Catalase Enzyme Lab
advertisement

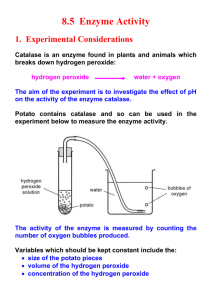
Catalase Enzyme Lab Catalase Enzyme Lab purpose: Explore how changing the environmental conditions of an enzyme affect the enzymes’ activity. In this lab the enzymes’ activity can be indirectly measured through temperature changes which indicate a release or intake of heat energy from the chemical reaction which the enzyme is catalyzing. Catalase Lab Background: of catalase enzyme so – the catalase enzyme for this lab will be extracted from chicken liver. All enzymes including Catalase enzyme only fold into their active shape under specific environmental conditions. An enzymes shape can be denatured by changes in temperature, pH and salt concentration. Why? Because the all changes interfere with the hydrogen bonds that help keep the enzyme folded properly (see figure3). Figure 1 catalase enzyme 2 Hydrogen peroxide 2 water + oxygen + heat energy Hydrogen Peroxide Hydrogen Peroxide Oxygen gas – O2 This is the Catalase enzyme in standard water environment Many cells produce Hydrogen peroxide as a toxic by product of their metabolic reactions. Cells also produce catalase enzyme which assists in the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into harmless water and oxygen gas (see figure 1). This reaction is exergonic -- energy Products: releasing (see figure 2). Water and Oxygen gas When you pour hydrogen Fig. 2 peroxide on a cut the catalase enzyme released Reactant: out of your damaged skin Hydrogen Peroxide cells and from your blood stream spead up Energy released in the the break down of form of Heat hydrogen peroxide and the observed bubbling is from the product oxygen. The liver is a good source This is the denatured Catalase enzyme in Acidic environment Figure 3: cartoon illustration comparing Standard Catalase enzyme to Acidified Catalase enzyme Cell Biology State standard 1b Students will learn that enzymes are Proteins that catalize( speed up) chemical reactions without being used up Students will learn that enzyme’s activity depends on temperature and pH (acidic or alkali) conditions of their environment Catalase Enzyme Lab Guide catalase enzyme 2 Hydrogen peroxide 2 water + oxygen + heat energy Results Data Table: Procedure: 1. Using a pencil, label one test tube HP for Control (hydrogen peroxide alone), another test tube needs to be labeled NC (catalase enzyme with no acid) and the final test tube AC (for acidified catalase enzyme) Temperature of Temperature of 8ml of 8ml of Control Hydrogen peroxide (Hydrogen Peroxide) combined with ½ ml of Normal Catalase Time (Sec) Control 0 seconds Temperature of 8ml of Hydrogen peroxide combined with ½ ml of Acidified Catalase NC with a pH of ____ AC with a pH of ____ C◦ C◦ C◦ ) (Before Enzyme is added! 2. Make Acidified Catalase: In the mixing container prepare the acidified Catalase by pippetting 2ml of Normal Catalase and 2ml of Acetic acid together. Let sit for 5 minutes (continue on with step 3 will not need until step 9) 30 seconds C◦ C◦ C◦ 60 seconds C◦ C◦ C◦ 90 seconds C◦ C◦ C◦ 3. Use the Graduated cylinder to measure 8 ml of Hydrogen peroxide into each test tube 120 seconds C◦ C◦ C◦ 4. Gather the data on the control: Record the temperature of the HP test tube of just hydrogen peroxide every 30 seconds for 120 seconds 5. Record the temperature of the NC (Normal catalase )test tube with just the hydrogen peroxide alone. 6. Leave the thermometer in the NC test tube and using the pipette to add ½ ml of Catalase to the NC test tube. 7. Swirl the NC test tube to ensure that the enzyme is mixed with the hydrogen peroxide. 8. Record the temperature every 30 seconds for 120 seconds. Conclusion Questions: 1. How did the Acetic acid affect the catalase enzyme (what did it do the structure of the enzyme and what was the temperature)? 2. Did the temperature make a difference in the level of bubble activity in the tests you did? 3. 2H2O2 2H2O + O2 is the chemical equation of the process you witnessed in this lab. What were the bubbles in this experiment made of? 4. What temperature was catalase most reactive? Mammals internal body temperature is close to 370C. How would body temperature affect catalse activity? 5. Hydrogen peroxide is a toxic molecule found in the cells of your body, why would most human cells have the enzyme catalase. 9. Repeat steps 4-7 with the ACIDIFIED CATALASE in the AC test tube 6. Identify the sources of error in the experiment (what went wrong in the lab and messed up your data)?