Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I How Plants Colonized Land

Chapter
29
Plant Diversity I
How Plants Colonized Land
Plants vs. Algae
•
Land plants evolved from __________( Chara ) green algae
• 4 key traits plants share with __________
(__________ and __________Evidence):
1. Rose-shaped complexes for __________ __________
2. Peroxisome __________
3. Structure of __________ sperm
4. Formation of a __________
5 key traits in nearly all land plants but are absent in the charophytes:
1. apical __________
2. multicellular dependent __________
3. __________ of __________
4. walled spores produced in __________
5. multicellular __________ females – archegonia & males – antheridia
Characteristics of all land plants:
• __________, __________, __________
• cell walls made mostly of __________
• chlorophylls a & b
• Domain __________, Kingdom __________
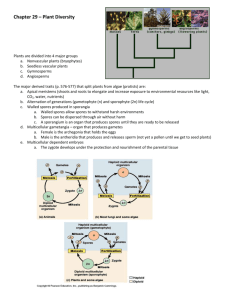
Nonvascular plants
1. Represented by three phyla: a. phylum Hepatophyta – __________ b. phylum Anthocerophyta – __________ c. phylum Bryophyta - __________
Liverworts
Hornworts
Moss
2. The __________ is the dominant generation in the life cycle
• gametophyte - mass of green, branched, one-cell-thick filaments
• sporophytes are smaller; only present part of the time
• spores germinate in favorable habitats sporophyte gametophyte sporophyte gametophyte
3.
Bryophyte sporophytes disperse enormous numbers of spores
• sporophytes remain attached to gametophyte throughout the lifetime
– depends on the gametophyte for sugars, amino acids, minerals and water.
• __________(site of meiosis and spore production) can generate over 50 million spores.
4. Bryophytes provide many __________ and
__________ benefits
• distributed worldwide
• common and diverse in moist forests and wetlands
• Some common in extreme environments (mountaintops, tundra, and deserts)
• Sphagnum , a wetland moss, is especially abundant and widespread.
• forms extensive deposits of undecayed organic material, called peat
• Wet regions dominated by
Sphagnum or peat moss are known as peat bogs
THE ORIGIN OF VASCULAR PLANTS
1. Two conducting tissues of the vascular system
A. __________–
Dead tissue, water-conducting
B. __________–
Living tissue, food-transporting
2. Water-conducting cells are strengthened by __________ and provide structural support
3. __________ generation is dominant in vascular plants.
Seedless vascular plants
4. Two modern phyla: a. phylum Lycophyta – __________ b. phylum Pterophyta - __________, __________, and
__________
Club moss
Horsetail
Whisk fern
Fern
5. Most seedless vascular plants are __________, producing one type of spore that develops into a bisexual gametophyte
• both archegonia (female sex organs) and antheridia (male sex organs)
•
Eg., ferns eggs sporophyte
Single type of spore
Bisexual gametophyte sperm
6. seedless vascular plants are most common in damp habitats
7. ferns produce clusters of sporangia, called sori , on the back of leaves