for bad and doubtful debts on debtors 3. Create provision of 2% for discount on debtors www.TrbTnpsc.com www.Padasalai.Net Give necessary adjustment entries and show how these items will appear in the Profit and Loss account and Balance sheet. 20 Marks (q.no.54) 1. From the following particulars taken from the books of Ganesh , prepare Final accounts for the year ending 31.3.1999 Trial balance as on 31.3.1999 Debit Balance RS Drawings Cash at bank Cash Wages Purchases Stock [1.4.1998] Buildings Debtors Bills Receivable Rent Commission General Expenses Furniture Credit balance 4,000 Capital 1,700 Sales 6,500 Creditors 1,000 2,000 6,000 10,000 4,400 2,900 450 250 800 500 40,500 Adjustment: 1.Stock on 31.3.1999 was Rs 4,000 2.Interest on Capital at 6 %to be provided 3.Interest on Drawings at 5% to beprovided RS 20,000 16,000 4,500 40,500 4.Wages yet to be paid Rs 100 5.Rent prepaid Rs 50 2.From the following Trial balance of Mr. Saravanan, Prepare Trading and Profit and Loss account for the Year ended 31st march 2009 and the Balance sheet as on that date: Trial Balance as on 31st march 2009 Debit Balance Cash in hand Cash at bank Drawings wages Purchases Opening stock Buildings Sundry Debtors Bills Receivable Commission General Expenses Insurance Adjustment: www.TrbTnpsc.com RS 45,000 20,000 30,000 15,000 60,000 50,000 1,00,000 85,000 20,000 8,000 10,000 7,000 4,50,000 Credit balance Capital Sundry creditors Sales Bills payable RS 2,00,000 50,000 1,70,000 30,000 4,50,000 www.Padasalai.Net 1.Closing stock Rs 30,000 2.Interest on capital 6% p.a to be provided 3.Depreciate Building by 10% 4.Outstanding wages Rs 2,000 5.Unexpired Insurance Rs 1,000 3.From the following Trial Balance of Mr. Imran as on 31st March 2005.Prepare Trading and profit and loss account for the year ending 31.3.2005 and balance sheet as on that date. Trial Balance as on 31st march 2005 Debit Balance RS Credit balance RS Purchase 1,50,000 Capital 3,00,000 Sundry debtors 80,000 Sundry Creditors 53,000 Investment 1,20,000 Sales 2,20,000 Rent 15,000 Commission received 7,000 carriage Inwards 10,000 Bills payable 20,000 Salaries 20,000 General Expenses 10,000 cash 30,000 Opening stock 75,000 Machinery 60,000 Drawings 30,000 6,00,000 6,00,000 Adjustment: 1.Clsoing stock Rs 1,00,000 2.Outstanding Rent Rs 2,000 3.Interest on capital at 6% is to be provided 4.Commission Received in advance Rs 1,000 5.Depreciate machinery at 10% p.a 4.The Trial Balance of Murugan as on 31.3.1994 is as follows Trial Balance as on 31st march 1994 Debit Balance Drawings Building Furniture & fittings Computer Interest on loan Loose tools Purchases Stock general expenses Freight inward Freight Outward Debtors Bank RS Credit balance RS 3,600 30,000 15,000 50,000 1,800 32,200 1,50,000 50,000 30,000 4,000 2,000 56,000 40,400 4,65,000 Capital Loan @ 6% Sales Commission received Creditors 2,00,000 30,000 2,00,000 15,000 20,000 Adjustment: 1.Closing stock Rs 64,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com 4,65,000 www.Padasalai.Net 2.Depreciate computer at 10% ,Buildings at 5% , Furniture and fittings 10% 3.provide interest in drawings at 6% and on capital at 6% Prepare Final accounts for the year ending on 31.3.1994. 5.From the following Trial Balance Of Mr. Arumugam ,Prepare Trading and Profit and loss account for the year ending 31.3.2003 and balance sheet as on that date: Trial Balance as on 31st march 1994 Debit Balance Cash in hand Cash at bank Drawings Wages Purchases Stock (01.04.2007) Buildings Sundry Debtors Bills Receivable Rent Commission general Expenses Furniture RS Credit balance 32,500 Capital 8,500 Sales 20,000 Sundry creditors 5,000 10,000 30,000 50,000 22,000 14,500 2,250 1,250 4,000 2,500 2,02,500 RS 1,00,000 80,000 22,500 2,02,500 Adjustment: 1.Closing stock was valued at Rs 20,000 2.Interest on capital at 6% is to be provided 3.Depreciated Buildings at 10% p.a 4.Wages yet to paid Rs 500 5.Rent prepaid Rs 250 6.From the following particulars taken from the books of Mr. Ganesh ,prepare Final accounts for the year ending 31.3.1999 Trial balance as on 31.3.1999 Debit Balance Drawings Cash at bank Cash Wages Purchases Stock [1.4.1998] Buildings Debtors Bills Receivable Rent Commission General Expenses Furniture Adjustment: www.TrbTnpsc.com RS Credit balance 40,000 Capital 17,000 Sales 65,000 Creditors 10,000 20,000 60,000 1,00,000 44,000 29,000 4,500 2,500 8,000 5,000 4,05,000 RS 2,00,000 1,60,000 45,000 4,05,000 www.Padasalai.Net 1.Stock on 31.3.1999 was Rs 40,000 2.Interest on Capital at 6 %to be provided 3.Interest on Drawings at 5% to be provided 4.Wages yet to be paid Rs 1,000 5.Rent prepaid Rs 500 7.From the following particulars taken from the books of Mr. Anbu , prepare Final accounts for the year ending 31.3.2006 Trial balance as on 31.3.1999 Debit Balance Cash in Hand Cash at bank Drawings Wages Purchases Opening stock Buildings Bills Receivable Sundry Debtors Commission General Expenses Insurance RS Credit balance 16,000 Capital 40,000 Sales 5,000 Sundry Creditors 4,000 25,000 37,000 1,50,000 13,000 87,000 4,000 11,000 8,000 4,00,000 RS 2,00,000 1,62,000 38,000 4,00,000 Adjustment: 1.Closing stock Rs 25,000 2.Outstanding wages RS 1,000 3.Unexpired Insurance Rs 2,000 4.Depreciate Buildings by 10% 5.Interest on Capital 6% p.a to be provided 8.From the following balances are extracted from the books of Mr. Kavin as on 31st march 2004 prepare trading account and Profit and loss account balance sheet as on that date: Trial balance as on 31.3.2004 Debit Balance General expenses Drawings Cash in hand Stock (1-4-2003) Furniture Purchases wages Insurance premium Salaries Sundry debtors Adjustment: 1.Closing Stock Rs 1,00,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com RS Credit balance RS 16,500 16,000 2,500 1,00,000 80,000 3,00,000 50,000 1,000 15,000 1,50,000 7,31,000 Capital Commission Bank over draft Sales Sundry Creditors Bills payable 1,20,000 11,000 25,000 5,00,000 50,000 25,000 7,31,000 www.Padasalai.Net 2.Wages yet to be paid RS 2,000 3.Commission accrued and not yet received Rs 1,000 4.Quarterly premium of Insurance is paid in advance 5.Depreciate furniture @ 10% 9.From the following Trial Balance of Mr. Karthick as on 31st March 2006 Prepare Trading account and Profit and loss account For the year ended 31.3.2006, And The balance sheet as on that Date; Trial balance as on 31.3.2006 Debit Balance Purchases Sundry Debtors Investment Rent Carriage Inwards Salaries General expenses Cash Opening stock machinery Drawings RS Credit balance RS 1,25,000 90,000 50,000 10,000 5,000 25,000 15,000 25,000 85,000 50,000 20,000 5,00,000 Capital Sundry Creditors Sales Commission Received Bills payable 2,50,000 60,000 1,60,000 10,000 20,000 5,00,000 Adjustment: 1.Closing stock RS 1,20,000 2.Outstanding Rent Rs 5,000 3.Commission Received in advance Rs 2,000 4.Depreciate machinery at 10% p.a 5.Write off Bad Debts Rs 2,000 10.From the following Trail Balance of Mr. Anand as on 31st March 2004,Prepare Trading account ,Profit and loss account for the year ended 31.3.2004 and the Balance sheet as on that date Trial balance as on 31.3.2004 Debit Balance Cash in hand Purchases Opening stock Sundry Debtors Plant & Machinery Furniture Bills receivable Rent & Taxes Wages Salaries Freight Inward Adjustment: www.TrbTnpsc.com RS 500 1,20,000 40,000 60,000 50,000 20,000 15,000 10,000 16,000 20,000 1,000 3,52,500 Credit balance Capital Bank loan @ 5% Bills payable Sales Sundry Creditors Interest RS 80,000 20,000 25,000 2,00,000 25,000 2,500 3,52,500 www.Padasalai.Net 1.Closing stock Rs 50,000 2.Provide for the following liabilities a]wages Rs 3,000 b]Salaries Rs 4,000 c]Rent & Taxes Rs 2,000 3.Depreciation on Plant and machinery @ 5% and Furniture 10% 4.Provide 5% interest on bank loan 5.Write off bad debts Rs 2,000 11.From the following Trial Balance of Mr.Ruso prepare the final accounts for the year ending 31.12.2005 Trial balance as on 31.3.2005 Debit Balance Cash in Hand Cash at Bank Drawings Wages Purchases Stock Buildings Sundry Debtors Rent General expenses RS Credit balance RS 65,000 Capital 2,00,000 17,000 Sales 1,60,000 40,000 Sundry Creditors 45,000 10,000 20,000 60,000 1,00,000 78,000 7,000 8,000 4,05,000 4,05,000 Adjustment: 1.Closing stock Rs 40,000 2.Interest on Drawings at 5% to be provided 3.Depreciate Buildings at 10% p.a 4.Write off bad debts Rs 1,000 5.Wages yet to be paid Rs 500 12.From the following Trial Balance of Mr.Abdul Hammed prepare the Final accounts for the year ending 31.12.2005 Trial balance as on 31.3.2005 Debit Balance Purchases Stock Buildings Sundry Debtors Rent General Expenses Cash in Hand Cash at Bank Drawings Wages Adjustment: 1.Closing stock Rs 40,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com RS Credit balance 60,000 Sales 1,80,000 Sundry Creditors 3,00,000 Capital 2,34,000 21,000 24,000 1,95,000 51,000 1,20,000 30,000 12,15,000 RS 4,80,000 1,35,000 6,00,000 12,15,000 www.Padasalai.Net 2.Interest on Drawings at 5% to be provided 3.Depreciate Buildings at 10% p.a 4.Write off bad debts Rs 4,000 5.Wages yet to be paid Rs 1,500 www.TrbTnpsc.com www.Padasalai.Net 31st 13.From the following Trial Balance Of Mr. Ashok as on March 2005 ,prepare Trading ,Profit and loss account and the Balance sheet as on that date Trial balance as on 31.3.2005 Debit Balance Purchases Sundry Debtors Investment Rent Carriage inwards salaries general expenses Cash opening stock Furniture Drawings RS Credit balance RS 75,000 80,000 35,000 10,000 5,000 20,000 15,000 15,000 80,000 45,000 20,000 4,00,000 Capital Sundry creditors Sales Bills payable Commission received 2,00,000 40,000 1,30,000 20,000 10,000 4,00,000 Adjustment: 1.Closing stock Rs 1,00,000 2.Outstanding salary Rs 2,000 3.Commission received in advance Rs 3,000 4.Depreciate Furniture at10% p. a 5.provide interest on capital at 6% p. a 14.From the following Trial Balance of Mr. Joseph prepare the final accounts for the year ending 31.12.2003 Trial balance as on 31.3.2003 Debit Balance Cash in hand Cash at bank Drawings Wages Purchases Opening stock Buildings Bills receivable Sundry debtors Rent Commission general expenses Insurance RS Credit balance 27,000 Capital 80,000 sales 10,000 Sundry creditors 8,000 50,000 75,000 3,00,000 25,000 1,75,000 5,000 8,000 22,000 15,000 8,00,000 Adjustment: 1.Closing stock Rs 50,000 2.Outstanding wages Rs 2,000 3.Prepaid Insurance Rs 5,000 4.Interest on Capital at 6% p.a to be provided www.TrbTnpsc.com RS 4,00,000 3,25,000 75,000 8,00,000 www.Padasalai.Net 5.Depreciate Buildings by 10% p.a 15.The following are the balances extracted from the books of Mrs.Thenmozhi as on 31.3.2006 Trial balance as on 31.3.2006 Debit Balance Drawings Cash in hand cash at Bank Wages Purchases Stock Buildings Sundry debtors Bills receivable Rent Commission General expenses Furniture RS Credit balance RS 40,000 17,000 65,000 10,000 20,000 60,000 1,00,000 44,000 29,000 4,500 2,500 8,000 65,000 4,65,000 Capital Sales Sundry creditors Bills payable 2,00,000 1,60,000 45,000 60,000 4,65,000 Adjustment: 1.Closing stock Rs 50,000 2.Interest On capital at 6% to be provided 3.Interest on Drawings art 5% to be provided 4.wages yet to be paid Rs 1,000 5.Rent prepaid Rs 900 Prepare Trading and Profit and loss account and balance sheet on 31.3.2006 16.The following are the balances extracted from the books of Mrs. Sundari as on 31st March 2006 Trial balance as on 31.3.2006 Debit Balance Furniture cash in hand Opening stock Purchases Investment @10% Drawings Salaries Insurance Rent Debtors Advertising General expenses RS 30,000 8,000 1,00,000 3,40,000 20,000 60,000 72,000 12,000 26,000 1,80,000 40,000 27,500 9,15,500 Adjustment: 1.Closing stock was valued at Rs 80,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com Credit balance Capital Commission Sales Creditors Interest received RS 2,00,000 14,000 6,00,000 1,00,000 1,500 9,15,500 2.provide for accrued interest on Investment Rs 500 www.Padasalai.Net 3.Commission received in advance Rs 4,000 5.provide an interest on capital @ 5% 4.Depreciation furniture by 10% Prepare Trading and Profit and loss account and balance sheet as on 31st March 2006 17.The following are the balances extracted from the books of Mr.Raja as on 31st March 2009 Trial balance as on 31.3.2009 Debit Balance Drawings cash in bank Cash in hand wages Purchases Stock Buildings Sundry debtors Bills receivable Rent General expenses Furniture RS 30,000 20,000 60,000 10,000 40,000 60,000 1,00,000 30,000 25,000 5,000 15,000 1,00,000 5,00,000 Credit balance RS Capital 2,00,000 Sales 1,10,000 Sundry creditors 50,000 Bank loan 1,00,000 Bills payable 40,000 5,00,000 Adjustment: 1.Closing stock Rs 50,000 2.Outstanding wages Rs 500 3.Interest on capital at 6% to be provided 4.Depreciate Buildings by 10% 5.Prepaid Rent Rs 1,000 Prepare Trading and Profit and loss account and Balance sheet as on 31st March 2009 www.TrbTnpsc.com Sri Vidhya Nikethan Matric Higher Secondary School, Varadhapampalayam. [chapter-2-Accounts from incomplete records –Single entry][ 5 marks]q.no39 1.calculate the missing information: Rs Profit made during the year 2,500 Capital at the end 6,000 Drawings 2,000 Capital at the beginning 1,200 2.Calculate the missing information: Profit made during the year 5,000 Capital at the end 12,000 Additional Capital 4,000 Drawings 2,400 Capital in the beginning ? 3.Find out profit or loss from the following : Opening capital 1,40,000 Closing capital 1,50,000 Additional capital 35,000 Drawings 10,000 4.Calculate the missing information: Drawings 50,000 Additional Capital 10,000 Opening capital 1,00,000 Profit made during the year 25,000 Closing Capital ? 5.Calculate the missing figure; Capital at the beginning Rs 60,000 Capital at the end Rs 80,000 Profit made during the year Rs 32,000 Additional capital Introduced Rs 10,000 Drawings ? 6.Calculate the missing figure: Capital at the end 12,000 Profit made during the year 5,500 Capital introduced during the year 4,000 Drawings 2,500 Capital at the beginning ? 7.From the following Find out the Total Sales Sundry Debtors (1-1-2005) 60,000 Cash received from sundry Debtors 90,000 Sales return 7,500 Closing (31.12.2005) Sundry Debtors 74,500 www.TrbTnpsc.com Cash Sales 65,000 8.Calculate the missing information; Closing capital 1,63,800 Additional capital 42,300 Drawings 25,200 Loss 12,600 Opening capital ? 9.Calculate the missing figure; Drawings 1,50,000 Additional capital 30,000 Capital in the beginning 3,00,000 Profit made during the year 40,000 Capital at the end ? 10.Calculate the missing information from the following: Profit made during the year Capital at the end Additional capital introduced during the year Drawings Capital in the beginning 11.Calculate the missing information: Drawings 55,000 Additional capital 10,000 Opening capital 1,20,000 Profit for the year 35,000 Closing capital ? 12.Find out profit or loss for the year; Opening capital 70,000 Closing capital 75,000 Additional capital 17,500 Drawings 5,000 13.Calculate the sundry debtors at the end: Opening sundry debtors 80,000 Total sales 3,20,000 Cash sales 40,000 Cash received from sundry debtors 1,56,000 Returns inwards 10,000 14.From the following details find out total purchases: Opening sundry creditors 1,50,000 Cash paid to sundry creditors 45,000 Discount received 30,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com 4,500 ? 4,000 2,400 9,600 Purchases returns 15,000 Closing sundry creditors 1,80,000 Cash purchases 80,000 15.From the following information , find out the total sales Sundry Debtors (1-04-2004) 50,000 Cash received from sundry Debtors 80,000 Sales return 5,000 Closing (31.03.2005) Sundry Debtors 75,000 Cash Sales 79,000 Discount allowed to debtors 2,000 16.Find out the profit or loss from the following: Opening capital 4,00,000 Closing capital 5,00,000 Drawings 90,000 Additional capital 30,000 17.From the following information calculate the missing information; Drawings 40,000 Additional capital 60,000 Opening capital 60,000 Profit during the year 50,000 Closing capital ? 18.Calculate the missing information: Capital at the end 80,000 Capital at the beginning 60,000 Profit for the year 32,000 Additional capital 10,000 Drawings ? www.TrbTnpsc.com [chapter-2-Accounts from incomplete records –Single entry][ 12 marks]q.no.45b 1.Mr Suresh started business with Rs 2,00,000 on 1.4.2003 .His books are kept under single entry. On 31.3.2004 his position was under Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Creditors 40,000 Cash 6,000 Bills payable 5,000 Cash at Bank 10,000 Outstanding expenses 7,500 Furniture 30,000 Plant & machinery 1,00,000 Debtors 50,000 Stock 90,000 Bills receivable 15,000 Ascertain Profit or Loss made by Suresh for the year ended 31.3.2004 2.Mrs.Sankari started business with Rs 1,50,000 as Capital as on 1.4.2006.During the year she has withdrawn at the rate of 3,000 per month. She introduced Rs 40,000 as additional Capital Rs Bank Balance 15,000 Stock 85,000 Sundry debtors 75,000 Machinery 45,000 Cash in hand 20,000 Sundry creditors 30,000 Prepaid expenses 4,000 She keeps her books under Single entry system Find out her Profit Or Loss for the year 2006-07 3.Mr.Anwar keeps his books by incomplete single entry. His assets and liabilities on 1.4.2006 and 31.3.07 stood as follows Cash in hand 1.4.2006 31.3.2007 Rs Rs 5,000 10,000 Sundry Debtors 70,000 85,000 Investment 30,000 30,000 Furniture 10,000 10,000 Sundry creditors 40,000 50,000 Stock 55,000 75,000 He introduced an additional capital of Rs 30,000.He withdrew fro Domestic purpose for Rs 50,000.Find out the Profit or Loss for the year 2006 -2007 www.TrbTnpsc.com 4.Raj keeps his books by single entry system .his position on 1.4.2003 and 31.3.2004 was as under; 1.4.2003 31.3.2004 Rs Rs Cash 500 6,000 Bank 10,000 15,000 Stock 7,000 10,000 Debtors 30,000 40,000 Furniture 6,000 6,000 Creditors 6,000 12,000 He introduced an additional capital of Rs 8,000 during the financial year. He withdrew Rs 14,000 for Domestic purposes . Find out the Profit or Loss for the year ended 31.3.2004 5.Mr.Sugan keeps his books by incomplete double entry. He started business with Rs 3,00,000 on 1.4.2005 On his position was as under: Cash in hand 8,000 Sundry creditors 50,000 Cash at Bank 20,000 Bills payable 10,000 Furniture 40,000 Outstanding expenses 8,000 Plant & machinery 2,00,000 Sundry debtors 1,50,000 Stock 1,50,000 Bills receivable 15,000 Additional Capital Rs 10,000 and drawings Rs 5,000 Ascertain the Profit or Loss for the year 2005-2006 6.Mr.Suresh Keeps his books by incomplete double entry system. He started business with Rs 1,10,000 on 1.4.2007.On 31.3.2008 his position was as under: Bank balance 20,000 Stock 30,000 Sundry debtors 70,000 Machinery 50,000 Cash in hand 10,000 Bills receivable 30,000 Sundry creditors 40,000 Bills payable 20,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com Outstanding Expenses 500 During the year he introduced Rs 35,000 as additional capital .he has withdrawn Rs 2,000 per month for his personal use. Find out his profit or Loss for the year 200708 7.The balances appear in Bharani’s books which are kept on single entry basis; Jan1,2001 Dec31.2001 Rs Rs Furniture 2,000 2,000 Stock 5,000 6,000 Sundry debtors 6,000 4,000 Cash 10,000 20,000 Sundry creditors 2,000 3,500 Bills receivable 1000 500 Loan(dr) 1,000 Investment 4,000 His drawings during the year were Rs 2,000 .Depreciate Furniture by 10% and provided a reserve for bad and doubtful debts at 5% on sundry debtors. Prepare a statement showing profit or Loss for the year 2001 8.Mohan maintain books on single entry. He gives you the following information Particulars Jan1,2006 Dec31.2007 Rs Rs Cash in hand 2,000 3,000 Cash at bank 1,000 2,000 Stock 16,000 18,000 Furniture 3,000 5,000 Sundry debtors 21,000 30,000 Creditors 5,000 7,000 He has taken Rs 4,000 from the business to meet his personal expenses. calculate the profit Or Loss for the year 2006 9.Mr.Kumar started business with Rs 2,15,000 as capital on 1.4.2005.During the year he has withdrawn at the rate of Rs 2,000 per month. He introduced Rs 25,000 as additional capital. His position on 31.3.2006 was as follows: Bank balance 10,000 Stock 95,000 Sundry debtors 65,000 Machinery 35,000 Cash in hand 25,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com Sundry creditors 20,000 Prepaid expenses 2,000 He keeps his books under single entry system. Find out his profit or loss for the year 2005-2006 10.Thiru Parthasarathy keeps his books by ‘single entry system’. His position on 1.4.2006 and 31.3.2007 was as follows: Particulars 1.4.2006 31.3.2007 Rs Rs Cash 500 6,000 Bank balance 10,000 15,000 Stock 7,000 10,000 Sundry debtors 30,000 40,000 Furniture 6,000 6,000 Sundry creditors 6,000 12,000 He introduced an additional capital of Rs 8.000,During the financial year .He withdrew Rs14,000 for domestic purposes. Find out the Profit or Loss for the year ended 31.3.2007 11.Mrs.vandana started business with Rs 1,20,000 as capital 