Sound Waves - Winchester Science Centre & Planetarium
advertisement

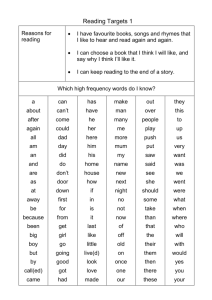
Sound Waves This shows how sounds of different frequencies travel through different materials Do - Think - Learn Sound is caused by something vibrating. We hear sound because our ears are sensitive to the vibrations. Sound is affected by the material it travels through. How will the different materials affect the sound? Place a material to test in position on top of the speaker. How has the sound changed? Select another sound to try. The Science Bit When something makes a sound, whether it is an organ or dog barking, some part of it will be vibrating. These vibrations disturb the air and produce sound waves. The sound waves travel through the air and if they reach someone’s ear drum it will begin to vibrate and we hear sound. In order for sound to be produced and to travel, there must be three things present: 1. there must be a source of vibration 2. there must be something to carry the waves, such as air 3. there must be something to receive the sound waves A good conductor of sound will make the sounds travel faster and further. There are many better conductors of sound than air, for example liquids such as water and solid substances such as iron and stone. The following absorb sound and are often used as sound proofing methods: Rubber Cork Cotton Felt. Curriculum Links Ourselves That we have five senses which allow us to find out about the world Sound and Hearing To explore sounds using their sense of hearing To make observations of sounds by listening carefully That there are many different sources of sounds To turn ideas about hearing into questions that can be tested That we hear with our ears That we use out sense of hearing for a range of purposes, including recognising hazards and risks That there are many different ways of making sounds That there are many ways of describing sound To explore sounds using the sense of touch Changing sounds That vibrations from sound sources travel through different materials to the ear To make careful observations to identify the types of material through which sound can travels That some materials are effective in preventing vibrations from sound sources reaching the ear To plan a test to measure or observe how well different materials muffle sound To use a prediction to help decide what evidence to collect To devise a fair comparison of different materials To decide how to use a sound source and a range of different materials to collect reliable evidence That the term ‘pitch’ describes how high or low a sound is That high and low sounds can be loud or soft That sounds are made when objects or materials vibrate To make careful observations To draw conclusions about sounds from their observations That sounds can be made by air vibrating