Practice Questions 1
advertisement

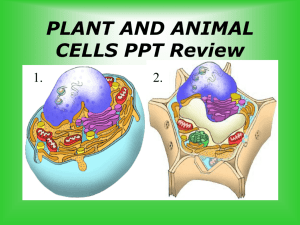
1. A molecule that is found on the surface of most cells is responsible for communication between the cells. This molecule is made up of long chains of amino acids and is specific to each cell type. This molecule is a A. B. C. D. lipid carbohydrate DNA strand Protein 6. Which pH indicates a substance that is more basic than a substance with a pH of 9? a. b. c. d. 7. Which of the following is a list of elements that make up the structure of a carbohydrate? 2. Which statement best describes the function of a lipid in a cell? a. b. c. d. storing and transmitting heredity forming part of biological membranes forming amino acid chains storing phosphorus 3. Which of the following factors is most likely to affect the function of an enzyme? A. B. C. D. catalysts size of beaker proteins temperature 4. Which of the following statements best describes a function of an enzyme? A. All enzymes work on all substrates. B. Enzymes are specialized proteins that serve as catalysts. C. Enzymes are carbohydrate-based molecules in all cells. D. The structure of enzymes is changed during a chemical reaction. 5. Which of the following substances would show a positive brown paper test for lipids? A. B. C. D. apples bacon crackers water 6 2 8 12 a. b. c. d. carbon, nitrogen, oxygen hydrogen, carbon, oxygen nitrogen, sulfur, oxygen oxygen, carbon, phosphorus 8. Which of the following is a function of proteins? a. b. c. d. storing energy storing waste growth and repair breaking chemical bonds 9. Which of the following organic molecule tests is correctly paired with its organic molecule? a. b. c. d. proteins – brown paper glucose – biuret starch - iodine lipid – benedicts 10. Which biomolecules store and transmit genetic information? a. b. c. d. carbohydrates lipids nucleic acids proteins 11. Which of the following best describes the function of carbohydrates? a. They code for proteins. b. They form biological membranes. c. They provide a source of energy for an organism. d. They control reaction rates in a cell. 12. If an organism does not have membrane-bound organelles, what is it called? a. b. c. d. 16. Which of the cell organelles labeled below helps you determine if this is an animal cell or a plant cell? simple eukaryotic prokaryotic complex 13. Which organelle pictured is responsible for transforming energy? a. b. c. d. A. B. C. D. nucleus cell wall ribosomes mitochondria 17. What is the function of the Golgi apparatus? 14. During the period from 1838-1855, German scientists Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolph Virchow contributed greatly to the understanding of plant and animal cells. Their cell theory includes all of the following ideas except which one? A. All living things are made of cells. B. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of living things. C. Cells come from pre-existing cells. D. Viruses are not made of cells. 15. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are distinguished from each other by which of the following? A. Prokaryotic cells include most cells, other than bacteria, and lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. B. Prokaryotic cells include mainly bacteria, and lack a nucleus as well as membranebound organelles. C. Prokaryotic cells include most cells, other than bacteria, and contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. D. Prokaryotic cells include mainly bacteria, and contain a nucleus as well as membranebound organelles. A. B. C. D. manufacture proteins package and transport proteins store proteins break down proteins to release energy 18. A student identifies an unknown cell as being eukaryotic. Which of the following did she most likely identify in order to draw this conclusion? A. B. C. D. nucleus cell wall chloroplasts cell membrane 19. Which of the following best describes the function of a ribosome? A. making proteins B. digesting lipids, carbohydrates and proteins C. storing water, proteins, salts and carbohydrates D. providing structural support for the cell