1.4.2004,During the year she has withdrew at the rate of 1,000 per month. She introduced Rs 20,000 as additional capital. Her position on 31.3.2005 was as follows: Bank 18,000 Stock 80,000 Sundry debtors 50,000 Furniture 5,000 Cash in hand 3,500 Sundry creditors Expenses outstanding 22,000 1,500 She keeps her books under single entry system Determine her profit or loss for the year ended 2004-2005 12.Mr.Ragupathi keeps his books by incomplete single entry .His assets and liabilities on 1.1.2004 and 31.3.2004 stood as follows; Particulars 1.1.2004 31.12.2004 Rs Rs Cash in hand 10,000 15,000 Sundry debtors 80,000 95,000 Investment 20,000 20,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com Furniture 5,000 5,000 Sundry Creditors 50,000 60,000 Stock 35,000 65,000 He introduced an additional capital of Rs 20,000.He withdrew Rs 40,000 for domestic purposes. Find out the Profit or Loss for the year 2004 13.Mrs.Rani started business with Rs 1,20,000 as capital on 1.4.2003.During the year she has withdrawn at the rate of 1,000 per month .She introduced Rs 20,000 as additional capital. His position on 31.3.2004 was as under: Bank balance 8,000 Stock 80,000 Sundry debtors 50,000 Furniture 2,500 Cash in hand 2,000 Sundry creditors 25,000 Expenses outstanding 1,000 She keeps her books under single entry system. Determine her profit or loss for the year 2003-2004 14.Mrs . Praveena keeps her books on single entry basis. Find out the Profit or loss for the period ending 31.3.2005.She started business with Rs 2,35,000 on 1.40.2004 .On 31.3.2005 her position was as under: particulars Rs Bank balances (Dr) 45,000 Cash in hand 3,000 Stock 40,000 Sundry debtors 76,000 Plant & machinery 2,00,000 Furniture 1,00,000 Sundry creditors 1,80,000 Mrs.Praveena had withdrawn Rs 1,00,000 for her personal use and had introduced fresh capital of Rs 40,000,A provision of 5% on debtors is necessary for doubtful debs .Write off depreciation on Plant & machinery at 10% and Furniture at 5% 15.Mr.Rajan keeps his books by single entry .he started business on 1st April 2003 with Rs 3,25,000.On 31st March 2004 his position was as under: Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Cash in hand 3,000 Plant & machinery 2,00,000 Sundry creditors 50,000 Sundry debtors 1,50,000 Cash at bank 25,000 Stock 1,50,000 Bills payable 12,000 Bills receivable 15,000 Furniture 40,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com Outstanding expenses 6,000 Additional capital Rs 40,000 and Drawings Rs 15,000.ascertain his profit or loss for the year 2003-2004 16.Mr.Rajaram keeps his books by incomplete single entry. He started business on 01.01.2005.His assets and liabilities on 01.10.2005 and 31.12.2005 stood as follows Particulars 1.1.2005 31.12.2005 Rs Rs Cash in hand 5,000 60,000 Sundry creditors 15,000 30,000 Furniture 15,000 15,000 Sundry debtors 75,000 1,00,000 stock 35,000 50,000 He introduced an additional capita; of Rs 15,000 during the year .He withdrew Rs 35,000 for domestic purposes. Find out the his profit or loss for the year 2005 17.Mr.Joseph started business with Rs 3,00,000 on 1st April,2003.His books are kept under incomplete double entry. On 31st March 2004 his position was as under: Stock 10,500 Furniture 2,20,000 Cash 40,500 Sundry debtors 1,50,000 Sundry creditors 2,00,000 Bills receivable 75,000 Loan 25,000 Investment 2,50,000 Mr.Joseph withdrew Rs 40,000 for his personal use and he introduced fresh capital of Rs 1,00,000.depreciate furniture by 10% per annum and provide reserve for bad and doubtful debts at 5% on sundry debtors. Ascertain profit or loss made for the year ended 31st March 2004 18.Mr.David started business with Rs 4,00,000 on 1st April 2003.is books are kept under incomplete double entry system. On 31st March 2004 his position was as under: Sundry creditors 3,00,000 Cash is hand 10,000 Cash at bank 60,000 Bills payable 50,000 Outstanding expenses 25,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com Furniture 1,00,000 Plant & machinery 4,00,000 Sundry debtors 2,50,000 Stock 1,50,000 Bills receivable 75,000 He introduced an additional capital of Rs 45,000 during the financial year .he withdrew Rs 20,000 for domestic purposes Ascertain the profit or loss for the year ended 31st March 2004 20 marks(Q.No 53 compulsory sums) 1 Kannan started business with Rs 2,62,500 on 1.4.2003 .he bought furniture for Rs 42,000 .he borrowed Rs 52,500 from Bank. He withdrew for personal expenses Rs 75,600. From the details given prepare final accounts on 31.3.2004: Credit sales 7,00,000 Cash sales 3,50,000 Credit Purchases 7,87,500 Cash Purchases 1,40,000 Wages 15,750 Discount Allowed 3,500 Salaries 17,500 Business Expenses 14,000 Advertisement 17,500 Closing sundry debtors 2,62,500 Closing sundry creditors 1,75,000 Closing stock 1,22,500 Closing cash balance 1,64,150 Depreciation to be provided on furniture @ 10% 2. Mr.Baskar keeps his books on incomplete double entry. From the following details prepare Trading and profit and Loss Account For the year ended 31st March 2006 and Balance sheet as on that date. Particulars 1.4.2005 31.3.2006 Rs Rs Stock 50,000 25,000 Sundry debtors 1,25,000 1,75,000 Cash 12,500 20,000 Furniture 5,000 5,000 Sundry Creditors 75,000 87,500 Other details: Cash received from debtors 2, 67,500 Cash paid to creditors Purchases returns www.TrbTnpsc.com 2, 25,000 2,500 Sales returns 7,500 Discount received 7,500 Discount allowed 5,000 Sundry expenses 17,500 Drawings 20,000 Cash sales 2,500 3. Mr.James maintained his account books on single entry system. On 1.4.2008 his capital was Rs 3, 50,000 Additional information; Opening stock 1, 88,000 Cash received from sundry debtors 38,000 Cash sales 1, 50,000 Cash paid to sundry Creditors 45,000 Opening sundry debtors 30,000 Opening Sundry creditors 1, 40,000 Business expenses 90,000 Freehold premises (31.3.2009) 3, 00,000 Furniture (31.3.2009) 15,400 Closing stock 1, 95,000 Closing Sundry debtors 60,000 Closing sundry creditors 1, 50,000 Closing Cash Balance 9,600 Prepare Trading and profit and loss account for the year ended on 31.3.2009 and Balance sheet as on that date. 4.Raj maintained his books by single entry system .from the following details prepare Final accounts for the year ending 31.3.2003.Depreciate machinery at 10% p.a Cash book Receipts Rs payments Rs To Balance b/d 16,000 By Purchases 28,000 To sales 80,000 By Creditors 40,000 To Debtors 60,000 By general Expenses 12,000 By Wages 4,000 By Drawings 16,000 By Balance c/d 56,000 1,56,000 1,56,000 Other Details: www.TrbTnpsc.com 31.3.2002 Rs 18,000 28,800 20,000 80,000 6,000 31.3.2003 Rs ? ? 32,000 80,000 6,000 Debtors Creditors Stock Machinery Furniture Additional details: Discount allowed 2,800 Discount received 3,400 Credit sales 68,800 Credit purchases 28,200 5.From the following information , prepare Trading and profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet as on 31.3.2005 Opening capital Rs 54,000 Particulars as on 31.3.2005 particulars Rs Sundry debtors 85,000 Sundry Creditors 37,000 Cash 80,000 Stock 75,000 Furniture 5,000 Computers 35,000 Drawings 12,000 Discount received 3,000 Discount allowed 7,000 Cash paid to suppliers 1,00,000 Cash received from customers 2,00,000 Purchases returns 5,000 Sales Returns 8,000 Salary 10,000 Rent 12,000 Charge depreciation on Furniture & Computers 10% 6.Mr.amy maintains his books under incomplete double entry system. From the following particulars you are required to prepare Trading and Profit and Loss account and Balance Sheet as on 231.3.2008 Particulars 1.4.2007 31.3.2008 Rs Rs Stock 75,000 37,500 Sundry debtors 1,87,500 2,62,500 Cash 18,750 30,000 Furniture 7,500 7,500 www.TrbTnpsc.com Sundry Creditors Other details: 1,12,500 1,31,250 Drawings 30,000 Discount received 11,250 Discount allowed 7,500 Sundry expenses 26,250 Cash paid to creditors 3,37,500 Cash received from debtors 4,01,250 Sales returns 11,250 Purchases Returns 3,750 Cash Sales 3,750 7.Mr.Apoorva commenced business on 1.4.2004 with a capital of Rs 75,000.he immediately bought Furniture for Rs 12,000 .During the year he borrowed Rs 15,000 from his wife as loan. He has withdrawn Rs 21,600 for his family expenses. From the following particular you are required to Prepare Trading and Profit and Loss account and Balance sheet as on 31.3.2005 Cash received from sundry debtors Cash paid to sundry creditors Cash sales Cash purchases Carriage inwards Discount allowed Salaries Office expenses Advertisement Closing Balance of sundry Debtors Closing balance of sundry Creditors Closing stock Closing Cash balance Provide 10% depreciation on Furniture 1,21,000 1,75,000 1,00,000 40,000 4,500 4,000 5,000 4,000 5,000 75,000 50,000 35,000 43,900 8. From the following details prepare Trading and profit and Loss Account For the year ended 31st March 2006 and Balance sheet as on that date. Particulars 1.4.2004 31.3.2005 Rs Rs Stock 50,000 25,000 Sundry debtors 1,25,000 1,75,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com Cash 12,500 Furniture 5,000 Sundry Creditors 75,000 Other details: Discount received Discount allowed Sundry expenses Cash paid to sundry creditors Cash received from sundry Debtors Drawings Sales Returns Purchases returns Charge depreciation on Furniture @ 5% 20,000 5,000 87,500 7,500 5,000 15,000 2,25,000 2,67,500 20,000 7,500 2,500 9.Mr.John maintain his books under incomplete Double entry system. You are required to Prepare Trading and Profit and Loss account and Balance sheet as on 31.3.2002 . Particulars 1.4.2001 31.3.2002 Rs Rs Stock 75,000 37,500 Machinery 7,500 7,500 Cash 18,750 30,000 Sundry debtors 1,87,500 2,62,500 Sundry Creditors 1,12,500 1,31,250 Other details: Cash received from debtors 4,05,000 Cash paid to creditors 3,37,500 Sales returns 11,250 Purchases returns 3,750 Discount received 11,250 Discount allowed 7,500 General expenses paid 26,250 Drawings 30,000 10.The books of Mr.Sankar revalued the following information on 1.4.2006 Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Capital 83,030 Goodwill 18,540 Sundry Creditors 9,010 Furniture 14,010 Sundry Debtors 46,830 Cash at bank 12,660 92,040 92,040 Other information: www.TrbTnpsc.com Cash received from sundry Debtors 2,12,460 Drawings 81,600 Salaries paid 18,300 Rent paid 9,450 Cash paid to sundry creditors 90,360 Sundry expenses 3,840 Closing stock (31.3.2007) 32,000 Sundry debtors (31.3.2007) 56,700 Sundry Creditors (31.3.2007) 16,000 Cash at Bank (31.3.2007) 21,570 Prepare Trading account and Profit and Loss account and a Balance sheet as on that 31.3.2007 11.Mr.Kavibharathi maintain her accounts books on single entry system. On 1.4.2003 her capital was Rs 2,50,000 Additional Information: Opening stock 1,25,000 Cash received from sundry debtors 25,000 Cash sales 1,00,000 Cash paid to sundry creditors 30,000 Opening sundry debtors 20,000 Opening sundry creditors 91,500 Business expenses 60,400 Freehold premises (31.3.2004) 2,00,000 Furniture (31.3.2004) 3,600 Closing stock 1,30,000 Closing sundry debtors 40,000 Closing sundry creditors 1,00,000 Closing cash balance 27,500 Prepare Trading and profit and Loss account For the year ended on 31.3.2004 and Balance sheet as on that date. 12.Mr.Arul maintained his account books on single entry system. On 1.4.2005 his capital was Rs 5,00,000 Opening Stock 2,50,000 Cash received from sundry debtors 50,000 Cash sales 2,00,000 Cash paid to sundry creditors 60,000 Opening sundry debtors 40,000 Opening sundry creditors 1,83,000 Business expenses 1,20,800 Land and Building (31.3.2006) 4,00,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com Furniture (31.3.2006) 7,200 Closing stock 2,60,000 Closing sundry creditors 2,00,000 Closing Sundry debtors 80,000 Closing cash balance 55,000 Prepare Trading and profit and Loss account For the year ended on 31.3.2006 and Balance sheet as on that date. 13. From the following details prepare Trading and profit and Loss Account For the year ended 31st March 2005 and Balance sheet as on that date. Particulars 1.4.2004 31.3.2005 Rs Rs Sundry creditors 37,500 43,750 Furniture 2,500 2,500 Cash 6,250 10,000 Sundry Debtors 62,500 87,500 Stock 25,000 12,500 Other details: Discount received 3,750 Discount allowed 2,500 Sundry expenses 8,750 Cash paid to sundry creditors 1,12,500 Cash received from sundry Debtors 1,35,000 Drawings 10,000 Sales Returns 3,750 Purchases returns 1,250 Charge depreciation on Furniture @ 5% p.a 14. Mr.X maintain his books under incomplete Double entry system. You are required to Prepare Trading and Profit and Loss account and Balance sheet as on 31.3.2005 Particulars Stock Sundry debtors Cash Furniture Sundry Creditors Other details: Discount received www.TrbTnpsc.com 1.4.2004 Rs 50,000 1,25,000 12,500 5,000 75,000 31.3.2005 Rs 25,000 1,75,000 20,000 5,000 87,500 7,500 Discount allowed 5,000 Sundry expenses 17,500 Cash paid to sundry creditors 2,25,000 Cash received from sundry Debtors 2,67,500 Drawings 20,000 Sales Returns 7,500 Purchases returns 2,500 Cash sales 2,500 15. Mr.Venugopal maintain his books on incomplete double entry .On 1.4.2003 his capital was Rs 2, 62,500 Additional information: Opening stock 1,31,250 Closing stock 1,36,500 Opening sundry debtors 21,000 Closing sundry debtors 42,000 Opening sundry creditors 96,075 Closing sundry creditors 1,05,000 Cash received from sundry debtors 26,250 Cash sales 1,05,000 Cash paid to sundry creditors 31,500 Business expenses 63,420 Land and Buildings (31.3.2004) 2,10,000 Furniture (31.3.2004) 3,780 Closing cash balance 28,875 Prepare Trading and profit and Loss account For the year ended on 31.3.2004 and Balance sheet as on that date. 16.Mr.Sundar keeps his books on incomplete double entry .from the following details, Prepare trading and profit and Loss account for the year ended 31st March 2004 and balance sheet as on that date: Particulars 1.4.2003 31.3.2004 Rs Rs Stock 1,10,000 55,000 Sundry debtors 2,75,000 3,85,000 Cash 27,500 44,000 Furniture 11,000 11,000 Sundry Creditors 1,65,000 1,92,500 Other details: www.TrbTnpsc.com Drawings Discount received Discount allowed Sundry expenses Cash paid to creditors Cash received from debtors Cash sales 44,000 16,500 11,000 38,500 4,95,000 5,88,500 5,500 CHAPTER-3 DEPRECIATION 5 MARKS (Q.NO:40) 1.Find out the rate of Depreciation under straight line method: Cost of the plant Installation charges Expected life in years Scrap value Rs 2,30,000 Rs 20,000 10years Rs 50,000 2.From the following particulars find out the rate of depreciation under straight line method: Cost of fixed assets Rs 20,000 Residual value Rs 2,000 Expected life 10 Years 3.M/S Vikram & co purchased a plant for Rs 5,00,000 Depreciation is to be provided annually according to the straight line method. The useful life of the plant is 10 years and the residual value is Rs 50,000.Find out the rate of depreciation 4.A Machine was bought for Rs 2,00,000 on 1.1.2000.This is expected to last for five years Estimated scrap at the end of five years is Rs 40,000.Find out the rate of Depreciation under straight line method. 5.A machine was purchased for Rs 3,00,000 on 1.4.2005.This is expected to last 10 years .Estimated scrap at the end of 10 years Rs 30,000.Find out the rate of Depreciation under straight line method. 6.From the following information find out the rate of depreciation under straight line method Cost of the plant Rs 2,10,000 Installation charges Rs 40,000 Expected life in years Rs 10years Scrap value Rs 50,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com 7.rakshitha Ltd purchased Plant and machinery for Rs 32,000.this is expected to last for 10 years. Estimated scarp value is Rs 3,200. Find out the rate of depreciation under straight line method. 8.A company purchased machinery for Rs 1,00,000 its installation costs amounted to Rs 10,000.Its estimated life 5 years and the scarp value is Rs 5,000.calculate the amount and rate of depreciation under straight line method. 9.Vasanth & co purchased a machine for Rs 1,25,000 its useful life is 10 years and the scrap value is Rs 25,000.Determine the rate of depreciation under the straight line method 10.From the following particulars find out the rate of depreciation under straight line method. Cost of fixed asset Rs 50,000 Residual value Rs 5,000 Estimated life 10 years 11.From the following particulars find out the rate of depreciation under straight line method. Cost of assets Rs 82,000 Installation charges Rs 6,000 Scrap value Rs 8,000 Expected life in years 10 Years 12.Find out the rate of depreciation under straight line method Cost of plant Rs 1,30,000 Installation charges Rs 20,000 Expected life in year 10 years Scrap value Rs 30,000 13. Find out the rate of depreciation under straight line method Cost of plant Rs 4,60,000 Installation charges Rs 40,000 Expected life in year 10 years Scrap value Rs 1,00,000 14.Gokul & co purchased a machinery for Rs 48,000 Its useful life 10 years and the scrap value is Rs 4,800.determine the rate of depreciation under the straight line method. 15. M/S Victory & co purchased a plant for Rs 5,00,000 Depreciation is to be provided annually according to the straight line method. The useful life of the plant is 10 years and the residual value is Rs 50,000.Find out the rate of depreciation 16.A limited company purchased a machine for Rs 12,000 Its useful life 10 years and the scrap value is Rs 1,200 Find out the amount of Depreciation and rate of depreciation under the straight line method www.TrbTnpsc.com 17.A company purchased a machine for Rs 15,00,000 Its useful life is 10 years and the scrap value is Rs 3,00,000 .determine the rate of depreciation under the straight line method 18. From the following particulars find out the rate of depreciation under straight line method. Cost of assets Rs 10,00,000 Scrap value Rs 50,000 Expected life in years 10 Years 12 MARKS (Q.NO:49) 1.On 1.10.2000 a company purchased a plant for Rs 6,00,000 .They spend Rs 40,000 on its erection The firm writes off Depreciation at the rate of 20% on Reducing Balance method. The books are closed on 31st March every year. Prepare Plant account and Depreciation account 2.Prakash Limited Company purchased a machine for Rs 3,00,000 on 1.4.2006.After having used it for three year , it was sold for Rs 2,30,000.Depreciation is to be provided at 10% p.a on straight line method. Accounts are closed on 31st March every year. Prepare machinery account and Depreciation account 3.Arul & co purchased a machinery for Rs 5,00,000 on 1.4.2005.after having used it for three years, it was sold for Rs 3,50,000 Depreciation is to provided at 10% p.a under Diminishing Balance method. Accounts are closed on 31st March of every year Prepare Machinery account and Depreciation account. 4.M& co bought a plant for Rs 4,70,000 on 1.7.2001.They spend Rs 30,000 on repairs and installed the plant. Depreciation is Written off at 10%p.a on the straight line method. On 30.9.2003 this was sold for Rs 3,50,000. Accounts are closed on 31st March of every year Prepare Plant account and Depreciation account 5.A firm purchased a machinery for Rs 4,60,000 on 1st July 2004.It spend Rs 40,000 on the repairs and installed the machinery .Depreciation is written off at 10% p.a. On diminishing balance method. after three years the machinery was found to be unsuitable and sold for Rs 4,10,000. Prepare machinery account and Depreciation account for three years, assuming that the accounts are closed on 31st March every years. 6.Jayalakshmi limited Company purchased a machinery for Rs 5,00,000 on 1st July 2006.It is depreciated at 10% per annum on straight line method. Having became obsolete it was sold for Rs 3,80,000 on 31.3.2009 7.Amritha &co Purchased a Machinery for Rs 64,000 on 1st April 1996.They spend Rs 28,000 on the repairs and installed the same. depreciation is written off at 10% p.a on the straight line method.On 30th June 1998 the machinery was found to be unsuitable and sold for Rs 61,000.assume that the accounts are closed on 31st December every year. www.TrbTnpsc.com Prepare machinery Account and Depreciation account for the three years 8.Nivetha manufacturing Company purchased on 1st April 2006 machinery for Rs 2,90,000 and spend Rs 10,000 on its installation .after having used it for three years it was sold for Rs 2,00,000 .depreciation is to be provided every year at the rate of 15% p.a on the Fixed installation method. Assuming that the financial year closes on March 31st For the first three years pass the necessary accounts. 9.Balaji Ltd purchased a machinery for Rs 3,00,000 on 1st October 2001.It is depreciated at 10% p.a On straight line method. Having became obsolete it was sold for Rs 2,00,000 on 31.3.2004 Prepare machinery account and Depreciation account for three years. Accounts are closed on 31st March every year 10.Parasuram company purchased on 1st April 2004 machinery for Rs 1,00,000.After having used it for three years it was sold for Rs 85,000.depreciation is to be provided every year at the rate of 10% per annum on fixed installment method. Books are closed on 31st March every year. Prepare machinery account and Depreciation account for three years. 