Nursing Flashcard - Acute Pulmonary Edema - Af
advertisement

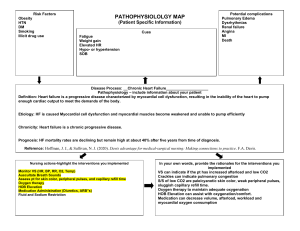
Nursing Flashcard – Acute Pulmonary Edema (APE) background 1) life-threatening medical emergency 2) consists in transudation of fluid into the pulmonary interstitium and alveoli 3) is one of the different clinical expressions of acute left ventricular failure etiology 1) cardiogenic pulmonary edema (the most frequent clinical pattern of APE) a) left ventricular failure b) valve dysfunction (mitral / aortic), myocardial dysfunction (AMI) c) arrhythmias with very high ventricular rate d) uncontrolled high blood pressure 2) non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema (less frequent) a) fluid overload b) acute respiratory distress syndrome (due to trauma, sepsis, CP bypass) c) increased permeability (drugs / infections / toxins) symptoms 1) breathlessness or equivalent (cough with frothy pink sputum) i) on exertion ii) waking in the night (paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea) iii) on lying down (orthopnea) 2) occasionally expiratory wheezes (cardiac asthma) 3) other symptoms, due to the different etiologies diagnostic evaluation 1) EKG (arrhythmias, myocardial injury / necrosis) 2) chest X-ray (signs of APE, cardiomegaly) 3) echocardiogram (valve and myocardial systolic & diastolic function evaluation) 4) lab: markers of cardiac necrosis, BNP, D-dimer, thyroid function 5) pulse oximetry / arterial blood gases (degree of hypoxemia / acidosis) complications 1) severe respiratory insufficiency with hypoxemia / acidosis 2) cardiac arrhythmias / arrest / shock death treatment 1) medical treatment: i) begin resuscitation protocol if necessary ii) first-line agents: 60%-100% oxygen by face mask + morphine + diuretics iii) aminophylline if necessary to relieve bronchospasm iv) intravenous nitrates / other vasodilators v) if hypotension treat as cardiogenic shock (inotropic agents) vi) specific treatment: AMI, arrhythmias, hypertension 2) aggressive i) respiratory support: mechanical ventilation / CPAP ii) DC shock for appropriate arrhythmias support urgent surgery (valve dysfunction) / IABP (AMI) / biventricular pacing or transplantation (cardiomyopathy)