Reconstruction PP PDF - Mercer Island School District
advertisement

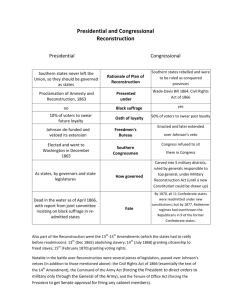
Important For What It Failed To Do Reconstruction 1864-1877 Outline 1. The Residue of War (1860-1865) 2. Presidential Reconstruction (18651867) 3. Congressional/Radical Reconstruction (1867-1877) 4. Abandoning Reconstruction (18771950?) 1. The Residue of War How wartime developments and destruction affected post-war decisions Lies, Damn Lies, and… • Some Statistics: • 285,000 dead Confederate Soldiers • 4 million freed slaves with nowhere to go and no resources • How many wounded? • How many maimed? • Psychological costs? • Damage to Southern Infrastructure Cold Harbor Charleston “They won their freedom and not much else” Legal Legacy of the War • Emancipation Proclamation, • January 1, 1863 • Gettysburg Address, • November 19, 1863 • Lincoln Assassinated, • April 14, 1865 • Thirteenth Amendment, • December 6, 1865 Practical Reconstruction, Practical Emancipation Out of necessity • By 1862, Lincoln had named military governors for Tennessee, Arkansas, and Louisiana Proclamation of Amnesty and Reconstruction (1863) • A rebel state could form a new state government when 10% of those who had voted in 1860 had taken an oath of allegiance to the union. • They also had to swear to support all laws and proclamations regarding emancipation • Some groups of Southerners, those considered particularly traitorous, such as military men who had been part of the army before the war, and high officials of the confederate government Walking the Line Presidential Reconstruction, 1865-1867 Not as obvious as it appears… • In most wars, how is peace made? • Why might this not work following the American Civil War? A Peculiar Problem • Premise of the war: The South has no right to secede • Technically they never left… • Do they need to be re-admitted? • The North never recognized the Confederacy as a real government • You cannot sign a peace treaty with a bunch of criminals, traitors, or rebels $1,000,000 Question • How were the Southern States to be brought back into the Union? The Issues • The Vote for Blacks? • Land for freed Slaves? • Loyalty of Southerners? • Confederate Soldiers/Traitors? • How to form new governments? • Who should pay to rebuild the Southern economy? Lincoln and Reconstruction • Moderate • More concerned with re-union than slavery • Puts forth a plan in 1863 Proclamation of Amnesty and Reconstruction The Lincoln Plan • Southern State governments accept slave emancipation • All southerners take an oath of loyalty to the Union • When 10% of the state has taken the oath, they can form a state government and will be readmitted Congressional Resistance •Republicans Control Congress during the Civil War when Southern Democrats withdrew and seceded •Republican Congress was determined to maintain their influence and not have their industrial legislative program overturned Wade-Davis Bill (1864) • • A majority (not 10%, but 51% had to take the oath) Appoint a provisional governor to each state to oversee the creation of state governments (South not to be trusted) • Former confederate soldiers could not vote in this initial creation Southern Reconstruction Plan - 1865 • Must put Emancipation in their new state constitutions • Wade-David bill passed and Lincoln vetoed it • They didn’t work it out before Lincoln was assassinated Andrew Johnson (not JohnsTon) • Lincoln’s VP • “War Democrat” from Virginia • Chosen to placate South in 1860 election • Initially continued Lincoln’s moderate policies Johnson Clashes With Congress • Johnson placates Southern leaders in hopes of extracting enough change to satisfy the radicals in Congress • Doesn’t work - the South makes few concessions, begins passing the Black Codes • Congress becomes increasingly alarmed “Cannon Conquer, but they do not necessarily convert” Southern Resistance to Reconstruction • “None of us realize that we are no longer wealthy—yet thanks to the Yankees, the cause of all this unhappiness, such is the case. As long as I thought we would conquer in our just cause, I cared nothing for the loss of property for I felt as if we would be rich if we had Our Rights & Our Country left us—but now they are lost too, & we have suffered in vain. In vain! There is where the bitterness lies!” • ~Amanda Worthington, Plantation mistress from Mississippi After the War • “It seems humiliating to be compelled to bargain and haggle with our servants about wages” Post-War Anger • “One mother said she trained her children to “fear God, love the South, and live to avenge her.” Political Resistance • Repealing vs. Repudiating Ordinances of Secession • Mississippi & Texas refuse to ratify 13th Amendment • Georgia ratified it on condition of slave holders being compensated • States refused to grant rights to former slaves • Passing of “Black Codes” A less-than-hidden agenda… • Legal for slaves to marry, own property, and sue in court • Required a special license for Blacks to work in any area except agriculture • Could not serve on juries and could not testify against Whites • Vagrancy Laws • “[Reconstruction included] a striking embodiment of the idea that although the former owner has lost his individual right of property in the former slaves, the blacks at large belong to the whites at large.” ~Carl Schurz, Republican politician What must Reconstruction do? • Reconstruction must “revolutionize Southern institutions, habits, and manners….The foundations of their institutions must be broken and relaid, or all our blood and treasure have been spent in vein.” • ~Thaddeus Stevens • The Freedmen will “be tyrannized over, abused, and virtually re-enslaved without some legislation by the nation for his protection.” • ~Lyman Trumbull, Senator Retribution Congressional (radical) Reconstruction 14th Amendment (Passed 1865) ▪Defined citizenship and guaranteed rights of the Constitution, by both the State and Federal government ▪Enforced suffrage for all adults males (nothing said about race) 14th Amendment • Ratifying the 14th Amendment was now the only requirement for Southern state readmittance to Union The Radical Congressional Program • Punish Confederate leadership, civilians and military • Actively protect legal rights of Blacks • Disenfranchise disloyal white Southerners • Confiscate land of wealthy Confederates and distribute it to freed Blacks Conspiracy? 