Genetic Code and Transcription
advertisement
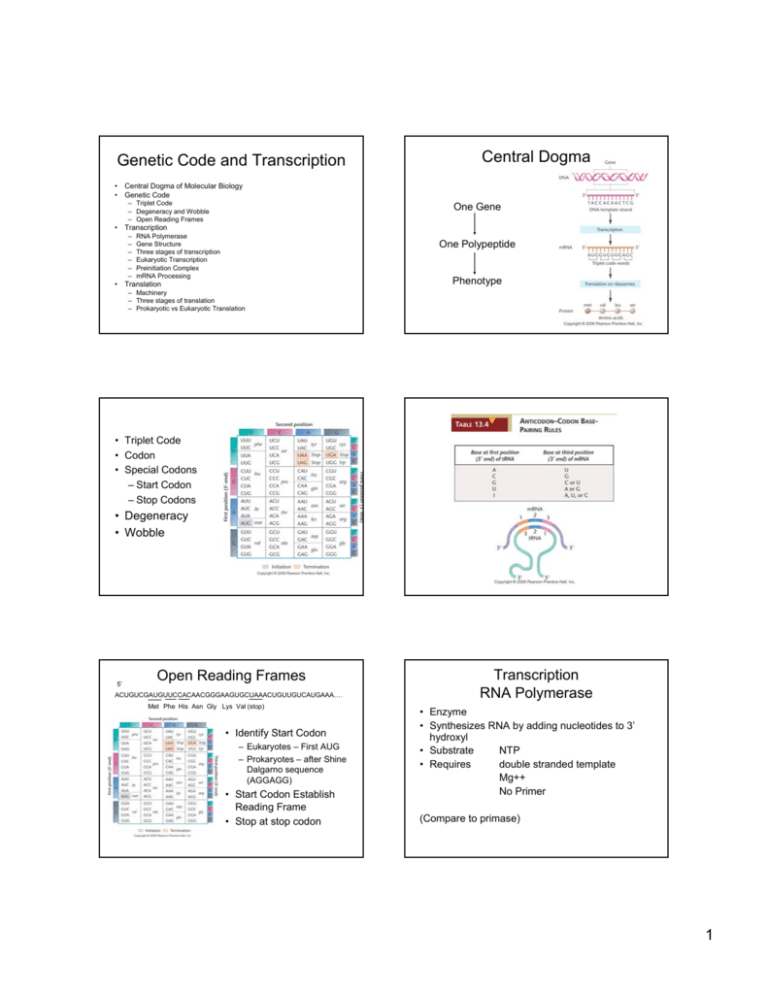
Genetic Code and Transcription Central Dogma • Central Dogma of Molecular Biology • Genetic Code – Triplet Code – Degeneracy and Wobble – Open Reading Frames One Gene • Transcription – – – – – – RNA Polymerase Gene Structure Three stages of transcription Eukaryotic Transcription Preinitiation Complex mRNA Processing One Polypeptide Phenotype • Translation – Machinery – Three stages of translation – Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Translation • Triplet Code • Codon • Special Codons – Start Codon – Stop Codons • Degeneracy • Wobble 5’ Open Reading Frames ACUGUCGAUGUUCCACAACGGGAAGUGCUAAACUGUUGUCAUGAAA…. Met Phe His Asn Gly Lys Val (stop) • Identify Start Codon – Eukaryotes – First AUG – Prokaryotes – after Shine Dalgarno sequence (AGGAGG) • Start Codon Establish Reading Frame • Stop at stop codon Transcription RNA Polymerase • Enzyme • Synthesizes RNA by adding nucleotides to 3’ hydroxyl • Substrate NTP • Requires double stranded template Mg++ No Primer (Compare to primase) 1 Gene Structure Three Parts to Transcription DNA 1. Initiation RNA Polymerase binds DNA – determine by promoter Short region double strand separated (transcription bubble) First two nucleotide attached 2. Elongation -1/+1 Promoter Start Codon Stop Codon Additional Nucleotides added one at a time RNA Polymerase moves down DNA Transcription bubble moves with polymerase Terminator 3. Termination 3’ UTR 5’ UTR Triggered when polymerase reaches terminator Start Codon Stop Codon Newly synthesized RNA released RNA polymerase released from DNA Transcription bubble closes mRNA Open Reading Frame (ORF) Prokaryotic Initiation Prokaryotic Consensus Promoter • RNA Polymerase Structure – Core Enzyme – Sigma Subunit • Holoenzyme • • • Eukaryotic Initiation • Three RNA Polymerases – RNA PolI – RNA PolII – RNA PolIII large rRNA mRNA snRNA tRNA 5SrRNA snRNA RNA Polymerase binds Promoter Release of Sigma subunit before elongation Alternative sigma subunits Preinitiation complex Assembly of complex Role of Mediator • Pol II Promoter – Proximal and distal sequences – TATA box most common pol II element – Consensus ATATAA -35 2 5’ Cap structure 7 methyl guanosine triphosphate mRNA Processing Eukaryotes • Three types of processing – 5’ CAP – 3’ PolyA tail – Spicing Capping Enzyme in Nucleus Protects RNA from 5’-3’ exonucleases Promotes export from nucleus Recruits Ribosome for Translation PolyA tail Splicing Spicosome Protein snRNA Remove introns that interrupt orf Alternative Spicing Cleavage Complex Poly A Polymerase Bound by PolyA binding protein – protects from 3’-5’ exonuclease Promotes Translation Alternative Spicing Translational Machinery • • • • • tRNA mRNA Ribosome GTP Protein Factors – Initiation Factors – Elongation Factors – Release Factors 3 tRNA Charging tRNA’s • • • • • Ribosomes Three Stages of Translation • Translational Initiation – 1 GTP • Translational Elongation • Delivery of charged tRNA – 1 GTP • Transpeptidase Activity • Translocation – 1 GTP • Translational Termination – 1 GTP 20 Amino Acids 20 Synthetase Cognate tRNA’s 2 ATP equivalents tRNA cycle tRNA binding sites Translational Initiation • Small subunit and initiator tRNA bind to start codon. – tRNAi is in P site • Large subunit binds clamping down on mRNA • GTP is hydrolyzed to allow large subunit binding 4 Elongation Cycle 1. Delivery of tRNA 2. Transpeptidase 3. Translocation Polysomes Translational Termination Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic • Prokaryotic transcription/translation coupled • Eukaryotes transcription and translation are temporally and spatially separated Initiation • Prokaryotes small subunit binds Shine Dalgarno sequence (AGGAGG) • Eukaryotes small subunit and tRNAi bind cap and scan to first start codon. # of ORFs • Prokaryotic mRNA often polycistronic – more than one orf • Eukaryotic mRNA usually monocistronic – one orf. 5