11.Sri & co Purchased a machinery worth Rs 3,00,000 on 1st October 2002.They spent Rs 20,000 on its erection. The firm writes off depreciation at the rate of 10% on the straight line method. The books are closed on 31st March every year. Prepare Machinery account and Depreciation account for first three years. 12.Sakthi Ltd purchased a machine for Rs 2,00,000 on 1.4.2002.after having used it for three years, it was sold for Rs 1,45,000.Depreciation is to be provided at 10% per annum. On straight line method. Accounts are closed on 31st March every year. Prepare Machinery account and Depreciation account for three years. 13.A garment company purchased a plant on 1st April 2001 for Rs 2,00,000.after having used it for three years it was sold for Rs 1,60,000.Depreciation is to be provided at 10% p.a On fixed installment method. Accounts are closed on 31st March every year. Prepare Plant account and Depreciation account for first three years. 14.On 1.4.2001 a Machinery was purchased for Rs 4,00,000 .On 1.10.02 a new machine costing Rs 2,40,000 was purchased .On 30.9.2003 the machinery purchased on 1.4.2001 having became obsolete was sold Rs 2,40,000 the accounting years ends on 31st March every year and depreciation is to be provided At 10% p.a on straight line method. Prepare machinery account and Depreciation account for 3 years. 15.Tata Ltd purchased a machinery for Rs 1,00,000 on 1.1.2003 On 30.6.2004 another machinery was purchased for Rs 70,000v on 30th September 2005 the first machinery was sold for Rs 57,000.depreciation is to be provided at 10% p.a on straight line method .The accounts are closed on 31st December every year. Prepare Machinery account and Depreciation account for first three years. www.TrbTnpsc.com 16.Ramulu Ltd Purchased a machine for Rs 3,75,000 on 1st July 2002 It is depreciated at 20% p.a on straight line method for three years .having became obsolete it was sold for Rs 75,000 on 31.3.2005. Prepare Machinery account and Depreciation account for first three years. Accounts are closed on 31st March every year. 17.A Company purchased a machine for Rs 4,00,000 on 1.4.2001 .after having used it for three years it was sold for Rs 2,60,000.depreciation is to be provided at 105 p.a on straight line method. Accounts are closed on 31st march of every year. Show the calculation of profit or loss on sale of the machine .Prepare machinery .Prepare machinery account and depreciation account. 18.A company purchased a machinery for Rs 5,00,000 on 1.4.2001 on 1.10.2002 another machinery was purchased for Rs 3,00,000.depreciation is to be provided at 10% p.a under Diminishing Balance method .accounts are closed on 31st March of every year. Prepare machinery .Prepare machinery account and depreciation account. www.TrbTnpsc.com CHAPTER-4 RATIO ANALYSIS 5 MARKS(Q.no:41) 1.Calculate stock Turn over ratio: Opening stock Rs 15,000 Closing stock Rs 25,000 Purchases Rs 60,000 2.From the following information calculate Debt equity Ratio: Debentures Rs 2,00,000 Loan from Banks Rs 1,00,000 Equity share capital Rs 1,25,000 Reserves Rs 25,000 3.From the following information calculate Capital turn over ratio: Sales Rs 3,75,000 Sales Returns Rs 25,000 Equity share capital Rs 1,00,000 Long term loan Rs 50,000 Reserves Rs 25,000 4.Compute Debtors turn over ratio Total sales Rs 7,50,000 Sales returns Rs 50,000 Opening debtors Rs 1,17,000 Closing debtors Rs 83,000 5.Calculate capital Turn over ratio: Sales Rs 10,20,000 Sales returns Rs 20,000 Equity share capital Rs 1,00,000 Preference Share capital Rs 50,000 Loans Rs 25,000 Reserves Rs 25,000 6.Calculate Fixed assets Turnover ratio: Sales Rs 6,00,000 Sales returns Rs 2,00,000 Fixed assets Rs 2,00,000 7.From the following information determine the stock Turnover ratio Opening stock Rs 40,000 Closing stock Rs 30,000 Purchases Rs 95,000 8.From the following information calculate Debts equity ratio: Equity share capital Rs 3,00,000 Loan from banks Rs 2,00,000 6% Debentures Rs 5,00,000 Reserves Rs 50,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com 9.Calculate Liquid Ratio Current assets Rs 20,000 Stock Rs 3,000 Prepaid Expenses Rs 1,000 Current liabilities Rs 8,000 10.Calculate creditors turnover ratio from the following: Credit purchases Rs 1,50,000 Opening creditors Rs 36,000 Closing creditors RS 24,000 11.From the following information calculate capital turnover ratio Sales Rs 6,20,000 Equity share capital Rs 1,00,000 Sales returns Rs 20,000 Loans Rs 50,000 Reserves Rs 50,000 12.Calculate stock turnover ratio from the following Cost of goods sold Rs 13,50,000 Stock at the beginning of the year Rs 2,00,000 Stock at the end of the year Rs 2,50,000 13.calculate the Capital turn over ratio from the following information: Cash sales Rs 4,00,000 Credit sales Rs 3,50,000 Sales return Rs 50,000 Equity share capital Rs 2,00,000 Long term loan Rs 1,00,000 Reserves Rs 50,000 14.Calculate Capital turnover ratio from the following information: Cash sales RS 2,00,000 Credit sales Rs 1,75,000 Sales return Rs 25,000 Equity share capital Rs 1,00,000 Long term loans Rs 50,000 Reserves Rs 25,000 15.From the following information calculate Debt equity ratio: Debentures Rs 2,00,000 Reserves Rs 25,000 Long term loans Rs 1,00,000 Equity share capital Rs 1,25,000 16.From the following particulars Calculate Stock turnover ratio: Cost of goods sold Rs 13,50,000 Opening stock Rs 2,00,000 Closing stock Rs 2,50,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com 17.Calculate Fixed assets turnover ratio from the following: Cash sales Rs 6,50,000 Credit sales Rs 4,00,000 Sales returns Rs 2,50,000 Fixed assets Rs 2,20,000 Depreciation Rs 20,000 12 MARKS (Q. No : 50) 1.From the following information calculate Operating profit ratio, Operating ratio , Gross Profit ratio , Net profit Ratio Sales Rs 1,00,000 Dividend Received Rs 400 Gross profit Rs 30,000 Net profit Rs 26,000 Administration Expenses Rs 1,000 Selling Expenses Rs 2,000 Loss on sale investments Rs 800 2.From the following details Calculate Current ratio Liquid Ratio and absolute Liquid Ratio Cash Rs 5,000 Debtors Rs 29,000 Bills Receivable RS 5,000 Short term investment Rs 15,000 Stock Rs 52,000 Creditors Rs 30,000 Bank overdraft Rs 14,000 Prepaid Expenses Rs 2,000 Bills payable Rs 10,000 3.From the following details calculate gross profit ratio and net profit ratio and stock turn over ratio Sales Rs 1,50,000 Cost of goods sold Rs 1,20,000 Closing stock Rs 31,000 Opening stock Rs 29,000 Net profit Rs 15,000 4.Calculate current Ratio and proprietory ratio from the balance sheet Balance sheet Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Share capital 2,00,000 Fixed assets 1,00,000 Reserves 50,000 Current assets 2,00,000 Bank overdraft 70,000 Investment (long term) 30,000 Other current liabilities 30,000 Preliminary expenses 10,000 Goodwill 10,000 3,50,000 3,50,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com 5.From the following calculate Gross profit , Net profit and Operating profit ratio Sales Rs 1,00,000 Selling Expenses Rs 2,000 Dividend Received Rs 400 Loss on sale investments Rs 800 Gross profit Rs 30,000 Net profit Rs 26,600 Administration Expenses Rs 1,000 6.From the following details calculate gross profit ratio, Stock turn over ratio and Net profit ratio Sales Rs 3,00,000 Closing stock Rs 60,000 Cost of goods sold Rs 2,10,000 Net profit Rs 60,000 Opening stock Rs 80,000 7.From the following calculate Liquidity ratios: Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Share capital 6,300 Fixed assets 5,100 Reserves 1,200 Stock 2,400 Bank overdraft 660 Debtors 660 Creditors 1,740 Cash 1,740 9,900 9,900 8.From the given data calculate gross profit ratio , Net profit Ratio, Current ratio Sales Rs 3,00,000 Current liabilities Rs 30,000 Net profit Rs 30,000 Cost of goods sold Rs 2,40,000 Current assets Rs 60,000 9.From the following details calculate Gross profit ratio , Stock turnover ratio, Debtors turn over ratio Sales Rs 3,00,000 Cost of goods sold Rs 2,40,000 Opening stock Rs 53,000 Closing Stock Rs 62,000 Debtors Rs 30,000 10.From the following information calculate Current ratio , Liquid ratio and absolute liquid ratio Cash Rs 2,400 Debtors Rs 13,600 Stock Rs 18,000 Bills payable RS 3,000 Bank overdraft Rs 9,000 Creditors Rs 5,000 11.From the following details calculate Gross profit and Net profit and Stock turn over ratio Sales Rs 1,50,000 Closing stock Rs 31,000 Cost of goods sold Rs 1,20,000 Debtors Rs 15,000 Opening stock Rs 29,000 Administration expenses Rs 15,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com 12.From the Following details Calculate Current ratio .Liquid ratio and Absolute liquid ratio Cash Rs 12,000 Debtors Rs 1,04,000 Bill Receivable Rs20,000 Bank overdraft Rs 6,000 Stock Rs 44,000 Short term investment Rs 40,000 Creditors Rs 92,000 Bills payable Rs 12,000 13.From the following calculate Gross profit , Net profit and operating profit ratio: Gross profit Rs 60,000 Sales Rs 2,00,000 Administration Expenses Rs 2,000 Selling expenses Rs 4,000 Loss on sale of Investment Rs 1,600 Dividend Received Rs 800 Net profit Rs 53,200 14.kevin Ltd provided the following information for year ending 31.3.2004.calculate Net profit ratio .Operating profit ratio and operating ratio Sales Rs 2,00,000 Office expenses Rs 6,000 Finance expenses Rs 3,000 Interest received Rs 500 Gross profit Rs 80,000 Selling expenses Rs 4,000 Loss on sale of plant Rs 400 Net profit Rs 67,100 15.From the following calculate Gross profit ,net profit and Operating profit ratio Sales Rs 1,00,000 Dividend Received Rs 400 Gross profit Rs 30,000 Administration Expenses Rs 1,000 Selling Expenses Rs 2,000 Loss on sale investments Rs 800 Net profit Rs 26,600 16.From the following you are required to calculate current ratio, Liquid ratio and absolute liquid Ratio: Debtors Rs 5,000 Creditors Rs 1,000 Cash Rs 4,000 Bills payable Rs 3,000 Bank Rs 6,000 Outstanding expenses Rs 250 Short term investment Rs 2,000 Bills receivable Rs 3,000 Prepaid expenses Rs 1,000 Closing stock Rs 8,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com 17.From the following calculate gross profit ratio, net profit ratio, Current ratio Sales Rs 3,00,000 Cost of goods sold Rs 2,10,000 Net profit Rs 45,000 Current assets Rs 60,000 Current Liabilities Rs 30,000 18.From the following calculate gross profit , Net profit and operating profit ratio Sales Rs 8,00,000 Office expenses Rs 50,000 Financial Expenses Rs 20,000 Interest received Rs 10,000 Gross profit Rs 3, 20,000 Selling expenses Rs 70,000 Loss on sale of machinery Rs 1, 60,000 20 MARKS(Q.No.55) 1.From the following balance sheet of J ltd calculate Current ratio ,Liquid Ratio, Debt equity ratio, proprietory Ratio Balance sheet Of J Ltd as on 31.3.2004 Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Share capital 20,000 Goodwill 12,000 Reserves 10,000 Fixed assets 28,000 Loans 20,000 Stock 10,000 Creditors 6,000 Debtors 2,000 Bank overdraft 4,000 Bills receivable 2,000 Cash 6,000 60,000 60,000 2.From the Trading and profit and loss account of surya Ltd.Company ascertain. a]Gross profit ratio b]Net profit ratio c]Operating ratio d]Operating profit ratio Dr Trading and profit and los account for the year ending 31.3.2005 Cr particulars Rs Particulars Rs To opening stock 35,000 By sales 4,00,000 To purchases 2,25,000 By Closing stock 50,000 To wages 10,000 To Gross profit 1,80,000 4,50,000 4,50,000 To Administration Expenses To interest To Loss on sale of Machinery To selling Expenses To Net profit www.TrbTnpsc.com By Gross profit 10,000 By Dividend 5,000 2,000 10,000 1,55,000 1,82,000 1,80,000 2,000 1,82,000 3.From the following Balance Sheet Calculate a]Current ratio b]Liquid Ratio Ratio d] Proprietory Ratio Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Equity share capital 1,00,000 Machinery 90,000 Preference share capital 25,000 Furniture 30,000 Reserve 25,000 Stock 20,000 Debentures 35,000 Sundry Debtors 35,000 Creditors 15,000 Cash 10,000 Bank overdraft 20,000 Bills Receivable 5,000 Bills payable 5,000 Short term investment 10,000 Goodwill 25,000 2,25,000 2,25,000 c]absolute Liquid 4.From the following Balance sheet calculate a]Current ratio b]Liquid ratio c]absolute Liquid Ratio d]Debtors and creditors turnover ratio Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Equity share capital 55,000 Land & Building 20,000 Preference share capital 15,000 Plant & Machinery 22,000 General reserve 25,000 Furniture 3,000 Debentures 35,000 Stock 47,000 Bills payable 3,000 Bills Receivable 10,000 Bank overdraft 3,000 Debtors 23,000 Creditors 8,000 Short Term Investment 5,000 Outstanding Expenses 6,000 Prepaid expenses 1,000 Cash 19,000 1,50,000 1,50,000 Additional Information: Credit sales Rs 1,65,000 Credit Purchases Rs 44,000 5.Calculate a]Current ratio b]Liquid Ratio Liabilities Rs Assets Share capital 1,40,000 Fixed assets Reserves 10,000 Stock Loans 75,000 Sundry Debtors Creditors 50,000 Bills receivable Bank overdraft 10,000 Cash Goodwill 2,85,000 c]Debt equity ratio Rs 1,30,000 30,000 60,000 20,000 10,000 35,000 2,85,000 d]proprietory ratio 6. From the following calculate Gross profit , Net profit and Operating profit ratio Sales Rs 1,00,000 Dividend Received Rs 400 Gross profit Rs 30,000 Administration Expenses Rs 1,000 Selling Expenses Rs 2,000 Loss on sale investments Rs 800 Net profit Rs 26,600 www.TrbTnpsc.com 7.From the following Balance sheet Calculate the i]Current ratio ii] Liquid ratio iii]Absolute liquid ratio iv] proprietory ratio Balance sheet as on 31st March 2006 Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Equity share capital 2,00,000 Machinery 1,80,000 Preference share capital 50,000 Furniture 60,000 Reserves 50,000 Stock 40,000 Debentures 70,000 Sundry Debtors 70,000 Creditors 40,000 Cash 20,000 Bank overdraft 30,000 Bills receivable 10,000 Bills payable 10,000 Short term investment 20,000 Goodwill 50,000 4,50,000 4,50,000 8.From the following Balance sheet of Sujata Industries Ltd Calculate a]Debt equity ratio b]proprietory Ratio c]Current ratio d]Fixed asset ratio Balance sheet as on 31.3.2006 Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Share capital 1,00,000 Fixed assets 1,00,000 General Reserve 20,000 Current assets 1,00,000 Debentures 30,000 Current liabilities 50,000 2,00,000 2,00,000 Credit Sales Rs 4,00,000 9.From the following Balance sheet Calculate i]Current ratio ii]Liquid ratio iii]Debt-equity ratio iv]proprietory ratio Balance sheet of Vasumathi Ltd as on 31.3.2004 Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Share capital 20,000 Goodwill 8,000 Reserves 10,000 Fixed assets 32,000 Loans 16,000 Stock 7,000 Debentures 8,000 Debtors 9,000 Creditors 10,000 Bills receivable 5,000 Bank overdraft 4,000 Cash 7,000 68,000 68,000 10.From the following Balance sheet Calculate i]Current ratio iii]Debt-equity ratio iv]proprietory ratio Balance sheet as on 31.3.2005 Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Share capital 2,00,000 Land & Buildings 1,40,000 Reserves 40,000 Plant & Machinery 80,000 6% Debentures 60,000 Furniture 20,000 Sundry Creditors 75,000 Stock 40,000 Bills payable 25,000 Bills Receivable 30,000 Sundry Debtors 80,000 Cash 10,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com ii]Fixed asset turn over ratio 4,00,000 4,00,000 Additional information: Sales for the year Rs 4,80,000 11.From the following Balance sheet calculate Debtors turn over ratio and Creditor turn over ratio and Fixed asset turn over ratio Balance sheet as on 31.3.2004 Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Share capital 4,00,000 Land & Buildings 3,00,000 Reserves 2,40,000 Plant & machinery 1,60,000 Creditors 2,60,000 Stock 2,96,000 6% Debentures 60,000 Debtors 1,42,000 Cash 62,000 9,60,000 9,60,000 Additional information; Credit purchases during the year Rs 10,40,000 Credit sales during the year Rs 4,26,000 12. From the following Balance sheet Calculate i]Current ratio iii]Debt-equity ratio iv]proprietory ratio Balance sheet as on 31.3.2005 Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Share Capital 2,00,000 Land & Buildings 1,40,000 General Reserve 40,000 Plant & Machinery 1,00,000 Debentures 60,000 Stock 80,000 Creditors 60,000 Debtors 60,000 Bank overdraft 40,000 Bills receivable 20,000 4,00,000 4,00,000 Additional information: Credit Sales for the year Rs 9,60,000 ii]Fixed asset turn over ratio 13.From The following Trading And profit & loss Account of a company ascertain the following ratios a]Gross profit ratio b[Net profit ratio c] Operating Ratio d]Stock turn over ratio Trading and profit and los account of J.J.D & Co for the year ending 31.3.2005 Dr Cr particulars Rs Particulars Rs To opening stock 1,99,000 By sales 17,00,000 To purchases 11,19,000 By Closing stock 2,98,000 To Gross profit 6,80,000 19,98,000 19,98,000 To Administration Expenses To selling Expenses To Financial Expenses To Loss on sale of Plant To Net profit www.TrbTnpsc.com 3,00,000 By Gross profit 60,000 By Dividend 30,000 8,000 3,00,000 6,98,000 6,80,000 18,000 6,98,000 14.From the following Trading and Profit & loss account and The Balance Sheet find out the Following ratios a]Gross profit ratio b[Net profit ratio c] Acid test ratio d]Stock turn over ratio Trading and Profit and Loss account for the year ending 31.12.2005 Particulars Rs Particulars Rs To Opening stock 10,000 By sales 1,00,000 To Purchases 50,000 By Closing Stock 15,000 To Direct Expenses 5,000 To Gross profit 50,000 1,15,000 1,15,000 To Administration Expenses By Gross profit 15,000 50,000 To Interest 3,000 To Selling Expenses 12,000 To Net profit 20,000 50,000 50,000 Balance sheet as on 31.12.2005 Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Capital 1,00,000 Land & Buildings 50,000 Current Liabilities 40,000 Plant & Machinery 30,000 Profit and Loss A/C 20,000 Furniture 20,000 Stock 15,000 Sundry Debtors 15,000 Bills Receivable 12,500 Cash in Hand 17,500 1,60,000 1,60,000 15.From the following Balance sheet calculate i] Current ratio ii]Liquid ratio iii]Absolute liquid ratio iv]Debt equity ratio Balance sheet as on 31st March 2005 Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Equity share capital 1,25,000 Machinery 2,75,000 Reserves 25,000 Furniture 1,00,000 Debentures 2,00,000 Stock 37,500 Long term loan 1,00,000 Sundry Debtors 63,500 Sundry Creditors 25,000 Cash 10,000 Bills payable 30,000 Bills Receivable 9,000 Bank overdraft 20,000 Short term Investment 30,000 5,25,000 5,25,000 16. From the following Balance sheet calculate i] Current ratio ii]Liquid ratio iii]Proprietory iv]Debt equity ratio Balance sheet as on 31st March 2005 Liabilities Rs Assets Rs Share capital 70,000 Fixed Assets 65,000 Reserves 5,000 Stock 15,000 Loans 37,500 Sundry Debtors 30,000 Creditors 25,000 Bills receivable 10,000 Bank overdraft 5,000 Cash 5,000 Goodwill 17,500 1,42,500 1,42,500 www.TrbTnpsc.com CHAPTER-5 CASH BUDGET 5 MARKS(Q.No 42 ) 1.The opening balance of Cash on 1.4.2009 was Rs 50,000 .estimated receipts during the month were Rs 80,000 and the estimated payments for the month were Rs 1,00,000 .determine the closing balance on 30.4.2009 2.The opening balance of cash in January 2002 is Rs 1,50,000.The estimated cash receipts are Rs 50,000 and the estimated cash payments are Rs 30,000 .What is the opening balance of cash in February 2002 ? 3.From the following information prepare cash budget for June 2005 Particular Amount Rs Cash in hand (1.6.2005) 10,000 Cash purchases-June 2005 70,000 Cash sales-June 2005 Purchases of furniture-June 2005 1,00,000 2,500 4.The opening balance of Cash In January 2007 Is Rs 90,000.The estimated receipts are Rs 1,40,000 and the estimated payments are Rs 1,00,000.Find out the closing balance of cash For January 2007 www.TrbTnpsc.com 20 Marks (Q.no 56) 1.Prepare a cash Budget for October ,November and December 2004 from the following information: Month Sales Purchases Expenses Rs Rs Rs September 2004 10,00,000 8,00,000 1,10,000 October 2004 12,00,000 12,00,000 1,30,000 November 2004 14,00,000 8,00,000 1,50,000 December 2004 16,00,000 10,00,000 1,70,000 Additional information: 1.All sales are for cash 2.The period of credit allowed by the suppliers is one month 3.Lag in payments fro expenses is one month 4.Opening balance of cash on 1.10.2004 is Rs 90,000 5.In December an asset of Rs 4,00,000 is to be bought. 2.Prepare cash budget for the month of March, April and May 2009 from the following information: Month Credit Sales Credit Purchases Office Expenses Rs Rs Rs January 50,000 30,000 5,000 February 75,000 40,000 7,000 March 1,00,000 65,000 15,000 April 1,25,000 75,000 10,000 May 1,30,000 80,000 20,000 Additional information: 1.Opening cash balance in March 2009 Rs 60,000 2.Period of credit allowed to customers-one month 3.period of credit allowed by suppliers –two month 4.Office expenses are payable in the same month. 