Periodic Table Presentation Lesson
advertisement
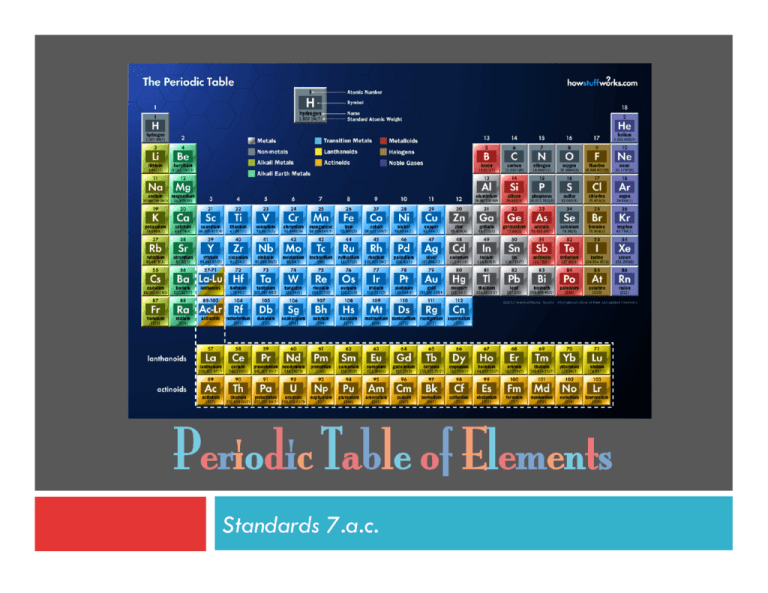
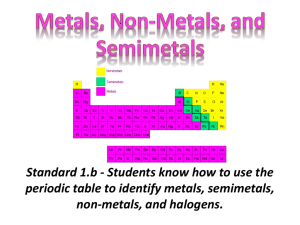
Periodic Table of Elements Standards 7.a.c. Topic 1: Elements and Their Properties Standards 7.c. Elements An element is a pure substance of one type of atom with a specific atomic number. ¨ Elements are represented by symbols with atomic numbers and atomic masses. ¨ The atomic number tells the number of protons. ¨ Element Properties ¨ ¨ Not only do elements differ based on their atomic number, but they also differ based on their properties. Every element has a different melting temperature, boiling point, density, hardness, electrical conductivity, and thermal conductivity. Element Properties No two elements will have the same properties. ¨ For example, Calcium has a density of 1.54g/mL with no other element having this same density. ¨ Think-Check ¨ A. B. C. What makes an oxygen element different from a calcium element? The atomic number which gives the number of neutrons. The atomic number which gives the number of protons. The atomic number which gives the number of electrons. ¨ Using the data on the table below. What can be concluded about the two substances? Melting Point (°C) A. B. C. Substance A 212°C Substance B 178°C The substances are different elements. The substances are the same element. The substances have the same number of protons. Topic 2: Regions of the Periodic Table Standard 7.a. Periodic Table & Elements ¨ ¨ There are over a hundred known elements in the universe. Elements are organized onto the periodic table. Periodic Table & Atomic Number ¨ ¨ The elements are arranged on the periodic table according to their atomic numbers. On the table the atomic numbers increase from left to right. Metals, Nonmetals, and Semimetals ¨ The periodic table of elements is organized into three regions: metals, nonmetals, and semimetals. Metals ¨ Metals are located on the left. Nonmetals and Inert Gases ¨ Nonmetals are located on the right with the inert gases on the far right (group 18). Semimetals ¨ Semimetals are found between the metals and nonmetals. Think-Check What pattern is observed on the periodic table? A. Density increases from left to right. B. Reactivity increases from left to right. C. The atomic number increases from left to right. ¨ ¨ Where are metals, nonmetals, and semimetals found on the periodic table? (3) (1) A. B. C. (2) 1= metals; 2 = semimetals; 3 = nonmetals 1 = metals; 2 = nonmetals; 3 = semimetals 1 = nonmetals; 2 = metals; 3 = semimetals The image cannot be displayed. Your computer may not have enough memory to open the image, or the image may have been corrupted. Restart your computer, and then open the file again. If the red x still appears, you may have to delete the image and then insert it again. Topic 3: Categories of Elements Standards 7.a.c. Metals What are metals? ¨ ¨ ¨ Metals are shiny, and they conduct heat and electric current. They also tend to be malleable and ductile. The most reactive of the metals are found on the far left of the periodic table (groups 1 and 2). Nonmetals What are nonmentals? ¨ ¨ ¨ Nonmetals are dull and poor conductors of heat and electric current. The solid nonmetals tend to be brittle and unmalleable. The most reactive of the nonmetals are found on the far right of the periodic table (group 17). Nonmetals - Inert Gases ¨ ¨ The inert gases, also known as noble gases, are found in group 18 and tend to be unreactive. In normal conditions, they do not react with other elements. Semimetals What are semimetals? ¨ ¨ Semimetals, also known as metalloids, have properties of both metals and nonmetals. Semimetals have unique electrical properties (semiconductors) that make them useful in computer chips. Think-Check ¨ A. B. C. What are properties of metals, nonmetals, and semimetals? Metals = dull Nonmetals = shiny Semimetals = semiconductor Metals = shiny Nonmetals = dull Semimetals = semiconductor Metals = shiny Nonmetals = semiconductor Semimetals = dull ¨ In what region would the most reactive elements be found? (1) (3) (2) A. B. C. 1 2 3