Section 4.5 Name: Day Title: Types of Matter Period:
advertisement

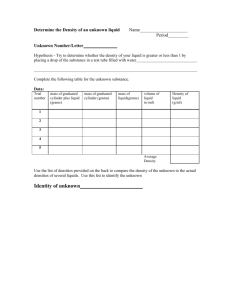
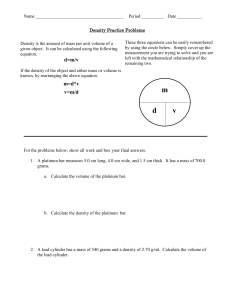
Section 4.5 Day Title: Types of Matter Name: Period: Review of Old Information: Yesterday you cooked some magnesium and had it combine with oxygen. You used the law of definite compositions to find how much oxygen actually combined. This is what you need to know for your test (4.6). Chemistry and it’s branches Matter and mass Pure and impure substances Mixtures and Compounds Heterogeneous and Homogeneous mixtures Law of Definite Proportions and the math Solutions, Suspension and Colloids Activity: 1. Name the branches of chemistry and what they study. 2. Explain the difference between mass and weight. 3. List the pure substances discussed in class. a. Give 2 examples of each. 4. List the and impure substances discussed in class. a. Give 2 examples of each. 5. Explain three differences between compounds and mixtures. 6. Explain the differences between homogeneous mixtures and heterogeneous mixtures. Give two examples of each. 7. Explain the difference between solutions, suspensions and colloids. Give one examples of each. 8. A 150 gram sample of H2SO4 has 97.5g of Oxygen, 49.5 grams of Sulfur and 3 grams of Hydrogen. a. How many grams of Sulfur would be in a 43 gram sample of H2SO4? b. If I have a sample of H2SO4 that has 45 grams of Oxygen, then how much Sulfur is in the sample? c. If I have sample of H2SO4 that has 250 grams of Hydrogen then how much H2SO4 do I have? 9. A 200 gram sample of H2CO3has 8 grams of Hydrogen, 38 grams of Carbon, and 154 grams of Oxygen. a. How many grams of Oxygen would be in a 113 grams sample of H2CO3? b. If I have a sample of H2CO3 that has 32 grams of Hydrogen then how much Carbon is in the sample? c. If I have sample of H2CO3 that has 145 grams of Carbon then how much H2CO3 do I have? 10. Convert the following using an equation, (not the number line). a. 400 hm to cm b. 54.3 dL to daL