Chemistry 1 Name : Chapter 10 Test: States of Matter
advertisement
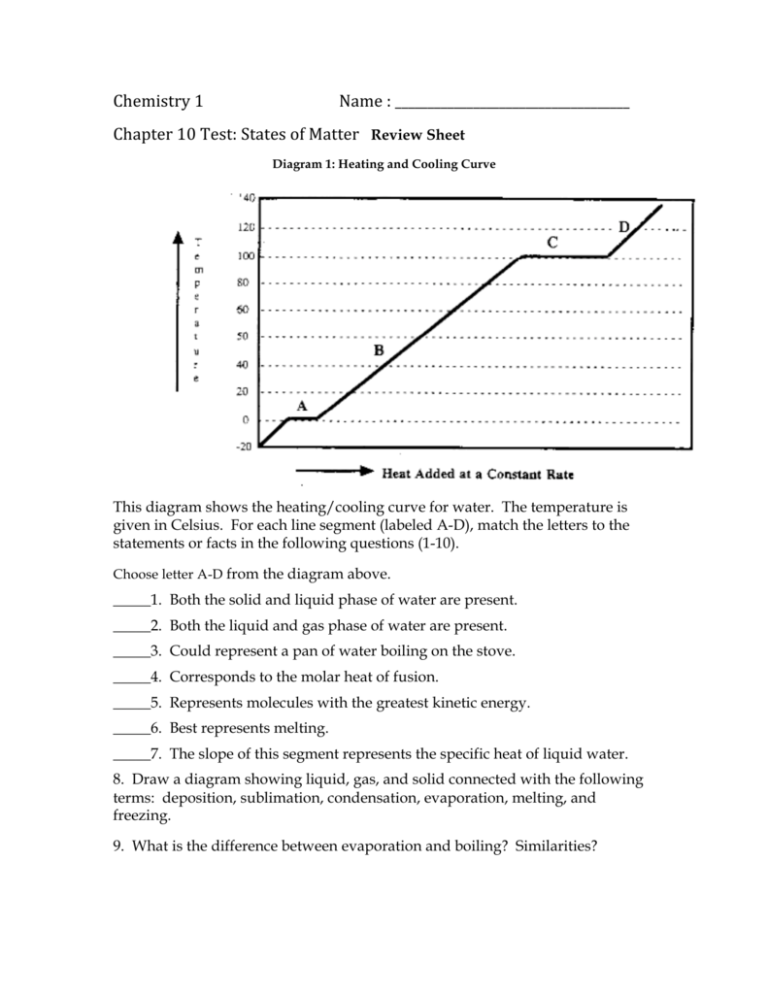
Chemistry 1 Name : ____________________________________ Chapter 10 Test: States of Matter Review Sheet Diagram 1: Heating and Cooling Curve This diagram shows the heating/cooling curve for water. The temperature is given in Celsius. For each line segment (labeled A-D), match the letters to the statements or facts in the following questions (1-10). Choose letter A-D from the diagram above. _____1. Both the solid and liquid phase of water are present. _____2. Both the liquid and gas phase of water are present. _____3. Could represent a pan of water boiling on the stove. _____4. Corresponds to the molar heat of fusion. _____5. Represents molecules with the greatest kinetic energy. _____6. Best represents melting. _____7. The slope of this segment represents the specific heat of liquid water. 8. Draw a diagram showing liquid, gas, and solid connected with the following terms: deposition, sublimation, condensation, evaporation, melting, and freezing. 9. What is the difference between evaporation and boiling? Similarities? 10. Explain the Kinetic-molecular Theory as it pertains to solids, liquids, and gases. 11. What are some unique processes that gases have? 12. Define Heat. (First section of chapter 16-thermochemistry) 13. Forces of attraction between molecules are called ________________forces. 14. Define molar heat of vaporization, molar heat of fusion and temperature. 15. Indicate whether each is a physical or chemical property of water? ______________ a. The density of ice is less than that of water. ______________ b. The normal boiling point of water is 1000C 22. If 25 kilojoules are needed to melt 15 grams of aluminum metal, what is the molar heat of fusion? 23. What is a phase diagram? Define triple point and critical point. Be sure you understand how to read a phase diagram, review the phase diagram on page 347 of your book. 23. You are given a 25.0 gram sample of a metal that has been heated to 100.0 ˚C. The hot metal is placed in a calorimeter that contains 9 grams of cool water. The initial water temperature is 19.0 ˚ C. The final temperature of the metal and the water in the calorimeter is 25.0 ˚C. Create a data table of the measurements given above. Then, using the specific heat table below, identify the metal. Show your work. Table 1: Specific Heat of Various Substances (J/g0C) Water Aluminum Carbon Iron Zinc Silver Mercury Gold 4.18 0.89 0.71 0.45 0.39 0.24 0.14 0.13