5.Dividend Rs 15,000 is receivable in March 2009 3.From the following information prepare a cash budget for June, July and August 2009 Month Credit Sales Credit Purchases wages Rs Rs Rs April 2009 2,50,000 1,80,000 25,000 May 2009 2,65,000 1,25,000 10,000 June 2009 3,25,000 1,75,000 25,000 July 2009 3,75,000 1,90,000 15,000 August 2009 3,50,000 2,25,000 20,000 Additional information: 1.Opening cash balance on 1st June 2009 Rs 1,20,000 2.period of Credit allowed to customer-one month 3.period of credit allowed by suppliers –two month 4.lag in payment of wages is one month www.TrbTnpsc.com 5.sale of machinery Rs 40,000 in July 4.Prepare a cash budget for the months of March, April and may 2005 from the following information: Month Credit Sales Credit Purchases Administration and Rs Rs selling expenses Rs January 2005 1,50,000 75,000 1,20,000 February 2005 1,35,000 1,00,000 1,35,000 March 2005 1,75,000 85,000 65,000 April 2005 1,20,000 1,25,000 70,000 May 2005 1,40,000 90,000 80,000 Additional information: 1.Expected cash balance on 1.3.2005 is Rs 80,000 2.Suppliers allowed a credit period of two months 3.A credit period of one month is allowed to customers 4.Expenses are paid in the same month 5.Sale of fixed assets Rs 25,000 in April 6.Purchases of fixed assets in May Rs 25,000 5.Prepare a cash budget for the month of March .April and May 2006 from the following information: Month Credit Sales Credit Purchases Expenses Rs Rs Rs January 2006 2,50,000 2,00,000 50,000 February 2006 3,00,000 3,50,000 60,000 March 2006 4,50,000 3,00,000 70,000 April 2006 2,00,000 4,00,000 80,000 May 2006 3,50,000 5,00,000 70,000 Additional information: 1.Expected cash balance as on 1.3.2006 Rs 75,000 2.Suppliers allowed credit of two months 3.Credit of two months is allowed to the customers 4.lag in payment of expenses one month 5.Sale of fixed assets in the month of April Rs 95,000 6.From the following information , prepare a cash budget for the month of March, April and May 2008 Month Credit Sales Credit Purchases Office Expenses Rs Rs Rs January 2008 60,000 40,000 12,000 February 2008 70,000 30,000 10,000 March 2008 80,000 35,000 9,000 April 2008 75,000 50,000 12,000 May 2008 72,000 55,000 11,000 Additional information: 1.Opening balance of cash on 1.3.2008 is Rs 15,000 2.Credit allowed by suppliers is two months 3.Credit allowed to customers is one month www.TrbTnpsc.com 4.Office expenses are payable in the same month 5.Interest payable in April Rs 3,500 7.Prepare a cash budget for the month of august and September 2004 from the following information: Month Cash sales Credit Sales Credit Purchases wages Selling Rs Rs Rs Rs expenses Rs June 2004 75,000 1,87,000 1,24,800 12,000 8,600 July 2004 60,000 1,92,000 1,83,600 14,000 4,800 August 2004 50,000 1,94,000 1,46,000 11,000 6,600 September 2004 45,000 1,26,000 1,73,400 10,000 7,500 Additional information: 1.Suppliers allowed two months credit 2.Customers were given one month credit 3.Wages are payable in the same month and delay in payment of selling expenses was one month 4.Commission receivable Rs 11,000 in august 5.estimated cash balance as on 1st august Rs 9,100 8. From the following information prepare a cash budget for June, July and August 2006 Month Credit Sales Credit Purchases wages Rs Rs Rs April 2006 2,25,000 1,60,000 20,000 May 2006 2,55,000 1,05,000 15,000 June 2006 3,00,000 1,50,000 18,000 July 2006 3,60,000 1,70,000 12,000 August 2006 3,15,000 2,10,000 14,000 Additional information: 1.Opening cash balance on 1st June 2006 Rs 2,00,000 2.Period of Credit allowed to customer-one month 3.Period of credit allowed by suppliers –two month 4.lag in payment of wages is one month 5.Sale of Machinery Rs 50,000 in July 6.Commission payable in August is Rs 20,000 9.Prepare cash Budget for the month Of June ,July and August 2007 From the following information 1.Opening cash balance in June Rs 7,000 2.Cash sales for June Rs 20,000:July Rs 30,000: And August Rs 40,000 3.Wages payable Rs 6,000 every month 4.Interest receivable Rs 500 in the month of august 5.Purchases of Furniture for Rs 16,000 in July 6.Ccash purchases for June Rs 10,000: July Rs 9,000 and August Rs 14,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com 10. Prepare a cash budget of Balachandar Ltd for the month of January to March 2004 from the following information: Month Credit Sales Credit Purchases Expenses Rs Rs Rs 2003 November 2,50,000 2,00,000 50,000 December 3,00,000 3,50,000 60,000 2004 January 4,50,000 3,00,000 70,000 February 2,00,000 4,00,000 80,000 March 3,50,000 5,00,000 70,000 Additional information: 1.Expected cash balance as on 1.1.2004 Rs 75,000 2.Suppliers allowed credit of two months 3.Credit of two months is allowed to the customers 4.lag in payment of expenses one month 5.Sale of fixed assets in the month of February Rs 95,000 11.prepare cash Budget for the month of April ,May and June 2006 from the following information Month Sales Purchases Expenses Rs Rs Rs March 2006 4,00,000 3,00,000 40,000 April 2006 5,00,000 5,00,000 60,000 May 2006 6,00,000 3,00,000 70,000 June 2006 8,00,000 5,00,000 90,000 Additional information: 1.All sales are for cash 2.Lag in payment of expenses is one month 3.The period of credit allowed by the suppliers is one month 4.Interest receivable is Rs 10,000 in the month of April 2006 5.In June 2006 Furniture For Rs 20,000 is to be purchased 6.Opening cash balance On 1st April 2006 is Rs 60,000 12.Prepare cash Budget for the months of June .July and August 2004 from the following information: 1.Opening cash balance in June Rs 21,000 2.Cash sales for June Rs 60,000:July Rs 90,000:and August Rs 1,20,000 3.Wages payable Rs 18,000 every month 4.Interest receivable Rs 1,500 in the month of August 5.Purchases Of machinery For Rs 48,000 in July 6.Cash purchases for June Rs 30,000:July Rs 27,000:August Rs 42,000 13.From the following information prepare a cash Budget for three months from October 2003 1.Opening cash balance in October Rs 6,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com 2.Cash sales :October Rs 50,000:November Rs 40,000:December Rs 30,000 3.Credit purchases :September Rs 20,000:October Rs 24,000:November Rs 28,000:December Rs 32,000 The period of credit allowed by suppliers is one month 4.Dividend to be received in December Rs 8,000 5.Sale of an old assets for Rs 24,000 during November 14. Prepare cash Budget for the months of June .July and August 20045from the following information: 1.Opening cash balance in June Rs 1,00,000 2.Cash sales for June Rs 60,000:July Rs 80,000:and August Rs 1,00,000 3.Wages payable Rs 15,000 every month 4.Interest receivable Rs 5,000 in the month of July 5.Purchases Of machinery For Rs 25,000 in the month of August 6.Cash purchases for June Rs 25,000:July Rs 40,000:August Rs 30,000 15. Prepare cash budget for the month of March, April and May 2005 from the following information: Month Credit Sales Credit Purchases Office Expenses Rs Rs Rs January 75,000 20,000 7,000 February 85,000 35,000 10,000 March 1,00,000 17,000 12,000 April 1,20,000 24,000 9,000 May 1,05,000 22,000 10,000 Additional information: 1.Opening cash balance in March 2005 Rs 50,000 2.Period of credit allowed to customers-one month 3.Period of credit allowed by suppliers –two month 4.Office expenses are payable in the same month. 5.Dividend Rs 10,000 is receivable in March 2005 6.Furniture Rs 15,000 is to be purchased in May 2005 CHAPTER-6 PARTNERSHIP-BASIC CONCEPT 5 MARK Q.NO 42 1.Three years purchases of the last four years average profit is agreed as the value of Goodwill. The profit and Losses for the last four years are Ist year Rs 50,000 II nd year Rs 80,000 III rd year Rs 30,000 (Loss) Iv th Year Rs 60,000 Calculate the amount of Goodwill www.TrbTnpsc.com 2.Calculate the amount of Goodwill on the basis of three years purchases of the five years average profits. The profits for the last five years Rs 2005 20,000 2006 24,000 2007 36,000 2008 19,000 2009 26,000 3.The goodwill is to be valued at two years purchases of last four years average profits. The profits were Rs 40,000 Rs 32,000 Rs 15,000 and Rs 13,000 respectively. Find out the value of goodwill 4.Calculate the amount of Goodwill on the basis of two years purchases of the last four years average profits The profits and loss of the last four years are 2003 profit 20,000 2004 profit 30,000 2005Loss 6,000 2006 profit 16,000 5.Mohan and Murugan are partners sharing profits and losses equally. Mohan draws regularly Rs 2,000 at the beginning of every month during the year. Murugan draws regularly Rs 3,000 at the end of every month during the year. calculate the interest on their drawings at 10% per annum. 6.Calculate the amount of Goodwill on the basis of three years purchases of the last four years average profits. The profits for the last four years are 2001 Rs 12,000 2002-Rs 18,000 2003Rs-16,000 2004 Rs 14,000 7.Surendar and Amrith are two partners sharing profits and losses equally. Surendar drew regularly Rs 2,000 at the end of every month during the year. Amrith draws Rs 4,000 regularly at the beginning of every month during the year .calculate interest on their drawings at 10% p.a 8.Calculate the amount of goodwill on the basis of three years purchases of the five years average profits .The profits for the last five years are : Rs 2001 15,000 2002 22,000 2003 36,000 2004 18,000 2005 17,000 9.Abi and Sibi had capitals of Rs 60,000 and Rs 40,000 respectively on 1.4.2002. Sibi withdrew Rs 5,000 from his capital on 30.09.2002.calculate interest on capital at 6% for the year ending 31st March 2003 www.TrbTnpsc.com 10.Kamala and Vimala are two partners sharing profits and losses equally. Kamala draws Rs 1,800 regularly in the middle of each month during the year 2006.Vimala draws Rs 10,800 at the end of each half year. Calculate interest on drawings at 5% p.a 11.Charles and Newman are partners. Charles draws Rs 2,700 regularly in the middle of each month during the year 2004.Newman draws Rs 5,400 at the end of each half year. Calculate interest on their drawings at 5% p.a 12.A and B are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3:2.a draws Rs 6,000 regularly at the end of every month during the year 2004.B draws Rs 20,000on 1.4.2004, Rs 12,000 on 30.6.2004, Rs 16,000 on 1.10.2004, and Rs 8,000 on 30.11.2004.Calculate interest on their drawings at 6% p.a 13.V and S are two partners sharing profits and losses as 7:5.V draws regularly Rs 400 at the end of every month during the year 2004.S draws Rs 800 regularly at the beginning of every month during the year. Calculate interest on their drawings at 10 % p.a 14.Calculate the amount of Goodwill on the basis of two years purchases of the last four years average profits. The profits /loss for the four years are 2001 profit Rs 10,000 2002 profit Rs 26,000 2003 loss Rs 12,000 2004 Profit Rs 36,000 15.Sulochana and Archana started business on April 1,2004 with capitals of Rs 2,00,000 and Rs 1,50,000 respectively. Sulochana introduced Rs 50,000 as additional capital on October 1 2004.Interest on capital is to be provided at the rate of 5% p.a. Calculate interest payable to Sulochana and Archana for the year ending March 31,2005 16.Sivagami and Sundari are partners profits and losses equally. Sivagami draws regularly Rs 3,000 at the beginning of every month during the year. Sundari draws regularly Rs 2,000 at the end of every month during the year. Calculate interest on their drawings at10% p.a 12 MARKS (Q.NO 51) 1.M and R are partners sharing profits in the ratio 3:2 with capital of Rs 50,000 and Rs 40,000 respectively. Interest on capital is agreed at 8% per annum. Interest on drawings is fixed at 10% p.a. The drawings of the partners M and R were Rs 15,000 and Rs 10,000 Respectively. The interest for M Rs 750 and R for Rs 500.M is entitled to a salary of Rs 12,000 p.a and R is entitled to a commission of 10% on the net profit before charging such commission. The net profit of the firm before making adjustment was Rs 60,000 for the year ended 31.3.2005 Prepare profit and loss Appropriation account and Capital accounts 2.Sathyaraj and Dharmaraj are partners sharing profits and losses equally. Their capitals on 1.4.2007 were Rs 1,00,000 and Rs 80,000 respectively. Interest on capital is agreed at 6% p.a. Interest on drawings is fixed at 8% p.a The drawings of the partners were Rs 15,000 and Rs 10,000 respectively. Interest on drawings were Sathyaraj and Dharmaraj Rs 600 and Rs 400 respectively. Sathyaraj is entitled to a salary of Rs 12,000 p.a and Dharmaraj is entitled to get a commission of Rs 3,420. The www.TrbTnpsc.com net profit of the firm before making the above adjustment was Rs 56,000 for the year ended on 31st March 2008 Prepare profit and loss Appropriation account and Capital accounts of the partners 3.Amar and Akbar are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2. Their capital on 1.4.2004 were Rs 1,50,000 and Rs 1,00,000 respectively. The net profit of the firm for the year ended 31st March2005 before making adjustment for the following items was Rs 70,000 .Drawings of the partners during the years were Amar Rs 15,000 and Akbar Rs 10,000 Their partnership deed provided for the following: i]Interest on capital at 6% p.a ii]Interest on drawings at 8% p.a being Amar Rs 600 and Akbar Rs 400 iii]Amar and Akbar to get a salary of Rs 10,000 each p.a iv]Amar to get a commission of Rs 3,600 Show the profit and loss Appropriation account and Capital accounts of the partners 4. A and B are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2. Their capital on 1.4.2003 were Rs 1,60,000 and Rs 1,20,000 respectively. The net profit of the firm for the year ended 31st March2004 before making adjustment for the following items was Rs 60,000 .Drawings of the partners during the years were A Rs 12,000 and B Rs 8,000 Their partnership deed provided for the following: i]Interest on capital at 5% p.a ii]Interest on drawings at 6% p.a iii]A and B to get a salary of Rs 10,000 each p.a iv]A to get a commission of 10% on the net profit before charging such commission. Show the profit and loss Appropriation account and Capital accounts of the partners 5.Show how the following items will appear in the capital accounts and Currents accounts of the partners Saleem and Simon when their capital are fixed Saleem Simon Rs Rs Capital on 01.04.2004 90,000 70,000 Drawings during 2004/2005 12,000 9,000 Interest on Drawings 360 270 Interest on Capital 5,400 4,200 Partners salary 12,000 -----Commission ------- 6,000 Share of profit for 2004-2005 6,000 4,000 6.Suja and Banu are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3:2. Their capitals on 1.4.2007 were Rs 2,00,000 and Rs 1,50,000 respectively. The net profit of the firm for the year ended 31st March ,2008 before making adjustment for the items below was Rs 75,000. Interest on Capital is at 6% p.a. They are entitled to get a salary of Rs 10,000 each p.a.Suja to get a commission of Rs 1,050 p.a. The drawings of the partners were Suja Rs 20,000 and Banu Rs 15,000 .Interest on drawings at6% p.a being Suja Rs 600 and Banu Rs 450 Prepare profit and loss Appropriation account and Capital accounts of the partners As on 31.3.2008 www.TrbTnpsc.com 7.Write up the capital and Current accounts of the partners, Rajani and sajani from the following details: Particulars Rajani Sajani Rs Rs Capital on 1.4.2003 1,00,000 60,000 Current a/c on 1.42003 3,000(Dr) 2,000(cr) Drawings during 2003-04 8,000 5,000 Interest on Capital @ 5% ? ? Interest on Drawings 240 150 Share of profit 2003-04 12,000 10,000 Partners salary 4,000 Interest on Rajani’s loan a/c 3,000 8. Mohan and Murugan are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2. Their capital on 1.4.2002 were Rs 80,000 and Rs 60,000 respectively. The net profit of the firm for the year ended 31st March2003 before making adjustment for the following items was Rs 30,000 .Drawings of the partners during the years were Mohan Rs 6,000 and Murugan Rs 4,000 Their partnership deed provided for the following: i]Interest on capital at 6% p.a ii]Interest on drawings at 8% p.a iii]Mohan and Murugan get a salary of Rs 5,000 each p.a Show the profit and loss Appropriation account and Capital accounts of the partners 9.Prepare Capital accounts of partners Ashwini and shivani from the following details assuming that the capital are fluctuating Particulars Ashwini Shivani Rs Rs Capital as on 1.4.2006 2,10,000 1,20,000 Drawings during 2006-07 18,000 12,000 Interest on Capital @ 6% ? ? Interest on Drawings 450 300 Share of profit 2006-07 24,000 18,000 Partners salary 6,000 Commission 4,800 3,600 Interest on Shivani’s loan a/c 3,000 10.Babu and Chandra are partners sharing profits and losses equally .Their capitals on 1.4.2005 were Rs 60,000 and Rs 40,000 respectively. Interest on capital is agreed at 6% p.a. Interest on Drawings is fixed at 8% p.a. The drawings of the partners were Rs 6,000 and Rs 4,000 respectively. Interest on Drawings were for Babu Rs 240 and for Chandra Rs 160.Babu is entitled to a salary to Rs 8,400 p.a and Chandra is entitled to get a commission of 10% on the net profit before charging such commission.net profit of the firm before making the above adjustment was Rs 54,000 for the year ended on 31st March 2006. Prepare profit and loss Appropriation account and Capital accounts of the partners www.TrbTnpsc.com 11.A and B are partners with Capital of Rs 60,000 and Rs 20,000 respectively on 1st January 2001. The trading profit (Before taking into account the provision of the deed) for the year ended 31.12.2001 was Rs 12,000 Interest on Capital is to allowed at 6% p.a. B is entitled to a salary of Rs 3,000 p.a The drawings of the partners were A Rs 2,000 and B Rs 1,000 The interest on drawings for a being Rs 100 and B Rs 50 Assuming that A and B are equal partners. Prepare profit and loss Appropriation account and Capital accounts of the partners 12.Rajan and Daniel are partners sharing profit in the ratio of 3:2 with capitals of Rs 50,000 and Rs 40,000 respectively. Interest on Capital is agreed at 8% p.a Interest on Drawings is fixed at 10% p.a. The drawings of the partners were Rajan Rs 15,000 and Daniel Rs 10,000.Rajan is entitled to a salary of Rs 12,000 p.a Daniel is entitled to a commission of 10% on net profit before making charging such commission. The Net profit of the firm before making the above adjustment was Rs 60,000 for the year ended 31st March 2005 Prepare profit and loss Appropriation account and Capital accounts of the partners 13.Ravi and Shankar are partners with capitals Rs 4,50,000 and Rs 3,00,000 respectively on 1st April. They share profit and losses are equally. Interest on Capital is agreed at8% p.a. The drawings of the partners were Rs 30,000 and Rs 20,000 respectively. Interest on Drawings for Ravi Rs 1,500 and Shankar Rs 1,000.Ravi is entitled to a salary of Rs 15,000 p.a and Shankar is entitled to get a commission of 15% on the net profit after charging such commission. The Net profit of the firm before making the above adjustment was Rs 1,30,000 for the year ended 31st March 2005 Prepare profit and loss Appropriation account and Capital accounts of the partners 14.Ganesh and Suresh are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3;2 with capital of Rs 3,00,000 and Rs 1,00,000 respectively on 1st April 2004.Interest on capital is agreed at 5% p.a. The interest on Drawings is fixed at 6% p.a. The Drawings Ganesh and Suresh were Rs 45,000 and Rs 30,000 respectively. Interest on Drawings for Ganesh 2,250 and Suresh Rs1,500.ganesh is entitled to a salary of Rs 20,000 p.a and Suresh is entitled to get a commission of 10% on the net profit before charging such commission. The net profit of the firm before making the above adjustment was Rs 90,000 for the year ended 31st March 2005 . www.TrbTnpsc.com CHAPTER-7&8 PARTNERSHIP ADMISSION AND RETIREMENT 5 Marks:(Q.No 43) 1. Sankar and Saleem were partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2.They admit Saimon into the partnership to 1/3rd share, the old partners sacrifice equally. Calculate the new profit sharing ratio 2.A and B are partners sharing the profits in the ratio of 3:2.They admit C into the firm for 1/5th share, which he acquired entirely from A. Calculate the new profit sharing ratio of A, B and C 3.Sindhu And Bindhu are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 7:3 .They admit Indhu into the partnership to 1/5th share , the old partners sacrificing equally, calculate the new profit ratio and sacrificing ratio 4.X and Y are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3:2. They admit Z for 1/6th share as new partner. Calculate new profit sharing ratio and sacrificing ratio of old partners. 