8 Men Out “Johnson himself was an intemperate and tactless man, filled with resentments and insecurities.” Election of 1866 After 1866, radical Republicans in Congress puts together a specific and coherent plan for Reconstruction (Democrats lost 9 seats) Re-Admittance • Under Lincoln and Johnson, all the Southern states had prepared to reenter the Union. • When Congress met in 1865, they refused to seat Southern Congressmen and senators sent by re-admitted states. • 10 States had satisfied the requirements for re-admittance under Lincoln and Johnson • Later, Congress rejected those governments 15th Amendment (1866) Congress added another requirement, the 15th Amendment Forbade states and the federal government to deny the suffrage to any citizen an account of “race, color, or previous condition of servitude.” Tenure of Office Act (1866) • Designed to keep the President from interfering with Congress plan for Reconstruction • Forbade him from removing executive branch officials confirmed by the Senate without the consent of the Senate. Impeachment • Johnson considered the act unconstitutional • Violated it in hopes of bringing about a court case • Congress used this as a pretext to impeach him • House only William Jefferson Clinton Impeachment • 1999, Impeached by House of Representatives • Acquitted by the Senate • Richard Nixon was not impeached The South Redeemed The End of Reconstruction Election of 1874 Blue=Democrats House=Democrats Senate=Republican Upper South • White majorities • Almost completely re-enfranchised by 1872 • Easy to take control Lower South • Black majorities • Intimidation and violence to undermine reconstruction • KKK & Knights of the White Camellia Strongest Weapon: Economic Pressure! “Some planters refused to rent land to Republican Blacks; storekeepers refused to extend them credit; employers refused to give them work.” ~Alan Brinkley Panic of 1873 • Collapse of the stock market • Subsequent depression lasted 6 years • Hurts Republicans in Congress • Efforts turn to economic recovery and away from Reconstruction and race politics D-O-N-E Done! • 13th, 14th and 15th Amendments • Blacks were free and had the Vote • Take care of themselves Election of 1876 Election of 1876 • Nearly dead-even Electoral college vote with 4 contested states • No procedures in Constitution for how the Congress should determine winner • Split legislature (Dem’s in house, Rep’s in Senate) could not agree • Popular vote had been for Democrat Samuel J. Tilden The Commission • 5 Republicans from Congress • 5 Democrats from Congress • 5 Supreme Court justices: 2 from each party plus one independent, David Davis ‘His Fraudulency” • Illinois legislature elected Davis to U.S. Senate • Resigned from Commission • Seat was won by a Republican justice • Vote went on party lines (8 to 7) for Republican candidate Rutherford B Hayes Compromise of 1877 • Democrats were going to filibuster • Parties negotiated behind the scenes • Democrats agree to drop filibuster in exchange for several guarantees •Included: withdraw federal troops from South and end Republican military governments – South would be solidly in Democratic hands Evaluating Reconstruction Can’t Please Anyone… • “To many white Southerners, Reconstruction was a vicious and destructive experience—a period when vindictive Northerners inflicted humiliation and revenge on the prostrate South.” – Alan Brinkley View from the North • Northerners “argued that their policies were the only way to prevent unrepentant Confederates from restoring southern society as it had been before the war; without forceful federal intervention, there would be no way to forestall the reemergence of a backwards aristocracy and continued subjugation of blacks—no way, in other words, to prevent the same sectional problems that had produced the Civil War in the first place.” Evaluating Reconstruction • Failure in most respects, at least in the long run • Failure to address issue of race, it would be addressed dramatically 100 years later • Embittered Americans about the race issue, made them hesitant to deal with it on a political level Why failure? • Inherent racism, North and South • Deeply imbedded values of states rights • Respect for private property and free enterprise made efforts at income redistribution weak The End of Reconstruction Industry and Capitalism 1877-1914? • • • • • • • • • Mass production Moving assembly line The railroads The corporation Social Darwinism, Herbert Spencer Carnegie, Gospel of Wealth Monopolies Immigration Working conditions, women and children at work, emerging unionism Urbanization • Conditions in the city • Ethnic city • Rise of mass consumption • Leisure and sport • Movies • Rise of education Populism • Populism • Silver and gold (standard) Imperialism • Hawaii and Samoa • Spanish American war • Philippines • Opening China • Boxer Rebellion Progressivism • Temperance • Socialism • TR • Panama canal WWI • Neutrality • Wilson • 14 points