Periodic Table: Metals, Nonmetals, Semimetals Worksheet
advertisement
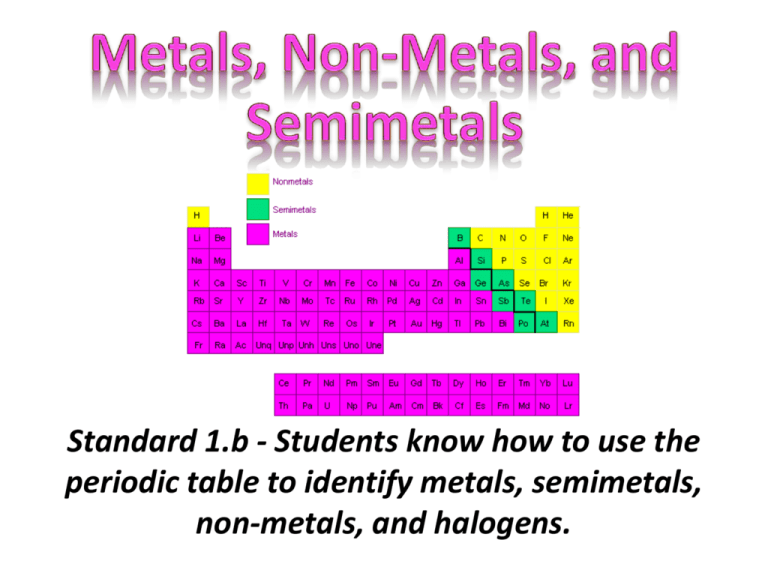
Standard 1.b - Students know how to use the periodic table to identify metals, semimetals, non-metals, and halogens. • Metals are on the left. • Nonmetals are on the right. • Hydrogen is the exception. Even though Hydrogen is on the left it is a nonmetal. and are (metalloids). by the • A diagonal (stair step) line from Boron (B) to Polonium (Po) separates the metals from the nonmetals. Most elements on this line are semimetals (metalloids). • • • • Good Conductors (Heat and Electricity) Malleable and Ductile Shiny, Metallic Appearance Most Solid at Room Temperature (except Mercury) • Loses Electrons • Low ionization (ability to lose electrons) • Low electronegativity (ability to gain electrons) • • • • • • Brittle Nonductile Solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature Gain Electrons High Ionization High Electronegativity • Electronegativities between those of metals and nonmetals • Ionization energies between those of metals and nonmetals • Possess some characteristics of metals/some of nonmetals • Reactivity depends on properties of other elements in reaction • Often make good semiconductors 1 IA 1 Stair Step line divides the Metals from the Non-Metals. Follow the Stair Step line to find the Metalloids! 18 VIIIA 2 IIA 13 IIIA 2 3 4 5 6 7 3 IIIB 4 IVB 5 VB 6 VIB 7 VIIB 8 9 VIIIB 10 11 IB 12 IIB 14 IVA 15 VA 16 VIA 17 VIIA Periodic Table Instructions • Complete Periodic Table #2 • Label: Metals, Semimetals, Nonmetals, and Halogens • Number the periods 1-7 • Number the Groups 1-18 • Identify the different areas on the periodic table. Chemistry - Shearer - Standard 1 9 Answer Questions on Left Side Opposite Your Periodic Table • How many Groups does the periodic table have? • How many Periods does the periodic table have? • Which side of the periodic table are the metals on? • Which side of the periodic table are the nonmetals on? • List the semimetals? • Which category has the largest number of elements? Chemistry - Shearer - Standard 1