5. krithika And Gomathi are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 9:7.Nischala is admitted as a partner .She acquires 3/16 of the profit entirely from Krithika .Calculate the new profit sharing ratio and sacrificing ratio 6.Vidhya and Priya were partners sharing profits in the ratio of 4:3.Ramya was admitted in the business as a partner with 3/7th share in the profits of the firm which she takes 2/7th from Vidhya and 1/7th from Priya. Find out the new profit ratio and Sacrificing ratio. 7. X and Y are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3:2. They admit Z for 1/3rd share as new partner. The old partners sacrifice equally .Calculate new profit sharing ratio and sacrificing ratio of old partners 8.priya and Sharmila are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3;2. They admit Sangeeta for 1/5th share which acquires equally from Priya and Sharmila. Calculate new profit sharing ratio and Sacrifice ratio. 9.Naveen and Praveen are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3:2. They admit Kunal as a new partners , who acquires 1/5th of Naveen’s Share and 2/5th of Praveen share. Calculate New profit sharing ratio and Sacrificing ratio. 10.Neela and Nikita were sharing profits in the ratio of 4:3 .Pooja was admitted with 1/5th share in profits of business. Calculate the new profit sharing ratio and Sacrificing ratio. 11. Neela and Sheela were sharing profits in the ratio of 4:3 .Heena was admitted with 1/5th share in profits of business. Calculate the new profit sharing ratio and Sacrificing ratio. 12.A and B and C are sharing profits in the ratio of 5:3:2 C retires and his share was taken up entirely by B. Find out the new profit sharing ratio. www.TrbTnpsc.com 13. A and B were sharing profits in the ratio of 3:2 .C was admitted with 3/10th share in profits of business. Calculate the new profit sharing ratio and Sacrificing ratio. 20 Marks (Q.No 53 b Compulsory) 1.P, S and V were partners of a firm sharing profits in the ratio of their capitals. Their balance sheet as on 31.12.2004 stood as follows Balance sheet as on 31.12.2004 Liabilities Creditors Reserve fund Capitals: P S V Rs Rs Assets Rs Rs 21,000 Cash at Bank 16,000 48,000 Debtors 20,000 (-)provision for 19,000 1,000 90,000 Doubtful debts 60,000 Stock 18,000 30,000 1,80,000 Machinery 48,000 Land & Buildings 1,00,000 Goodwill 48,000 2,49,000 2,49,000 On 1.1.2005 S retires from the firm on the following terms; i]Goodwill of the firm was estimated at Rs 36,000 ii]Land and Building was appreciated by 10% iii]Provision for Doubtful debts was reduced by Rs 600 iv]Out of the amount of Insurance which was debited entirely to profit and Loss account Rs 2,000 be carried forward for unexpired insurance v]A provision of Rs 3,000 was made in respect of an outstanding bill for repairs Show Revaluation account and Capital account and the Balance sheet of the Reconstitute Partnership 2.Vijay and Vikram are partners sharing profits and Losses in the ratio of 3;2. Their balance sheet as on 31st Match,2009 is given below: Liabilities Creditors Bills payable General Reserve Capital: Vijay Vikram 1st Rs 80,000 40,000 Rs 70,000 20,000 40,000 Balance sheet as on 31.3.2009 Assets Rs Cash Debtors Stock Machinery Buildings Profit & Loss A/C 1,20,000 2,50,000 Rs 15,000 70,000 30,000 25,000 1,00,000 10,000 2,50,000 On April 2010 they agreed to admit Mr.Vinod into the firm for share of future profit on the following terms: i]Vinod to bring Rs 50,000 Capital ii]Stock is revalued at Rs 21,500 iii]Provision for bad and doubtful debts be created at 5% iv]Buildings is revalued at Rs 1,20,000 v]Goodwill is raised at Rs 40,000 Prepare Revaluation Account , Capital account and Balance sheet of the reconstitute firm www.TrbTnpsc.com 1/5th 3.Karthick ,David and Venkat were partners of a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2:1. Their balance sheet as on 31st December 2006 is as follows: Balance sheet as on 31.12.2006 Liabilities Sundry Creditors Bills payable General Reserve Capital account: Karthick David Venkat Rs Rs Assets Rs Rs 25,000 Cash 63,000 15,000 Bills Receivable 10,000 30,000 Sundry Debtors 30,000 Stock 42,000 80,000 Furniture 15,000 50,000 Buildings 80,000 40,000 1,70,000 2,40,000 2,40,000 Venkat retired from the partnership on 1st January 2007 on the following terms: a]Goodwill of the firm was to be valued at Rs 30,000 b]Assets are to be valued as under: Stock Rs 50,000:Buildings Rs 1,00,000 c]Furniture was to be depreciated by Rs 3,000 d]A provision for doubtful debts be created at Rs 1,000 e] Venkat was to be paid off at once Show Revaluation account and Capital account and the Balance sheet of the Reconstitute Partnership 4.A & B are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2.Their balance sheet as on 31.12.2001 stood as under: Balance sheet Liabilities Reserve fund Creditors Bills payable Capital accounts A B Rs Assets Rs Rs 10,000 Land & Buildings 40,000 16,000 Plant & Machinery 10,000 6,800 Investments 10,000 Stock 11,000 30,000 Profit & loss a/c 10,000 5,000 25,000 55,000 Debtors (-) Provision for doubtful debts 4,800 200 Cash 2,000 87,800 87,800 They decided to admit c into partnership with effect from 1.1.2002 i]That C shall bring as a capital of Rs 20,000 for 1/3rd profits ii]That the goodwill of the firm was valued at Rs 36,000 iii]Land was to be valued at Rs 45,000 and investment at Rs 25,000 iv]Stock was to be written down by Rs 2,000 v]That provision for doubtful debts was to be increased to Rs 300 vi]Creditors include Rs 500 no longer payable and this um was to be written off Prepare Revaluation account, capital account of the partners and Balance sheet of the reconstitute partnership www.TrbTnpsc.com Rs 5.Amar and Akbar and Antony were partners of a firm sharing profit and loss in the ratio of 6:5:4. The balance sheet as on 31.3.2003 is given below Balance sheet as on 31.3.2003 Liabilities Sundry Creditors Bills payable Bank Overdraft General Reserve Profit & Loss a/c Capital accounts: Amar Akbar Antony Rs 50,000 40,000 30,000 Rs 30,000 21,000 40,000 30,000 24,000 Assets Cash Sundry debtors Stock Furniture Plant & Machinery Land and Buildings Rs Rs 25,000 25,000 35,000 15,000 75,000 90,000 1,20,000 2,65,000 2,65,000 Akbar retired from the partnership firm on 1.4.2004 i]That goodwill is raised at Rs 30,000 ii]The value of Land and Buildings is to be increased by Rs 10,000 iii]That Furniture and Plant were to be depreciated by Rs 2,000 and Rs 2,000 Respectively iv]That Rs 10,000 is to be paid immediately to Akbar and the remaining balance is to be transferred to his loan account Show Revaluation account and Capital account and the Balance sheet of the Reconstitute Partnership 6.Ravi ,Venkat and Kumar are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2:1. Their balance sheet as on 31.3.2008 is given below: Liabilities Sundry creditors Bills payable General reserve Capital accounts: Ravi Venkat Kumar Rs 1,80,000 1,20,000 90,000 Rs Assets 90,000 Cash at Bank 30,000 Sundry debtors 90,000 Stock Plant & Machinery Land and Buildings Rs Rs 1,41,000 39,000 90,000 1,20,000 2,10,000 6,00,000 6,00,000 Kumar retired from the partnership from 1.4.2008 on the following terms: i]goodwill was to be raised at Rs 1,08,000 ii]the value of land and Buildings was to be increased by Rs 30,000 iii]Plant and machinery was depreciated by Rs 9,000 iv]The provision for outstanding bill for repairs was to be made of Rs 12,000 v]Kumar was to be paid off at once Show Revaluation account and Capital account and the Balance sheet of the Reconstitute Partnership 7.Naveen and Nithin were partners of a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 7:5 set out below was their balance sheet as on 31st December 2004 Liabilities Rs Rs Assets Rs Rs www.TrbTnpsc.com Sundry creditors General reserve Workman compensation fund Capital accounts Naveen Nithin 40,000 Bank 72,000 Sundry Debtors Stock 60,000 Machinery Profit & loss A/c 52,000 40,000 72,000 1,60,000 48,000 1,20,000 80,000 2,00,000 3,72,000 3,72,000 st Nithin Retires from the partnership from 1 January 2005 and that Naveen will take over the business on the following terms: a]Goodwill of the firm was to be valued at Rs 36,000 b]Machinery was depreciated at 10% c]A provision for doubtful debts be created at 5% on sundry debtors d]The liability on workman compensation fund is determined at Rs 36,000 Show Revaluation account and Capital account and the Balance sheet of Naveen after the adjustment have been made. 8.The following is the Balance sheet of Siva and Panner sharing profits 3:2 as on 31.3.2006 Liabilities Rs Rs Assets Rs Rs Sundry creditors 30,000 Bank 10,000 Bills payable 28,000 Sundry debtors 30,000 Bank overdraft 20,000 Stock 20,000 General reserve 30,000 Machinery 40,000 Capital accounts: Land and buildings 70,000 Siva 40,000 Profit & loss a/c 8,000 Panner 30,000 70,000 1,78,000 1,78,000 On 1.4.2006 they decided to admit Gopinath into partnership on the following terms: i]That Gopinath shall bring in a capital of Rs 30,000 ii]That goodwill of the firm being valued at Rs 20,000 iii]That Land & Buildings be appreciated by 10% iv]That stock be depreciated by Rs 3,000 and provision for outstanding liability be created at Rs 2,000 Pass journal entries, Also show Revaluation account and Capital account and the Balance sheet 9.Sekhar and Suresh are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio 3:2.Their balance sheet as on 31st March 2004 is given below: Liabilities Rs Rs Assets Rs Rs Bills payable 75,000 Cash 15,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com Creditors Loan General Reserve Capital: Sekhar Suresh 1,20,000 Stock 30,000 1,35,000 Debtors 1,50,000 45,000 Machinery 75,000 Buildings 4,50,000 3,00,000 Investment 1,00,000 2,25,000 5,25,000 Goodwill 80,000 9,00,000 9,00,000 st On 1 April 2004 they agreed to admit Sundar into the firm for 1/5th share of future profits on the following terms: i]Sundar to bring Rs 1,50,000 as Capital ii]Goodwill was valued at Rs 1,00,000 iii]Buildings was to be depreciated by Rs 20,000 iv] Creditors include Rs 30,000 no longer payable and this sum was to be written off Show Revaluation account and Capital account, cash account and the Balance sheet of the Reconstitute Partnership 10.The following is the Balance sheet of Viji and Raji sharing a profit and Loss as to Viji 65% and Raji 35% as on 1st April 2006 Liabilities Rs Rs Assets Rs Rs Sundry creditors 25,000 Cash 2,000 Bank overdraft 13,000 Debtors 30,000 Profit and loss a/c 14,000 Stock 20,000 Capital Furniture 8,000 Viji 40,000 Land & Buildings 50,000 Raji 30,000 70,000 Goodwill 12,000 1,22,000 1,22,000 They agreed to take Vinitha into partnership to 1/10th share of the following terms: i]Vinitha shall bring in a capital of Rs 30,000 ii]The goodwill of the firm be increased to Rs 15,000 iii]A provision of Rs 1,000 be made for outstanding repairs bill iv]The value of land and Buildings be brought up to Rs 60,000 being their present worth prepare Revaluation account ,capital account, bank account and the Balance sheet of the new firm 11.Dhiya and Gaya sharing profits in the ratio 3:2 admit Riya as a partner with 1/3rd share in profits on 1.1.2001. The terms agreed upon were 1]Riya has to contribute Rs 30,000 2]Goodwill of the firm be valued at Rs 28,000 3]Land & Buildings be appreciated by 40% 4]Depreciated plant& Machinery by 10% 5]The provision for doubtful debts was to be increased by Rs 800 www.TrbTnpsc.com 6]A liability of Rs 1,000 include in the sundry creditors is not likely to arise The balance sheet of Dhiya and Gaya as on 31.12.2000 before admission of Riya was as follows: Liabilities Rs Rs Assets Rs Rs Sundry creditors 29,000 Cash at Bank 9,000 Bills payable 6,000 Land & Buildings 25,000 Capital Plant & Machinery 30,000 Dhiya 50,000 Stock 15,000 Gaya 85,000 Sundry Debtors 20,000 35,000 General reserve 16,000 (-)provision for doubtful debts 19,000 1,000 Goodwill 10,000 Profit and loss account 28,000 1,36,000 1,36,000 Prepare Revaluation account , Capital account, bank account and the new Balance sheet as on 1.1.2001 after the admission of Riya 12.Suriya, Vijay and Vikram were partners of a firm sharing profit and losses in the ratio of 3:2:1 .Their balance sheet as on 31st December 2005 is as follows Balance sheet as on 31st December 2005 Liabilities Sundry Creditors Bills payable General Reserve Capital accounts: Surya Vijay Vikram Rs Rs Assets 50,000 Cash in hand 30,000 Sundry debtors 60,000 Stock Furniture Buildings Rs 1,60,000 1,00,000 80,000 3,40,000 4,80,000 Rs 1,36,000 58,000 72,000 14,000 2,00,000 4,80,000 Vikram retired from the partnership on 1st January2006 on the following terms: a]Goodwill of the firm was to be valued at Rs 60,000 b]Buildings was to be appreciated by Rs 40,000 c]Furniture was to be depreciated by Rs 3,000 d]A provision for doubtful; debts be created at Rs 1,000 e] Vikram was to be paid off at once Show Revaluation account and Capital account, cash account and the Balance sheet of the Reconstitute Partnership 13.Rani and Deepa were partners sharing profit and loss in the ratio of 7:5 their Balance sheet as on 31st December 1995 is as under: Balance sheet as on 31st December 2005 Liabilities Capital Rani Deepa Reserve fund Sundry creditors www.TrbTnpsc.com Rs Rs Assets Land & buildings 60,000 Plant & Machinery 50,000 1,10,000 Investment 20,000 Stock 32,000 Sundry debtors Rs 10,000 Rs 80,000 20,000 40,000 22,000 Bills payable 13,600 (-)Provision for doubtful debts 9,600 400 Cash 4,000 1,75,600 1,75,600 st They decided to admit Leena into the partnership with effect from 1 January 1996 on the following terms: 1]Leena shall bring in a capital of Rs 40,000 for 1/3rd share of profits 2]Goodwill of the firm was valued at Rs 72,000 3]Land was to be appreciated by 10% and Investment was to be revalued at Rs 52,000 4]Stock was to be written down by Rs 4,000 5]provision for doubtful debts was to be increased to Rs 600 6]Creditors include Rs 1,000 no longer payable and this sum was to be written off Pass journal entries, Also show Revaluation account and Capital account and the Balance sheet . 14.Jayaseelan,Anbarasu and Inbanathan were partners of a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 1/2 , 1/3 and 1/6 respectively .Set out below was their Balance sheet as on 30.06.2005 Balance sheet as on 30th June 2005 Liabilities Rs Rs Assets Rs Rs Sundry creditors 1,20,000 Cash in hand 8,000 Bills payable 40,000 Cash at Bank 1,80,000 General reserve 1,20,000 Sundry debtors 52,000 Profit and Loss a/c 90,000 Stock 1,20,000 Capital accounts: Furniture 80,000 Jayaseelan 2,40,000 Plant 1,60,000 Anbarasu 1,60,000 Buildings 2,90,000 Inbanathan 1,20,000 5,20,000 8,90,000 8,90,000 Inbanathan retired from the partnership from 1st July 2005 on the following terms: 1]Goodwill was to be raised at Rs 1,44,000 2]The value of Buildings was to be increased by Rs 40,000 3]Furniture and Plant were to depreciated by Rs 4,000 and Rs 12,000 respectively Pass journal entries, Also show Revaluation account and Capital account and the Balance sheet . 15.Amar ,Akbar and Antony were partners of a firm sharing profits and losses in proportion of their capital. Set out below their Balance sheet as on 31st March 2004 Balance sheet as on 31st March 2004 Liabilities Rs Rs Assets Rs Rs Sundry creditors 2,00,000 Cash at Bank 2,50,000 Bills payable 1,00,000 Sundry Debtors 4,00,000 Loan 3,25,000 Stock 75,000 Reserve fund 1,00,000 Machinery 2,00,000 Profit and loss 2,00,000 Land and Buildings 4,00,000 Capital accounts: Amar 2,00,000 Akbar 1,20,000 Antony 80,000 3,00,000 13,25,000 13,25,000 www.TrbTnpsc.com On 1st April 2005 Antony retired from the firm on the following terms; i]Antony was to be paid off at once ii]Goodwill of the firm to be valued at Rs 50,000 iii]Machinery was to be depreciated at 10% per annum. iv]The value of Land and Building was to be appreciated by 20% p.a v]A provision of bad and Doubtful debts be created at 5% on debtors Show Revaluation account and Capital account, Bank account and the Balance sheet of the Reconstitute Partnership 16.Sankar and Saleem are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2 .Their Balance sheet as on 31st March 2005 is given below Balance sheet as on 31st March 2005 Liabilities Rs Rs Assets Rs Rs Creditors 80,000 Cash 10,000 Bills payable 50,000 Debtors 1,00,000. General reserve 30,000 Stock 20,000 Loan 90,000 Furniture 50,000 Capitals: Buildings 3,00,000 Sankar 2,00,000 Goodwill 75,000 Saleem 1,50,000 3,50,000 Profit and Loss a/c 45,000 6,00,000 6,00,000 On 1st April 2005 they agreed to admit Solomon into the firm for 1/5th share of future profits on the following terms: i]Solomon to bring Rs 1,00,000 as capital ii]Goodwill was valued at Rs 50,000 iii]Provision for bad and doubtful debts is made at 5% p.a iv]Investment of Rs 10,000 be brought into books v]creditors include Rs 20,000 no longer payable and this sum was to be written off Show Revaluation account and Capital account, Cash account and the Balance sheet of the Reconstitute Partnership www.TrbTnpsc.com CHAPTER-9 COMPANY ACCOUNTS 5 MARKS (Q.No42) 1. The directors of S ltd forfeited 2000 shares of Rs 10each for non payment of final call of Rs 2.50 Give necessary Journal entries for forfeiture of shares. 2. Jasmine Limited Company issued 50,000 shares of Rs 10e ach at a premium of Rs 3.Give journal entry. 3. Global Ltd Company issued 10,000 shares of Rs 100 each at a discount of 10% .Give journal entry. 4. Vinod Company Ltd issued 40,000 preference shares of Rs 10 each at premium of Rs 3.Give Journal entry 5. Z Ltd issued 40,000 shares of Rs 10 each at a premium of Rs 2 per share. Give journal entry. 6. A limited company issued 1,00,000 shares of Rs 10each payable Rs 2 on application. The company received application for 1,10,000 shares .The Excess application were rejected and money refunded .pass necessary journal entries to record these transactions only. 7.Vanathi Ltd issued 30,000 shares of Rs 100 each at a premium of Rs 25 per share fully paid. Pass journal entry 8. Latha ltd issued 2,00,000 equity shares of Rs 10each at a discount of 10% per share/Give journal entry. 9. Suresh Ltd. issued 50,000 shares of Rs 100 each at a discount of 10% .Give journal entry 10. Balagobal Ltd issued 2,00,000 equity shares of Rs 10each at a premium of 10% per share fully paid. Give journal entry. 11. Sandeep Limited issued 30,000 shares Rs 100 each at a discount of 10%.Give journal entry. 12. Jasmine ltd forfeited 600 shares of Rs 10each fully called up for non payment of final call of Rs2 each. These shares were reissued for Rs 5,400 as fully paid up. Give necessary journal entry. 13.A company forfeited 400 shares of Rs 10 each on which the first call money of Rs 3 per share was not received, the final call of Rs 3 is yet to be made. These shares were Subsequently reissued at Rs 7 per share at Rs 8 paid up. Pass necessary journal entry 14.The directors of Kumar Ltd forfeited 4,000 shares Of Rs 10 each for non-payment of final call of Rs 3.2500 of these shares were reissued for Rs 7 per share fully paid up. Pass necessary journal entry 15.Success Ltd forfeited 500 shares of Rs 10 each fully called up for non payment of final call money of Rs 4 per share. Out of these 300 share were reissued for Rs 8 each fully paid up. Pass necessary journal entries. www.TrbTnpsc.com 16.success Ltd issued 1,00,000 equity shares of Rs 10each at a premium of 20% per share, Fully paid. Give journal entry 17.A company forfeited 6,000 shares of Rs 100 each fully called up for non-payment of final call money of Rs 30per share. These shares were reissued for Rs 4,80,000 as fully paid up. Give necessary journal entries. 18.A company forfeited 5,000 shares of Rs 10each fully called up for non-payment of final call money of Rs 3 per share. These shares were reissued for Rs 30,000 as fully paid up. Pass necessary journal entries 12 Marks(Q.no52) 1.A company forfeited 100 equity shares of Rs 100 each issued at premium of 10% on which first call money of Rs 30 per share and final call of Rs 20 per share were not received. These shares were subsequently re-issued at Rs 90 per share as fully paid up Give necessary Journal entries regarding forfeiture and reissue of shares. Also prepare share forfeiture account and Capital reserve account. 2.Sathya Ltd, Company issued 3,000 equity shares of Rs 10 each fully called up on which the final call of Rs 3 has not been paid. Out of these 1,500 shares were reissued at Rs 8 each fully paid. Give necessary journal entries and Prepare Ledger account for forfeiture shares account and Capital Reserve account . 3. G Ltd forfeited 20 shares of Rs 10each fully called up held by Gopi for non-payment of Final call of Rs 4 per share. These shares were reissued to Mohan for Rs 8 per share as fully paid up. Pass entries for the forfeiture and reissues of shares .Also prepare share Forfeiture account and Capital reserve account 4.The directors of a company forfeited 3,000 shares of Rs 10 each fully called up for non-payment of first call Rs 3 and final call for Rs 2 per share. 