Lesson 4 – Control of the Cell Cycle
advertisement

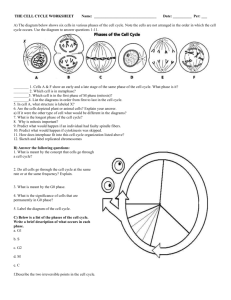
Lesson 4 – Control of the Cell Cycle 1.2 Cell Growth and the cell cycle (continued) How is the cell cycle controlled? As you have seen the cell cycle is a sequence of very precise events with exact outcomes. Any variation from this could be disastrous! Think of ways that things could go wrong if it wasn’t carefully controlled. Cells keep dividing - cancer Cytokinesis happens too soon – cell dies Cells don’t start dividing – no growth Cells enter G2 without proper checks on replication – mutations arise Timing Timing is essential because: 1. Different cell types need to replicate at different times and in different quantities. 2.Each event within the cell cycle must be complete before the start of the next event. Growth Factors During the various stages of the cell cycle growth (in may forms) occurs. Over 50 different growth factors have been identified as important to the cell cycle. Without these growth factors the cell will stop growing and enter a phase know as G0 – a nongrowing phase. Checkpoints A checkpoint is when the cycle gets regulated by stop and start signals. There are 3 main checkpoints. Checkpoint 1 – Towards the end of G1 phase Remember that in G1 growth and synthesis of organelles occurs. What do you think this checkpoint will be for? Assessment of cell size – if it is large enough and the environment is favourable to undergo cell division it moves onto the S phase for DNA replication Checkpoint 2 – at the end of the G2 phase By the end of G2 DNA replication has occurred. Success of Replication - This checkpoint is essential in making sure that replication has been successful. Assessment of Cell Size - The size of the cell is also checked and the environmental conditions assessed. Checkpoint 2 and Mitosis Promoting Factor (MPF) Once the checks are completed at Checkpoint 2 the cell is ready for mitosis. The start of mitosis is triggered by a complex called mitosis promoting factor (MPF) which itself is controlled by a number of other cell cycle signals. Checkpoint 3 – during metaphase This is known as the M Checkpoint and occurs during metaphase. The main checks here are: Correct spindle formation – is the spindle fibre attached to the choromosome? Correct chromosomal alignment chromosomes arranged so that each daughter cell receives one of each chromosome? Cell Cycle Animation What happens when there is a problem? We know that the cell is checking – so what if an error is found? There are 2 possible outcomes: 1. The cell cycle is stopped while the problem is repaired OR 2. The cell is instructed to kill itself (apoptosis). Your Tasks 1. Revise the stages of mitosis by listing the names of each stage along with the activities that distinguish it. You will have a quiz next week where you will be given images and need to decide what stage they are. 2. Research Mitotic Index. What is it? How is it used? How is it measured? How would you measure it using equipment in the school? 3. Begin a glossary using all the terms you have learned so far. (You can have a jotter for this if you like). 4. Try the quiz here: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/novella/MixQuizProcessingServlet