CHAPTER 2 BASIC CHEMISTRY
advertisement

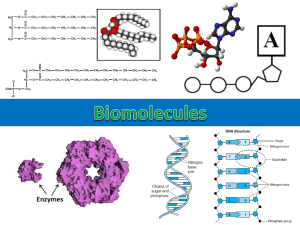
CHAPTER 2 BASIC CHEMISTRY MAJOR ELEMENTS OF LIFE Ezymatic action STRUCTURE OF AN ATOM THE 4 MAJOR ELEMENTS OF LIFE 3 ADDITIONAL MAJOR ELEMENTS Figure 02.03: Formation of an ion Chemical Bonding Figure 02.04: Chemical bonding Hydrogen bonds form between polar groups or molecules • Polar molecules • Meaning and example in water Figure 02.05: Hydrogen bonding between water molecules Covalent bonds share electrons 2.3 Water and pH Figure 02.06: Solutes dissolve in water ACID, BASE, AND SALT Figure 02.09: Organic compounds in cells 2.4 Major Organic Compounds of Living Organisms Functional groups define molecular behavior • Major functional groups: Hydroxyl (—OH) Methyl (---CH3) Amino (—NH2) Sulfhydryl (—SH) Carboxyl (—COOH) Phosphate (—OPO3-2) Carbohydrates provide energy and building materials • • • • • Chemical structure and uses Monosaccharides Disaccharides Polysaccharides Importance in microorganisms Structural Formulas for Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, and a Polysaccharide LIPIDS • One glycerol plus 3 fatty acids covalently linked together will make one fat molecule. STRUCTURE OF GLYCEROL AND ONE FATTY ACID ONE FAT MOLECULE CONSISTS OF ONE GLYCEROL AND 3 FATTY ACIDS Lipids store energy and are components of membranes PHOSPHOLIPID STRUCTURE a major component of plasma membranes Proteins are the workhorses of cells • Chemical components and combination of amino acids • Peptide bond formation • Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary protein structure and examples AMINO ACID STRUCTURE Figure 02.16: Formation of a dipeptide by dehydration synthesis Examples of Amino Acids MORE AMINO ACIDS Protein Folding Nucleic acids DNA and the RNA’s DNA The Molecular Structures of Nucleotide Components and the Construction of a DNA STRUCTURE OF ATP