2,000 of these shares were reissued at Rs 7 each fully paid up. Pass necessary journal and Ledger account 5.The Directors of Good luck ltd Forfeited 2,000 equity shares of Rs 10each fully called up for non payment of first call Rs 3 and Final call Rs 2 per share Out of these 1,000 shares were reissued at Rs 8 each fully paid. Give necessary journal; entries and prepare ledger account for forfeiture account and capital Reserve account 6.A company forfeited 200 shares of Rs 100 each issued at a premium of 10% (Received on allotment) for the non payment of first call of Rs 30 and Final call of Rs 20 per share. These shares were reissued at Rs 70 per share as fully paid up. Give necessary Journal entries for forfeited and reissue of share. 7.Acharya Ltd. Forfeited shares 300 shares of Rs 10 each fully called up held bu Kumar for non payment of first call money of Rs 3 per share and final call money of Rs 4 per share .Out of these shares 250 were re issued to Illangovan for Rs 2,000 .Give all the journal entries for forfeited and re issue and prepare ledge accounts. www.TrbTnpsc.com 8.The Directors of Everest Ltd. Forfeited 500 equity shares of Rs 100 each fully called up for non payment of first call Rs 30 and final call Rs 10 per share. Out of these 300 share were re issued at Rs 70 each fully paid. Give necessary journal entries and prepare ledger accounts for forfeited shares account and capital reserve account. 9.The directors of a company after due notice forfeited 100 shares of Rs 10 each on which the final call money of Rs 3 was not paid. Later these shares were reissued at Rs 8 per share. Pass Journal entries and shoe the share forfeiture and Capital Reserve account 10.The directors of a company forfeited 500 shares of Rs 10 each fully called up for non payment of first call of Rs 2 per share and final call of Rs 3 per share .300 of shares were subsequently reissued at Rs 7 per share fully paid up .pass necessary entries to record the above and prepare share forfeiture account. 11.Gem Ltd. forfeited 1,000 equity shares of Rs 10 each fully called up on which the final call of Rs 3 has not been paid. Out of these 800 shares were reissued at Rs 8 each fully paid. Give necessary Journal entries and Prepare Ledger accounts for forfeited shares account and Capital Reserve account. 12. Poorani Ltd. Forfeited 2,000 shares of Rs 10 each issued at a discount of 10% for non payment of first call Rs 2 and second Call Rs 3.These shares were reissued to Mrs. Merlin upon a payment of Rs 14,000 as fully paid. Give necessary Journal entries and Prepare Ledger accounts for forfeited shares account and Capital Reserve account 13.The directors of Arun Ltd forfeited 500 equity shares of Rs 100 each at a premium of 10% on which first call money of Rs 30 per share and final call Rs 20 per share was not received. Out of these 300 shares were reissued at Rs 80 per share as fully paid. Give necessary Journal entries and Prepare Ledger accounts for forfeited shares account and Capital Reserve account 14.The Directors of Lucky Ltd forfeited 1,000 equity shares of Rs 10 each fully called up for non payment of first call Rs 3 and final Rs 3 per share. Out of these 400 share were reissued at Rs 8 each fully paid. Give necessary Journal entries and Prepare Ledger accounts for forfeited shares account and Capital Reserve account 15.The directors of mercury Ltd. forfeited 3,000 equity shares Of Rs 10 each fully called up for non payment of first call Rs 2 and Final call Rs 3 per share .Out of these share 2,000 shares were Reissued at Rs 9 each fully paid. Give necessary Journal entries and Prepare Ledger accounts for forfeited shares account and Capital Reserve account www.TrbTnpsc.com 16.The directors of a company forfeited 5,000 shares of Rs 100 each fully called up for non payment of final call Rs 20 per share. These shares were reissued at Rs 70 each as fully paid. Give necessary Journal entries and Prepare Ledger accounts for forfeited shares account and Capital Reserve account 17.The Directors of accompany forfeited 4,000 shares of Rs 10 each fully called up for non payment of first call Rs 3 and final call Rs 2 per share .Out of these 1,000 shares were reissued at Rs 7 each as fully paid. Give necessary Journal entries and Prepare Ledger accounts for forfeited shares account and Capital Reserve account 20 Marks (Q.N 57) 1.M ltd offered for subscription 20,000 shares of Rs 10 each payable at a premium of Rs 2.50 per share payable as follows: On Application Rs 2.50 On Allotment Rs 5.00 (Including premium) On First call Rs 3.00 On Final Call Rs 2.00 Application were received for 30,000 shares Application for 5,000 shares were rejected. Application for other 5,000 shares were adjusted towards allotment. The balance money was received in due time. Pass journal entries and ledger account and balance sheet 2.Bharath company Ltd. issued 30,000 shares of Rs 100 each at a premium of Rs 10 each payable as follows On Application Rs 20 On Allotment Rs 40 (Including premium Rs 10) On First call Rs 20 On Final Call Rs 30 The company’s shares were fully subscribed .Both the calls were made and all the money were duly received. Pass Journal entries. Prepare Bank account, Share Capital account ,Securities premium account and Balance sheet 3.Shenbagam Ltd Company issued 2,00,000 shares of Rs 10 each at premium of Rs payable as follows : On Application Rs 2 On Allotment Rs 5 (Including premium Rs 2) On First call www.TrbTnpsc.com Rs 3 On Final Call Rs 2 All the shares were fully subscribed .Both the calls were made and all the money were duly received. Pass Journal entries. Prepare Bank account, Share Capital account ,Securities premium account and Balance sheet 4.S ltd. Issued 1,70,000 shares of Rs 10 each at a discount of 10% .The shares were payable as under: On Application Rs 3 On Allotment Rs 4(With the adjustment of discount) On First call & Final Call Rs 2 Public applied for 1,60,000 shares and the shares have been duly allotted. All money were duly received. pass entries and Prepare Bank account , Share Capital account, Discount account, and also Show the Balance sheet 5.Sun Ltd issued 20,000 shares Of Rs 10 each payable at a premium of Rs 3 per share On Application Rs 3 On Allotment Rs 5 (Including premium Rs3) On First call Rs 3 On Final Call Rs 2 Applications were received for 30,000 shares Application for 5,000 shares were rejected. Applications for other 5,000 shares were adjusted towards allotment. The balance money was received in due time. Pass Journal entries. Prepare Bank account, Share Capital account, Securities premium account and Balance sheet 6.Vasanth Ltd issued 20,000 shares of Rs 100 each at Rs 120 payable as follows: On Application Rs 20 On Allotment Rs 50 (Including premium Rs20) On First call Rs 30 On Final Call Rs 20 All the shares were fully subscribed .Both the calls were made and all the money were duly received. Pass Journal entries. Prepare Bank account, Share Capital account , Securities premium account and Balance sheet www.TrbTnpsc.com 7.Santhosh Ltd issued 10,000 shares of Rs 100 each at Rs 120 payable as follows: On Application Rs 25 On Allotment Rs 45 (Including premium) On First call Rs 20 On Final Call Rs 30 9,000 shares were applied for and allotted . All money was received with the exception of final call on 200 shares held by Sanjay. Pass Journal entries. Prepare Bank account, Share Capital account, Securities premium account and Balance sheet 8.Nagesh Ltd. issued 6,000 shares of Rs 10 each at a premium of Rs 2 per share payable Rs 2 on application, Rs 5 on allotment( including premium), Rs 3 on First call and Rs 2 on final call. All these shares were duly subscribed and money due were fully received. Pass Journal entries. Prepare Bank account, Share Capital account, Securities premium account and Balance sheet 9.Maruti Ltd issued 1,00,000 shares of Rs 10each at a premium of Rs 2 each payable as follows On Application Rs 2 On Allotment Rs 6(Including premium) On First call Rs 3 On Final Call Rs 1 All the shares were fully subscribed .Both the calls were made and all the money duly received. Pass Journal entries. Prepare Bank account, Share Capital account, Securities premium account and Balance sheet 10. Kalyana Sundaram Ltd issued 10,000 shares of Rs 100 each at a premium of Rs 20 each payable as follows: On Application Rs 20 On Allotment Rs 50 (Including premium) On First call Rs 30 On Final Call Rs 20 The Company received application for 15,000 shares. Applications for 10,000 shares were accepted in full, and the money on remaining 5,000 applications were rejected and refunded. Both calls were made and all the money were duly received www.TrbTnpsc.com Pass Journal entries. Prepare Bank account, Share Capital account, Securities premium account and Balance sheet 11. Pavitra Ltd offered for subscription 20,000 shares of Rs 10 each payable at a premium of Rs2 per share. The shares were payable as under: On Application Rs 2 On Allotment Rs 5 (Including premium) On First call Rs 3 On Final Call Rs 2 Applications were received for 30,000 shares Application for 5,000 shares were rejected. Applications for other 5,000 shares were adjusted towards allotment. The balance money was received in due time. Pass Journal entries. Prepare Bank account, Share Capital account, Securities premium account and Balance sheet 12. Texmo Ltd issued 20,000 shares of Rs 100 each at a premium of Rs 10 each payable as follows: On Application Rs 30 On Allotment Rs 40 (Including premium) On First call Rs 20 On Final Call Rs 20 The Company received application for 25,000 shares. Applications for 5,000 shares were rejected. Both the calls were made and all the money were duly received. Pass Journal entries. Prepare Bank account, Share Capital account, Securities premium account and Balance sheet 13. Raja & Company invited application for 20,000 equity shares of Rs 100 each at a discount of Rs 10 per share (Allowed at the time of allotment) The amount was payable as follows On Application Rs 20 On Allotment Rs 40 On First call & Final Call Rs 30 The public applied for 18,000 shares and these were allotted. All Money due was collected with the exception of allotment and the first and final call on 800 shares. Pass Journal entries. Prepare important ledger accounts. 14. Tamil Selvan co ltd offered for subscription 5,000 shares of Rs 100 each at a premium of Rs 20 on the following terms: On Application www.TrbTnpsc.com Rs 20 On Allotment Rs 50 (Including premium) On First call Rs 30 On Final Call Rs 20 Application were received for 8,000 shares, excess application money was refunded. All the money due on shares were duly received except final call on 500 shares. Pass Journal entries .Prepare necessary ledger accounts and show the balance sheet 15. Sarawathi Ltd issued 30,000 shares of Rs 100 each at Rs 120 payable as follows On Application Rs 25 On Allotment Rs 45 (Including premium) On First call Rs 25 On Final Call Rs 25 All the shares were fully subscribed .Both the calls were made and all the money duly received. Pass journal entries. Prepare necessary ledger accounts and the balance sheet 16. Naveena Ltd issued 50,000 shares of Rs 10 each at a premium of Rs 2 each payable as follows On Application Rs 2 On Allotment Rs 5 (Including premium) On First call Rs 3 On Final Call Rs 2 The company received application for 70,000 shares. Applications for 50,000 shares were accepted in full and the money on remaining 20,000 applications which rejected was refunded. Both the calls were made and all the money were duly received. Pass journal entries. Prepare necessary ledger accounts and the Balance sheet. 17. Alpha Ltd, issued 10,000 shares of Rs 100 each at a discount of 10% payable as under: On Application Rs 30 On Allotment Rs 40 (With discount adjustment) On First call & Final Call Rs 20 Public applied for 8,000 shares and the shares have been duly allotted..all money were duly received. www.TrbTnpsc.com Pass journal entries. Prepare Bank account, Share capital account, Discount on issue of Shares Account and Balance sheet. 18. Global Ltd. Issued 20,000 shares of Rs 100 each at Rs 110 payable as follows: On Application Rs 20 On Allotment Rs 40 (Including premium) On First call Rs 30 On Second and Final Call Rs 20 The Company’s shares were fully subscripted both the calls were made and all the money were duly received. Pass journal entries. Prepare Bank account, Share Capital account, Securities Premium Account and Balance sheet. www.TrbTnpsc.com ACCOUNTANCY Chapter-1 Final accounts-With adjustment I. Fill in the blanks: 1. Net Profit is transferred from Profit and loss account to ________ account. 2. Closing stock is valued at Cost Price or ________ price whichever is lower. 3. Outstanding expenses are shown on the ________ side of the balance sheet. 4. Prepaid expenses are shown on the ________ side of the balance sheet. 5. Income accrued but not received will be shown on the ________ side of the Balance sheet. 6. Income received in advance will be shown on the ________side of the Balance sheet 7. Interest on capital is debited in ________ account 8. Interest on drawings is credited in ________ account. 9. Interest on loan borrowed unpaid is shown on the ________ side of the Balance sheet. 10. Depreciation is deducted from the concerned ________ in the Balance sheet. 11. Provision for Bad and Doubtful debts is deducted from ________ in the Balance sheet. 12. Provision for discount on creditors is deducted from ________in the Balance sheet. 13. Debts which are not recoverable from Sundry debtors are termed as ________. II. Choose the correct answer 1. Returns inwards are deducted from a) Purchases b) Sales c) Returns outward 2. The Profit and Loss account shows a) Financial position of the concern b) Net profit or Net loss c) Gross profit or Gross Loss 3. Rent outstanding is a) a liability b) an asset c) an income 4. Closing stock is shown in a) Profit and loss account b) Trading account and Balance sheet c) None of the above. 5. Opening stock is shown in a) Balance sheet b) Profit and Loss account c) Trading account 6. Gross Profit is transferred to a) Capital account b) Profit and loss account c) None of the above 7. Interest on capital is added to a) Expense A/c b) Income A/c c) Capital A/c 8. Interest on drawings is deducted from a) Income A/c b) Capital A/c c) Expense A/c 9. Outstanding interest on loan borrowed is to be added to a) Asset A/c b) Income A/c c) Loan A/c 10. All the items given in the adjustment will appear at _________ in the Final accounts. a) Three places b) Two places c) One Place Chapter-2 Accounts from incomplete Records-Single entry I. Fill in the blanks: 1. Incomplete records are those records which are not kept under ________ system. 2. Statement of affairs method is also called as ________ method. 3. ________ capital can be found by preparing a statement of affairs at the beginning of the year. 4. A statement of affairs resembles a ________. 5. Closing capital can be found by preparing a statement affairs at the ________ of the year. 6. In ________ system, only personal and cash accounts are opened. 7. Credit purchase can be ascertained as the balancing figure in the ________. 8. The excess of assets over liabilities is ________. www.TrbTnpsc.com 9. The total assets of a proprietor are Rs.5,00,000. His liabilities Rs.3,50,000. Then his capital in the business is ________. 10. A firm has assets worth Rs.60,000 and capital Rs.45,000. Then it’s liabilities is ________. II. Choose the Correct Answer: 1. Under the networth method the basis for ascertaining the profit is a) the difference between the capital on two dates. b) the difference between the liabilities on two dates. c) the difference between the gross assets on two dates. 2. Incomplete records are generally used by a) Small traders b) Company c) Government 3. Credit sales is obtained from a) Bills Receivable account b) Total debtors account c) Total creditors account 4. Single Entry System is a) a Scientific method b) an Incomplete Double Entry System c) None of the above. 5. The capital of a business is ascertained by preparing a) Trading account b) Statement of profit or loss c) Statement of affairs Chapter-3 Depreciation I. Fill in the blanks: 1. All assets whose benefit is derived for a __________ period of time are called as Fixed Assets. 2. The estimated sale value of the asset at the end of it’s economic life is called as ________ value. 3. ________ method of depreciation is calculated on the original cost of assets. 4. Under ________ method, depreciation is calculated on the book value of the asset each year. 5. _______ method of depreciation is used in the case of Lease. 6. Under insurance policy method, cash is paid by way of _______ every year. 7. ________ method of depreciation is suitable for special type of asset like Loose tools II. Choose the correct answer: 1. Depreciation arises due to a) wear and tear of the asset b) fall in the market value of asset c) fall in the value of money 2. Under straight line method, rate of depreciation is calculated on a) Original cost b) Written down value c) Cost less scrap value 3. Under diminishing balance method, depreciation a) decreases every year b) increases every year c) constant every year 4. The term depletion is used for a) Intangible assets b) Fixed assets c) Natural resources 5. If selling price is more than the book value of the asset on the date of sale, it is a) a loss b) an income c) a profit 6. If selling price is less than the book value of the asset it denotes a) loss b) capital profit c) expenditure 7. Profit made on sale of fixed asset is debited to a) Profit and Loss account b) Fixed Asset account c) Depreciation account 8. Loss on sale of fixed asset appear on the a) credit side of Depreciation account b) debit side of fixed asset account c) credit side of fixed asset account 9. The amount of depreciation charged on a machinery will be debited to a) Machinery account b) Depreciation account c) Cash account 10. Total amount of depreciation provided on the written down value method at the rate of 10% p.a. on Rs.10,000 for first three years will be a) Rs. 2,107 b) Rs. 2,710 c) Rs. 2,701 www.TrbTnpsc.com Chapter-4 Ratio analysis I. Fill in the blanks: 1. _______ is a mathematical relationship between two items expressed in quantitative form. 2. Ratio helps in _______ forecasting. 3. _______ Ratio measures the firm ability to pay off its current dues. 4. _______ are those assets which are easily convertible into cash. 5. Bank overdraft is an example of _______ liability. 6. Liquid ratio is used to assess the firm’s _______ liquidity. 7. Liquid assets means current assets less _______ and _______. 8. _______ ratio is modified form of liquid ratio. 9. Liquid liabilities means current liabilities less _______. 10. Proprietory ratio shows the relationship between _______ and total tangible assets. 11. Gross profit can be ascertained by deducting cost of goods sold from _______. 12. Stock turnover ratio is otherwise called as _______. 13. 100% – Operating profit ratio is equal to _______ ratio. 14. When total sales is Rs.2,00,000, cash sales is Rs.65,000, then credit sales will be Rs._______. 15. Liquid ratio is otherwise known as _______. II. Choose the correct answer: 1. All solvency ratios are expressed in terms of a) Proportion b) Times c) Percentage 2. All activity ratios are expressed in terms of a) Proportion b) Times c) Percentage 3. All profitability ratios are expressed in terms of a) Proportion b) Times c) Percentage 4. Liquid liabilities means a) Current liabilities b) Current liabilities – Bank overdraft c) Current liabilities + Bank overdraft 5. Shareholders funds includes a) Equity share capital, Preference share capital, Reserves & Surplus b) Loans from banks and financial institutions c) Equity share capital, Preference share capital, Reserves & Surplus and Loans from banks and financial institutions 6. Which of the following option is correct a) Tangible Assets = Land + Building + Furniture b) Tangible Assets = Land + Building + Goodwill c) Tabgible Assets = Land + Furniture + Goodwill + Copy right 7. Gross profit ratio establishes the relationship between a) Gross profit & Total sales b) Gross profit & Credit sales c) Gross profit & Cash sales 8. Opening stock is equal to Rs.10,000, Purchase Rs.2,00,000 and closing stock is Rs.5,000. Cost of goods sold is equal to a) Rs. 2,15,000 b)Rs. 2,10,000 c) Rs. 2,05,000 9. Operating ratio is equal to a) 100 – Operating profit ratio b) 100 + Operating profit ratio c) Operating profit ratio 10. Total sales is Rs,3,40,000 and the gross profit made is Rs.1,40,000. The cost of goods sold will be _____ a) Rs.2,00,000 b) Rs. 4,80,000 c) Rs. 3,40,000 11. Total sales of a business concern is Rs.8,75,000. If cash sales is Rs.3,75,000, then credit sales will be www.TrbTnpsc.com a) Rs.12,50,000 b) Rs.5,00,000 c) 12,00,000 12. Cost of goods sold is Rs.4,00,000 and average stock is Rs.80,000. Stock turnover ratio will be a) 5 times b) 4 times c) 7 times 13. Current assets of a business concern is Rs.60,000 and current liabilities are Rs.30,000.Current ratio will be a) 1 : 2 b) 1 : 1 c) 2 : 1 14. Equity share capital is Rs.2,00,000, Reserves & surplus is Rs.30,000. Debenture Rs.40,000 and the shareholders funds will be a) Rs.2,00,000 b) Rs. 2,30,000 c) Rs. 1,90,000 Chapter-5 Cash Budget I. Fill in the blanks: 1. The term ‘cash’ in cash budget stands for __________ and__________. 2. Cash budget is also called as __________. 3. There are __________ methods by which a cash budget is prepared. 4. The opening balance of cash in April is Rs.1250. Total receipts for the month are Rs.4300 and total payments amounted to Rs.3750. Opening balance of cash in May will be __________ 5. Cash budget is a useful tool for __________. 6. The closing balance of one month will be the __________ balance of the next month. II. Choose the correct answer: 1. Budget is an estimate relating to __________ period. a) future b) current c) past 2. Budget is expressed in terms of a) Money b) Physical units c) Money & Physical units 3. Cash budget deals with a) Estimated cash receipts b) Estimated cash payments c) Estimated cash receipts & Estimated cash payments 4. Purchase of Furniture is an example for a) Cash receipts b) Cash payments c) None of the above 5. The opening balance of cash in January is Rs.9,000. The estimated receipts are Rs.14,000 and the estimated payments are Rs.10,000. The opening balance of cash in February will be a) Rs. 21,000 b) Rs. 11,000 c) Rs. 13,000 Chapter-6 Partnership accounts-Basic Concept I. Fill in the blanks: 1. A sole trader business is owned and managed by ________ person. 2. Indian Partnership Act was enacted in the year ________. 3. Mutual and ________ agency is the essence of a partnership. 4. The profits and losses of the business will be shared among the partners in the ________ ratio. 5. Under fluctuating capital method, profit or loss in a year, will be transferred to the respective ________ accounts. 6. The capital accounts of partners may be ________ or fluctuating. 7. Under __________ capital arrangement, current accounts will not be maintained. 8. The debit balance of the current account, will be shown in the ________ side of the balance sheet. 9. Interest on partners’ capital is allowed, only when the ________ specifically provides for it. 10. Money lent to the business by a partner is credited to his ________ account and not his capital account. 11. Interest on partners’ loan should be paid, even if there is no ________ in a year. 12. Goodwill is an _______ asset. 13. The excess of average profit over normal profit is _______. 14. In the absence of partnership deed, no interest is to be charged on ________. 15. A partnership can be formed only for a ________ business. www.TrbTnpsc.com 16. The persons who entered into partnership are collectively known as ________. b) Choose the correct answer: 1. The minimum number of persons in a partnership firm is ______ a) one b) two c) seven 2. In a partnership business, agreement is _______ a) compulsory b) optional c) not necessary 3. In a partnership, partners share their profits and losses in _______ ratio a) their capital b) equal c) agreed 4. Under fixed capital system, the profits and losses of partners will be transferred to their _______ account a) current b) drawings c) capital 5. Interest on capital is calculated on the a) Opening Capital b) Closing Capital c) Average Capital 6. Current accounts for partners will be opened under a) Fixed capital method b) Fluctuating capital method c) Either fixed capital method or fluctuating capital method 7. In the absence of an agreement profits and losses are divided a) in the ratio of capitals b) in the ratio of time devoted by each partner c) equally 8. X and Y are partners sharing the profits and losses in the ratio of 2:3 with capitals of Rs.1,20,000 and Rs.60,000 respectively. Profits for the year are Rs.9,000. If the partnership deed is silent as to interest on capital. Show how profit is shared among X and Y. a) Profit : X - Rs. 6,000; Y - Rs.3,000 b) Profit : X - Rs. 3,600; Y - Rs.5,400 c) Profit : X - Rs. 3,000; Y - Rs.6,000 9. Where a partner is entitled to interest on capital such interest will be payable, a) Only out of profits b) Only out of capital c) Out of profits or out of capital 10. In the absence of partnership deed, partners shall a) be paid salaries b) not to be paid salaries c) paid salaries to those who work for the firm 11. Under fixed capital method salary payable to a partner is recorded a) in Current Account b) in Capital Account c) either in Current Account or Capital Account. 12. If a firm is maintaining both ‘Capital Accounts’ and ‘Current Accounts’ of the partners A and B. Additional capital introduced by B will be recorded in a) B’s Current Account b) B’s Capital Account c) either B’s Capital Account or Current Account Chapter - 7 Partnership accounts - Admission I. Fill in the blanks: 1. In the event of admission of a new partner, legally there is _______ of old partnership. 2. At the time of admission of a new partner, _______ profit ratio should be found out. 3. At the time of admission of a new partner, _______ of assets and liabilities should be taken up. 4. When the value of an asset increases, it results in _______. 5. When an unrecorded liabilities is brought into books, it results in _______. 6. The balance of revaluation account shows __________ on revaluation. 7. The revaluation profit or loss is transferred to the old partners’ capital accounts, in their _______. 8. The difference between old profit sharing ratio and new profit sharing ratio at time of admission is _______ ratio. 9. Undistributed Profit will appear on the _______ side of the Balance sheet. 10. At the time of admission, when goodwill is raised, the old partners capital account will be credited in the _______ ratio. www.TrbTnpsc.com 11. The partner admitted into partnership firm acquires two rights i.e., right to share in the _______ of the partnership and right to share in the _______. 12. The new profit sharing ratio will be determined by how the new partner acquires is _______ from the old partners. 13. Under _______ goodwill account is raised by crediting the old partners capital accounts in the old profit sharing ratio. II. Choose the correct answer: 1. When A and B sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2, they admit C as a partner giving him 1/3 share of profits. This will be given by A and B. a) Equally b) In the ratio of their capitals c) In the ratio of their profits. 2. In admission, profit from revaluation of assets and liabilities will be transferred to the capital accounts of the old partners in the a) Old profit sharing ratio b) Sacrifice ratio c) New profit sharing ratio 3. If new share of the incoming partner is given without mentioning the details of the sacrifice made by the old partners then, the presumption is that old partners sacrifice in the _______. a) Old profit sharing ratio b) Gaining ratio c) Capital ratio 4. In order to maintain fair dealings, at the time of admission, it is necessary to revalue assets and liabilities of the firm to their ______. a) cost price b) cost price less depreciation c) true value 5. On admission of a partner if goodwill account is to be raised this should be debited to a) Partners’ capital account b) Goodwill account c) Revaluation account 6. When A and B sharing profits and losses in the ration 3:2, admit C as a partner giving him 1/5 share of profits. This will be given by A and B. a) Equally b) in their capitals ratio c) in their profit sharing ratio 7. On admission of a new partner, increase in value of assets is debited to a) Asset account b) Profit & Loss adjustment account c) Old partners capital account 8. On admission of a new partner balance of General Reserve Account should be transferred to the capital account of a) all partners in their new profit sharing ratio b) old partners in their old profit sharing ratio c) old partners in their new profit sharing ratio 9. The old partners share all the accumulated profits and reserves in their a) new profit sharing ratio b) old profit sharing ratio c) capital ratio 10. The reconstitution of the partnership requires a revision of the_______ of the existing partners a) Profit sharing ratio b) Capital ratio c) Sacrificing ratio 11. ________ ratio is computed at the time of admission of a new partner a) Gaining ratio b) Capital ratio c) Sacrificing ratio Chapter - 8 Partnership accounts – Retirement I. Fill in the blanks: 1. The retiring partner should be paid off or the amount due to him, will be treated as his _______ to the firm. 2. At the time of retirement of partners, the existing partners stand to _______. 3. If the value of liabilities decrease, it results in __________item. 4. At the time of retirement, the increase in the value of goodwill will be transferred to the _______ side of the capital accounts of all the partners. 5. At the time of retirement, the profit on revaluation of assets and liabilities will be transferred to the _______ side of the capital accounts of all the partners. 6. At the time of retirement, the revaluation profits of business will be shared by _______ partners. www.TrbTnpsc.com 7. In the absence of any specific agreement between the partners, partners loan to the firms will carry an interest at the rate of ______ percentage. 8. The accumulated reserves will be transferred to the old partners Capital account in the _______ ratio at the time of his retirement 9. The amount due to the retiring partner is either ______ or is paid in ______. 10. _______ is calculated to determine the amount of compensation to be paid by each of the continuing partners to the outgoing partners. 11. A, B and C shares profit as 1/2 to A, 1/3 to B and 1/6 to C. If B retires then, the new profit sharing ratio is _________. 12. Sacrificing ratio is the ratio in which the old partners (existing) have agreed to sacrifice their _______ in favour of _______. II. Choose the correct answers: 1. At the time of retirement of a partner, calculation of new profit ratio is _______ a) not necessary b) necessary c) optional 2. Undistributed profits and losses ______ transferred to all the partners account at the time of retirement of a partner. a) should be b) should not be c) may be 3. At the time of retirement Balance sheet items like Profit & Loss account and General Reserve must be transferred to a) Revaluation A/c b) Partner’s Capital A/c c) None of the above 4. If the goodwill account is raised for Rs.30,000, the amount is debited to: a) The capital accounts of partners b) Goodwill Account c) Cash Account 5. ________ ratio is calculated by taking out the difference between new profit sharing ratio and old profit sharing ratio. a) Gaining b) Capital c) Sacrifice 6. On retirement of a partner goodwill amount is credited to the account of a) only retiring partner b) all partners including retiring partner c) only remaining partner 7. A, B and C are sharing profits in the ratio of 2/5 : 2/5 : 1/5. C retired from business and his share was purchased equally by A and B. Then new profit sharing ratio shall be a) A – 1/2 & B – ½ b) A – 3/5 & B – 2/5 c) A – 2/5 & B – 3/5 8. When the amount due to an outgoing partner is not paid immediately, then it is transferred to a) Capital A/c b) Loan A/c c) Cash A/c 9. If the amount due to the outgoing partner is transferred to loan account then he is entitled to interest at ______ untill it is paid out. a) 9% b) 5% c) 6% Chapter-9 Company accounts I.Fill in the Blanks: 1. Companies have been defined in Section ___________ of the Companies Act, _______. 2. __________ is considered as the official signature of the company. 3. The management of a company is done by __________. 4. The liability of share holders are __________ in a company. 5. Audit of accounts are done by practicing chartered accounts who are appointed by __________ at the __________. 6. ________ is the maximum amount of capital that can be issued by a company. 7. Nominal capital is the capital mentioned in the _______________ of the company. 8. That part of the authorised capital not offered for subscription to the public in known as _________. 9. Reserve capital can be issued only at the time of __________. 10. A public issue can not be kept open for more __________ days. 11. Minimum subscription that should be received by the company is ______% of the issued capital. www.TrbTnpsc.com 12. When excess application money is adjusted towards allotment it is called as __________ allotment. 13. There should be a time gap of ____________ between two calls. 14. Capital Reserve represents __________ profit. 15. Forfeited shares have to be reissued at a price __________ than the face value. 16. Securities premium is shown in the __________ side of the Balance Sheet. II. Choose the correct answer: 1. According to Companies (Amendment) Act 2000, a company limited by share can issue _______ kinds of shares. a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 2. The public issue must be kept open for atleast a) 3 days b) 5 days c) 7 days 3. Minimum amount to be collected by a company as application money according to SEBI is _____% of the issue price. a) 10% b) 25% c) 50% 4. When more number of applications are received than that are offered to the public, it is called ____________. a) Over subscription b) Under subscription c) Full subscription 5. The maximum calls that a company can make is a) one b) two c) three 6. According to Table A, interest charged on calls-in-arrears is______%. a) 4% b) 5% c) 6% 7. According to Table A, interest charged on calls in advance is_______%. a) 4% b) 5% c) 6% 8. A company can issue shares a) at par only b) at par and at premium c) at par, at premium & at discount 9. When the company issue shares at a price more than the face value it is called as an issue at ________. a) Par b) Premium c) Discount 10. Normally companies can issue shares at ________% of discount a) 5 b) 10 c) 20 11. When shares are forfeited the share capital of the company will_______. a) remain same b) reduce c) increase 12. Securities premium will appear in the ________ side of the Balance Sheet. a) Asset b) Liability c) Assets & Liabilities 13. The balance of forfeited share account is________ in the Balance Sheet. a) added to paid up capital b) added to authorised capital c) deducted from paid up capital. 14. Calls-in-arrears is shown in the Balance Sheet as a) deduction from called up capital b) addition to paid up capital c) addition to issued capital 15. Capital Reserve is shown on the ________ side of Balance Sheet. a) Asset b) Liability c) Both www.TrbTnpsc.com Chapter-1 1.The Trial Balance as on 31.3.2004 shows Capital Rs 6,00,000 and Drawings Rs 40,000. Interest on Drawings at 5% p.a is _______________ 2.Trial Balance as on 31.3.2005 shows sundry debtors Rs 1,05,000.As per given adjustment if Rs 5,000 is to be written off as bad debts, the provision for bad and doubtful debts at 5% will be_______________ 3.Trial Balance as on 31.3.2005 shows Bank Loan Rs 1,00,000 at 10% p.a on 1.4.2004.Interest paid Rs 4,000 .Interest outstanding is _________ 4.Trial Balance as on 31.3.2004.shows sundry debtors Rs 1,25,000 as per given in adjustment if Rs 5,000 is to written off as bad debts the provision for bad and doubtful debts at 5% will be_____________ 5.Trial Balance shows bank deposits Rs 3,00,000 @ p.a on 1.1.2006. Interest received is Rs 25,000.accrued interest is Rs ___________on 31.12.2005 6. Trial Balance as on 31.12.2005 shows sundry debtors as Rs 69,000 .Write off bad debts Rs 4,000 .The amount of bad and doubtful debts at 5% will be ___________ 7.Trial Balance shows bank loan Rs 7,00,000 @ 10% on 1.4.2003.Interest paid Rs 50,000 interest outstanding is Rs ________________as on 31.3.2004 8.Trial balance as on 31.3.2005 shows sundry debtors as Rs 50,500.Also write off Rs 500 as bad debts. The amount of provision for bad and doubtful debts at 5% will be______________ 9.Trial balance shows on 31.3.2005 investment @ 10% Rs 2,00,000.Interest received Rs 15,000.Accrued interest is___________ 10.The Trial Balance as on 31.3.2005 shows sundry debtors Rs 30,800. Write off Rs800 as bad debts. The amount provisions for bad and doubtful dents at 5% will be______ 11.The Trial Balance shows as on 31st March ,2004 Sundry debtors Rs 30,500. Adjustment. Write off Rs 500 as bad debts. The provision for bad and doubtful debts at 5% is___________ 12.The Trial Balance as on 31.3.2004 shows sundry creditors Rs 25,000. The amount pf provision for discount on creditors @2% will be is___________ 13.The Trial Balance as on 31.3.2006 shows capital Rs 5,00,000 . Interest on capital at 6% p.a is ____________ 14.The Trial Balance as on 31.3.2006 shows sundry debtors Rs 25,000. Write off Rs 1,000 as bad debts. The amount of provision for bad and doubtful debts as 5% will be___________ www.TrbTnpsc.com 15.The Trial Balance as on 31.3.2004 shows as on capital Rs 5,00,000 and drawings Rs 50,000.Interest on drawings @6% will be__________ 16. Trial Balance Chapter-2 1.Debtors on 1st April,2004 Rs 50,000 and on 31st march Rs 60,000 .Cash received from debtors during the year Rs 1,00,000.Then credit sales made during the year is 2.Creditors on 1st April Rs 1,00,000 and on 31st March 2005 Rs 1,10,000 cash paid to creditors during the year Rs 1,90,000.Then credit purchases made during the year is _____________ 3. The total assets of a proprietor are Rs 5,00,000 .His liabilities are Rs 3,50,000.His capital in the business is __________ 4. Creditors on 1.1.2005 Rs 60,500 and on 31.12.2005 Rs 65,000 .Cash paid to creditors during the year Rs 1, 04,500 Thus credit purchases made during the year is___________ 5. Debtors on 1.4.2004 Rs 39,600 and on 31.3.2005 Rs 49,900.Cash received from debtors during the year Rs 69, 500. Thus credit sale made during the year is _________ 6.Creditors on 1st April 2002 Rs 8,000 and on 31st March 2003 Rs 13,500 .Cash paid to creditors Rs 31,000.Credit Purchases made during the year is ___________ 7.Creditors on 1st April 2004 Rs 1,50,000 and 31st March 2005 Rs 1,80,000 Cash paid to sundry creditors Rs 45,000. Thus the credit purchases made during the year is___________ 8.A firm has capital Rs 60,000 and liabilities Rs 40,000.Then its assets_________ 9. Creditors on 1.4.2006 Rs 80,000 and on 31.3.2007, Rs 65,000, Cash paid to creditors during the year is RS 1,10,000. Then the credit purchases during the year is ____________ 10.In a business closing capital is Rs 20,000,Drawings Rs 5,000. Additional Capital Rs 7,000,Profit Rs 3,000___________is the opening capital Chapter-3 1.Selling price of a plant is Rs 10,00,000 .If loss on sale is Rs 1,00,000 the book value of the plant is ______________ 2.Cost of an asset is Rs 3,00,000 Rate of depreciation is at 10% p.a Depreciation is calculated under straight line method Book value of asset at the end of third year is www.TrbTnpsc.com 3.Selling price of a plant is Rs 5,00,000.If profit on sale two items is Rs 50,000 The book value of the plant is ________ 4.Cost of an asset is Rs 2,00,000.Rate of depreciation is at 10% per annum .Depreciation is calculated under Diminishing Balance method. Book value of asset at the end of third year is _______________ 5.Selling price of a fixed assets is Rs 75,000 .The book value of the asset at the time of sale is Rs 60,000.Profit on sale is Rs _____________ 6.Cost of an asset Rs 5,00,000 rate of depreciation is 10% p.a Depreciation is provided under written down value method. Book value of the asset at the end of second year is _____________ 7.Selling price of plant Rs 5,00,000 profit on sale was Rs 59,000. The book value of the plant is____________ 8.Under the written down value method if depreciation is at rate of 10% p.a on Rs 10,000, then the book value of the asset at the end of third year is____________ 9.Total amount of depreciation provided on the written down value method at the rate of depreciation 10% p.a on Rs 20,000 for first three years will be___________ 10. Total amount of depreciation provided on the straight line method at the rate of 10% p.a on Rs 50,000 for first three years will be_____________ 11. Cost of an asset is Rs 4,00,000. Rate of depreciation is at 10% p.a. Depreciation is calculated under written down value method. Book value of the asset at the end of third year is _________ Chapter-4 1.Current assets of a business concern is Rs 60,000 and current liabilities are Rs 30,000,Current ratio will be____________ 2.The opening stock are Rs 72,000 and closing stock are Rs 78,000. Then the average stock is_____________ 3.Liquid liabilities of a business is Rs 80,000, Bank overdraft RS 25,000. Current liabilities will be______________ Chapter-5 www.TrbTnpsc.com 1.The opening balance of cash in January is Rs 15,000.The estimated cash receipts are Rs 20,000 and the estimated cash payments are Rs 10,000.The opening balance of cash in February will be ____________ Chapter-6 1.A , B and C are sharing profits in the ratio of 5:3:2.If B retires the new profit sharing ratio of A and C is______________ 2. A , B and C were sharing profits in the proportion of ½, 1/3,and 1/6 .If A retires the new profit sharing ratio of B and C is______________ Chapter-9 1.A company issued 2,00,000 shares of Rs 10each to the public but only 1,50,000 shares were subscribed .Its subscribed capital is ___________________ 2.The directors of a company forfeited 100 shares of Rs 10 each on which the final call money of Rs 3 was not paid. Later these shares were reissued for Rs 800 capital reserve will be________ 3.A company had authorized Capital of Rs 4,00,000 divided into 4,000 shares of Rs 100 each .It offered 3,000 shares to the public. Its issued capital is__________ 4.The directors of a company forfeited 500 shares of Rs 10 each on which the final call money of Rs 2 was not paid later these share issued at Rs 8 per share Capital Reserve will be __________ 5.U ltd issued 70,000 shares of Rs 10 each fully subscribed by public Rs 7 per shares been called up. Then Rs __________will represent uncalled capital 6.G ltd issued 1,00,000 shares of Rs 10 each ,fully subscribed by public . Rs 7 per share has been called up. Then Rs ___________will represent uncalled capital 7.The amount credited to share forfeited account is RS 3,000. The discount on reissue of forfeited shares is Rs1,500.capital reserve will be_________ 8.A ltd company issued 50,000 shares of Rs 10 each fully subscribed by public Rs 8 per shares been called up, then __________will represent uncalled capital. 9.The amount credited to share forfeiture account is Rs 6,000. The loss on reissue of forfeited shares is Rs 3,000, Capital reserve will be_________ 10.A company issued 20,000 shares of Rs 100 each to the public, but only 18,000 shares were subscribed, Its subscribed capital is Rs __________ www.TrbTnpsc.com 11.The amount credited to share forfeiture account is Rs 5,000.The discount on the reissue of forfeited shares is RS 1,000.capital reserve will be ____________ COMMERCE Lesson:1 Organisation I. Choose the correct answer: 1. Which of the following is not the characteristic of sole proprietorship a] Single ownership b] One man control c] Whole profit to proprietorship d] Non-flexibility 2. What is the advantage of sole proprietorship a. Small capital b. Hasty decision c. Limited capital d. Limited managerial ability 3. The agreement of partnership a. Must be oral b. Must be in writing c. Must be writing in the stamp paper d. Can be either oral or in writing 4. Partnership may come into existence a. By the operation of law b. By an express agreement c. By an express or implied agreement d. By inheritance of property 5. Management of a Jointstock company is entrusted to. a. The Registrar of companies b. The Board of Directors c. The shareholder d. The debenture holders 6. Registration is compulsory in the case of a. A Sole trader b. A partnership c. A joint stock company d. A joint hindu family business 7. In a co-operative society a. One share one vote principle is followed b. One man one vote principle is followed c. A member must have 2 votes d. Shares are transferable. 8. Co-operative society can be started a. Only in villages b. In towns and villages c. Only in cities d. Only in State headquarters 9. The most suitable form of organisation for operating defence industries is a. Government Company b. Public corporation c. Departmental organization d. Board organization 10. The share capital of the government company must not be less than a. 75% b. 60% c. 95% d. 51% 11. A multinational company is also known as a. Global giant b. Partnership c. Co-operative society d. Public corporation 12. Membership by birth is main feature in a. Sole trader b. Joint Hindu family business c. Co-operative society d. Partnership II Fill in the blanks 1. Division of work is called ____________ www.TrbTnpsc.com 2. Delegation means the ___________ of part of the work 3. The liability of sole trader is __________________ 4. Partners share profits and losses _______________ 5. In India registration of partnership is _____________ 6. In co-operative society all members are ________ 7. A company is regarded as a __________________ 8. Broadcasting comes under____________ form of organization 9. Public corporation is known as _________________ corporation 10. Tamilnadu Electricity Board is the example of ____________ 11. Government policy is also favourable towards _____________ 12. Government Company employees are not _______________ Lesson: 2 Sole Trader I. Choose the correct answer: 1. Sole trading business can be started by: a) At least two persons b) At least seven persons c) Any one person 2.The liability of a soletrader is: a) Limited only to his investment in the business b) Limited to total property of the business c) Unlimited 3.Sole proprietorship is suitable for: a) Large scale concerns b) Medium scale concerns c) Small scale concerns 4.Decision-making process in soletrading business is: a)Quick b) Slow c) Neither quick nor slow 5.A soletrader: a) Cannot keep his business secrets b) Can keep his business secrets c) None of the above Lesson:3 Partnership I. Choose the correct answer: 1.A partnership is formed by a) Agreement b) Relationship among persons c) The direction of government 2. The basis of partnership is a) Utmost good faith b) Money available for investment c) Desire to work together 3. A partnership firm may be registered under a) 1949 Act b) 1956 Act c) 1932 Act 4. Registration of partnership is a) compulsory b) optional c) not necessary 5. In partnership there exists a relationship of a) principal and agent b) owner and servant c) employer and employee. II. Fill in the blanks 1. The profit and loss of a partnership firm is shared in the _______ among the partners. www.TrbTnpsc.com 2. The partners liability in India is ___________________ 3. The maximum number of members in non-banking firm is_______________ 4. A partner who does not take part in the working of the firm is called________ partner. Lesson:4 Joint Stock Companies-1 I. Choose the correct answer: 1. Registration of a joint stock company is a.) compulsory b) optional c) compulsory for public limited companies and optional for private limited companies d) optional for public limited companies and compulsory for private limited companies 2. The minimum number of members for a public limited company is a) 2 b) 3 c) 7 d) 10 3. The liability of shareholders of a private limited company is limited to a) the paid up value of the shares b) amount remaining unpaid on the shares c) the extent of private assets d) amount called up 4. A private limited company can commence business a) immediately on receiving the certificate of incorporation b) only after the certificate of commencement of business is received c) on getting name approval from the Registrar d) on filing all the documents necessary for formation with the Registrar 5. The existence of a company comes to a close a) on the death of all its promoters b) on death of all the directors of the Board c) on transfer of shares by most of its original members d) none of the above 6. Table A of the Companies Act is a a) model minutes book b) model form of balance sheet c) model of Articles of Association d) model of memorandum of association 7. Which of the following documents define the scope of a company’s activities? a) Momorandum of Association b) Articles of Association c) Prospectus d) Statutory Declaration 8. Which of the following is created by a Special Act of Parliament or in State Assemblies? a) Chartered company b) Foreign company c) Government company d) Statutory company 9. Which of the following companies must file with the Registrar a statement in lieu of prospectus? a) a public limited company which raises funds from the public through issue of shares b) a public limited company which has made arrangement for racing its capital from directors and their relatives c) a private limited company (d) all of them 10. The minimum subscription specified in the prospectus must be received within a) 90 days b) 120 days c) 130 days d) 60 days www.TrbTnpsc.com 11. A preference share has priority in a) dividend only b) only in return of capital at the time of winding up c) voting rights d) both dividend and return of capital on winding up 12. Shares can be forfeited for a) Non-payment of any debt due to the company b) Not attending three annual general meetings consecutively c) For non payment of call money d). for violent activities at the annual general meetings 13. Where the shares are issued at a discount and the nominal value of share is Rs.100, the maximum discount that can be allowed is a) Rs.5 b) Rs.10 c) Rs.20 d) Rs.15 14. Debenture holders of a company are its a) Creditors b) Members c) Credit customers d) Borrowers 15. Debenture holders are entitled to receive interest in the following circumstances a) when there are profits b) when shareholders also get dividend c) every year irrespective of loss d) all the above II.Fill in the blanks with suitable word or words. 1. The minimum of a number of members in a public limited company is ____________ 2. The liability of a member of a company limited by guarantee is________ 3. The minimum number of members in a private company is _____ 4. A company, the members of which not less than fifty one percent of the paid-up-share capital is held by a state Government, is known as ________ company. 5. The company, which need not have separate Articles of Association of its own is ___________company limited by shares. 6. The manner in which the internal management of a company carried on is contained in _____________ 7. An advertisement inviting the public to buy the debenture of a public company is known as _____________ 8. Preference shares which carry a right to arrear dividend are known as ___________ 9. Such shares, as are entitled to a further dividend in addition to the usual fixed rate of dividend are known as _________shares. 10. A private company should have at least _________directors. 11. The aggregate nominal value of qualification shares shall not exceed _______ rupees. 12. When a company has issued shares of Rs. 6000 each only, the minimum number of qualification shares that a director should hold is______________ Lesson:5 Joint Stock Companies-II I. Choose the correct answer: 1. First directors are appointed by a) members in statutory meeting b) members in the first Annual General meeting c) by being named in the Articles of Association d) Registrar of Companies 2. A director is acting as a) agent of the company b) trustee of the company c) chief executive officer of the company d) all of these 3. A person can hold directorship of not more than _________ public limited companies www.TrbTnpsc.com a) 10 b) 15 c) 20 d) limitless 4. The value of qualification shares of a director in a public limited company shall not exceed a) Rs.5000 b) Rs.5,00,000 c) Rs.50,000 d) Rs.500 5. The overall maximum managerial remuneration in a public limited company shall not exceed a) 11% of net profits b) 11% of paid up capital and free reserves c) 5% of net profits d) 5% of paid up capital and free reserves 6. A company secretary is appointed by a) Government b) The Institute of Company Secretaries of India c) The Board of Directors d) Shareholders in Annual General Meetings 7. A company should compulsorily appoint a qualified company secretary, having a paid up capital of more than a) Rs. 5 Lakh b) Rs.50 Lakh c) Rs.25 Lakh d) Rs.15 Lakh 8. Which of the following must hold a statutory meeting ? a) Statutory Companies b) Private Limited Companies c) Public Limited Companies d) Chartered Companies 9. The interval between two annual general meetings shall not exceed a) 15 months b) 12 months c) 18 months d) 20 months 10 Which of the following business is not transacted at the Annual General Meeting a) appointment of auditors b) issue of debentures c) appointment of directors in place of those retiring d) declaration of dividend 11. Who can call Extraordinary General Meeting ? a) Company Law Tribunal b) Board of Directors on its own or on the requisition of members c) By the requisitionists themselves on Board’s failure to convene d) all of these II. Fill up the blanks with suitable word or words 1. Directors act as _________trustess and officers of the company 2. The share holders are the real ______________ of the company 3. First directors are usually named in the ____________ 4. Statutory meeting must be held not later than _____________ and not earlier than __________ from the date on which a public company is entitled to commence business 5. A statutory report must be sent to every member of the company atleast _______________days before the meeting is to be held. 6. The time between two consecutive annual general meetings should not exceed _______________ months. 7. Altering the Articles of Association requires ___________ Resolution 8. A person Appointed to attend a meeting on behalf of a share holder is known as _____ 9. The Quorum for a General Meeting of members of a public company is _____________ 10. The minimum number of members required for a meeting is known as ____________ 11. Auditors are generally appointed and their remuneration, fixed at the ______________ meeting. 12. The notice calling the annual general meeting, must, be given to all its members at least _______________ days before the date of the meeting. www.TrbTnpsc.com Lesson:6 Stock Exchange I. Choose the correct answer: 1. The first issues are floated in a) Primary market b) Secondary market c) Commodity market d) Regulated market 2. The popular method of sale of new shares in India is a) Public issue b) Offer for sale c) Managing brokers d) Underwriting 3. Stock exchanges deal in a) Goods b) Services c) Financial securities d) Country’s currency 4. Number of recognised stock exchange in India a) 2 b) 21 c) 22 d) 24 5. Stock exchange allow trading in a) All types of shares of any company b) Bonds issued by the Government c) Listed securities d) Unlisted securities 6. Jobbers transact in a stock exchange a) For their clients b) For their own transactions c) For other brokers d) For other members 7. A pessimistic speculator is a) Stag b) Bear c) Bull d) Lame duck 8. An optimistic speculator is a) Bull b) Bear c) Stag d) Lame duck 9. Securities Contract Regulation Act was passed in a) 1952 b) 1956 c)1964 d) 1966 10. SEBI is formed as per a) Securities contract (Regulation) Act b) Securities and Exchange Board of India Act c)Companies Act d) Indian constitution 11. A bull operator believes in a) Increase in prices b) Decrease in prices c) Stability in prices d) No change in prices 12. Stock exchange …………… speculation in shares a) Does not allow b) discourage c) encourage d) prohibits 13. A cautious speculator is known as a) Stag b) Bull c) Lame duck d) Bear 14. A stock exchange is a place to a) Exchange one security for another b) Buy and sell financial securities c) Float new shares d) Buy and sell stock of goods. 15. SEBI has the following number of members including chairman. a) 5 b) 7 c) 6 d) 8 II. Fill in the blanks: 1. Large scale undertakings are organised in the form of _______. 2. Joint stock companies require __________________________ www.TrbTnpsc.com 3. The long term capital required by the company is divided into small units of fixed amount called __________ 4. Shares represent _______________ interest. 5. Debentures denote ________________ interest. 6. _______ is an acknowledgement for raising loan from the public. 7. Primary market is concerned with ___________ 8. Secondary market deals with ________ traded in primary market. 9. Companies are assisted by _____________to make new issues. 10. _____________ is a commonly used method of issuing shares. 11. __________________act as intermediary to float new shares. 12. ________is an invitation to the public to subscribe for the shares. 13. After allotment of shares, allottees become the ___________of the company. 14. Application money should not be less than ________ percent of the value of a share. 15. Minimum subscription is fixed at _______of the issued capital. 16. The volume of business in secondary market depends on____ 17. Secondhand securities are traded in _____________________ 18. There are __________ regional stock exchanges in India. 19. Inclusion of securities in the official list of stock exchange is called ____________ 20. Listing is ________________ for public companies. 21. Cleared securities are also called _______________ 22. _____________ order gives a freehand to the brokers of a client to buy or sell a particular security for any price. 23. Ready delivery contracts are also called as ______________ 24. Investors retain securities for ____________________period. 25. _____are the employees of the members of a stock exchange. 26. Stag is called ______________ 27._______________ is the supervisory body established to regulate Indian stock market. 28._______________ enables small investors to participate in the investment on share capital of large companies. 29. ______________ act as a substitute for initial public offering. 30. BOLT is the online trading system in use at ______________ stock exchange. Lesson-7 Co-operative Societies I. Choose the correct answer: 1. Co-operative society can be started a) Only at villages b) In towns and Villages c) Only in cities d) Only in urban areas 2. The minimum number of members required to from a co-operative society is a) 2 b) 7 c) 10 d) 25 3.Dividend is declared in a co-operative store to its members. a) Share capital b) Number of shares purchased c) Amount of patronage given d) None of the above 4. The basic objective of a co-operative society is. a) Earn profit b) Organise some essential service for the benefit of its member c) Organize essential services to the community. d) Arrange for enough of quality goods for the community 5. In a co-operative society, the shares of a member www.TrbTnpsc.com a) Can be transferred b) Can be repaid c) Cannot be transferred d) None of the above 6. Maximum membership in a co-operative society is a) 50 b) 60 c) 100 d) Unlimited 7. A co-operative super market supplies a) Credit b) service c) Goods d) Cash 8. Consumers co-operation was first successful in a) England b) USA c) Swiss d) India 9. Minority interest can be protected in a) Sole trader b) Partnership c) Co-operative societies d) Public Company 10. Central Co-operative bank is established at a) Villages b) Districts c) State head quarters d) Urban areas II. Fill in the blanks 1. The Latin word co-operari means ______________________ 2. The father of the co-operative movement was ____________ 3. Only ____________ of the profits to be distributed as dividend 4. The liability of the members of a Co-operative Society is _______ 5. Transfer of shares are possible in_______________ and not possible in ___________ 6. Management of a Co-operative Society is fully _______________ 7. Service is the main objective of _____________________ 8. Agriculture credit societies are classified into a). Rural credit society b). ____________ 9. An industrial co-operative is organized by _________________ 10. Super market refers to large scale ____________________ Lesson:8 GOVERNMENT IN BUSINESS I. Choose the correct answer: 1. Government companies are registered under a) Special statute of Government b) Companies Act, 1956 d) Royal charter d) Order of the Government 2. In a public corporation the management has a) Limited freedom b) No freedom of action c) Controlled freedom d) Unrestricted freedom of action. 3. For the efficient working of state enterprise the form of organisation generally considered suitable is a) Departmental organisation b) Public corporation c) Government company d) None of these 4. Public can also subscribe to the share capital of a) Public corporation b) Departmental undertaking c) Government company d) None of these 5. In a government company the share capital of the government must not be less than a) 51% b) 60% c) 75% d) 90% II. Fill in the blanks with suitable words: 1. ___________ is an undertaking owned and controlled by Government. 2. The primary aim of state enterprises is ___________ www.TrbTnpsc.com 3. Public corporations are created by _______of central or state Government. 4. In a Government company atleast ____________shares are owned by the Government. 5. The oldest from of public enterprise is ————————— 6. When the Government takes over an existing private concern it is called ____________ 7.The most suitable form of organisation for manufacturing defence goods is __________ 8._______________ checks concentration of economic power in the hands of few. 9. Exploitation of consumers and employees is a feature of _____ 10. Public corporations are managed by a ___________nominated by the Government. Prepared by Arjunan PG teacher in Accountancy SVNM School Kangayam www.TrbTnpsc.com